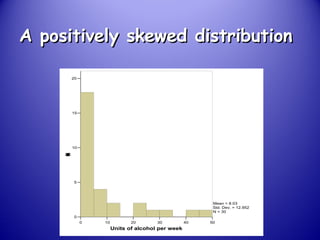
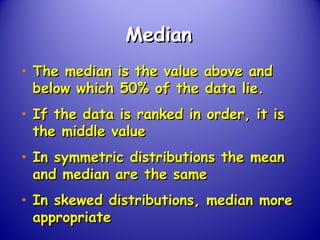
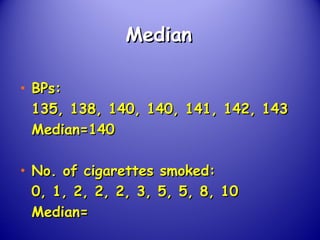
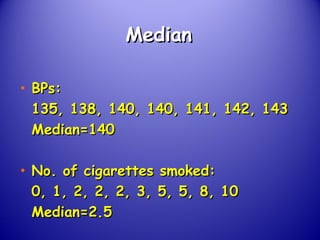
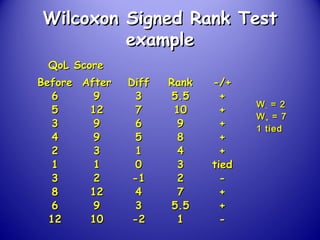
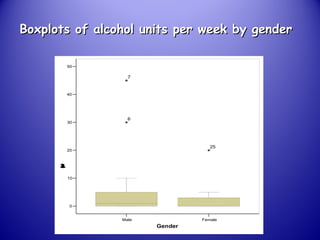
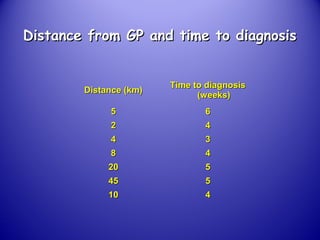
This document provides an introduction and overview of non-parametric statistical methods, including ranks and the median, Wilcoxon signed rank test, Mann-Whitney test, and Spearman's rank correlation coefficient. It defines what non-parametric tests are, discusses their advantages over parametric tests in situations where data is not normally distributed, and provides examples of calculating and interpreting several non-parametric tests in SPSS.