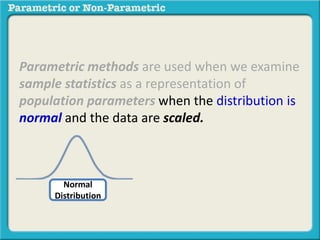
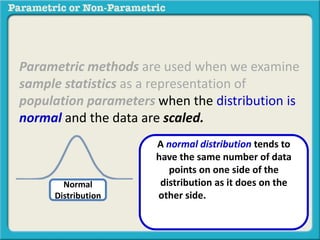
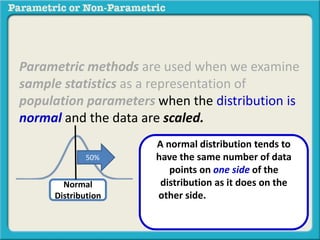
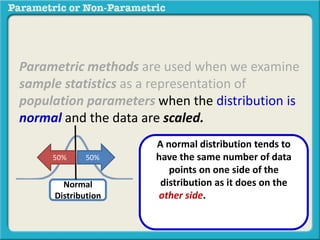
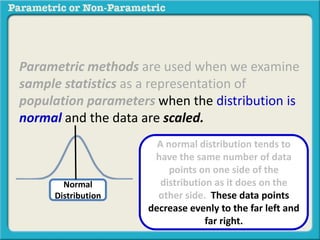
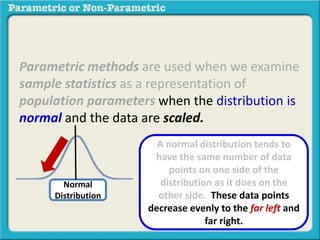
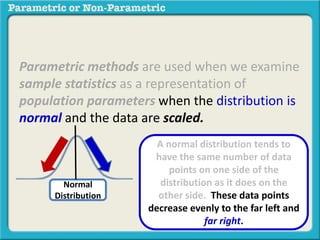
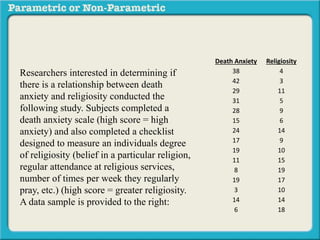
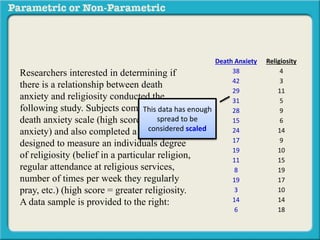
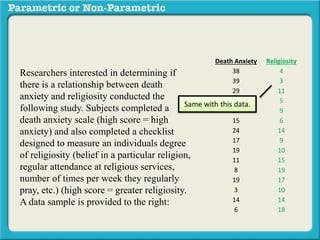
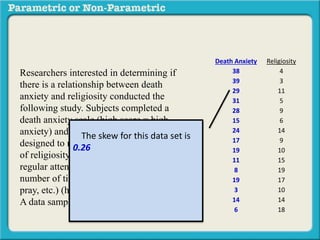
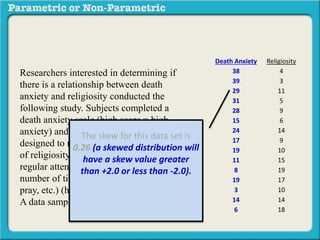
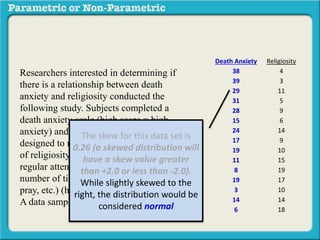
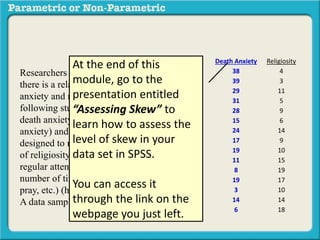
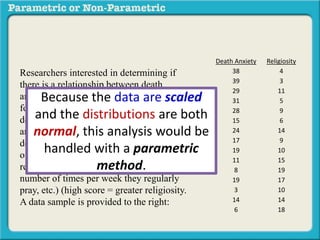
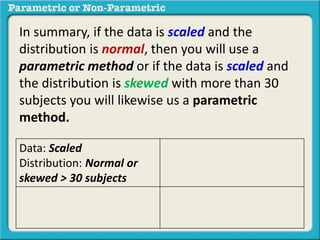
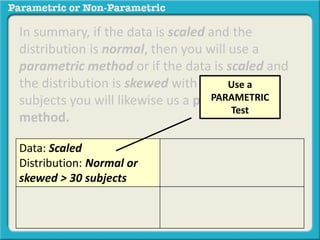
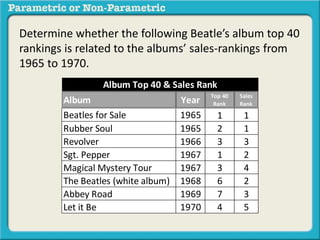
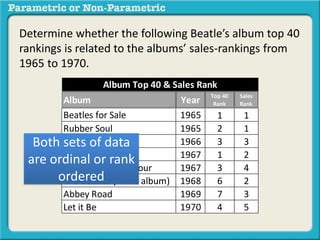
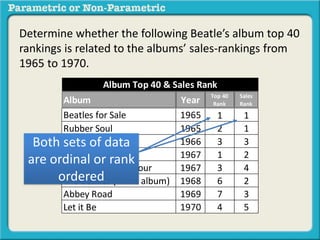
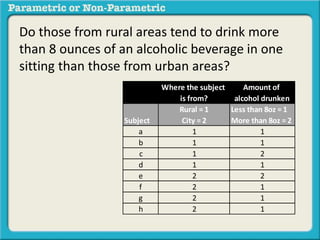
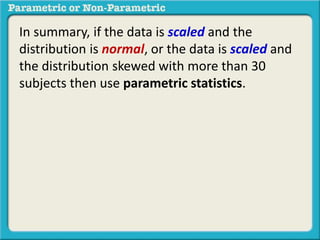
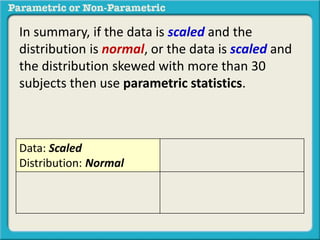
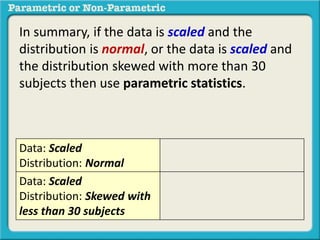
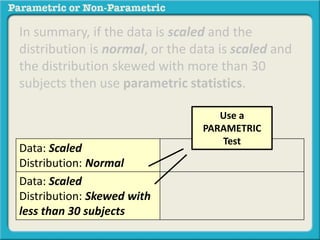
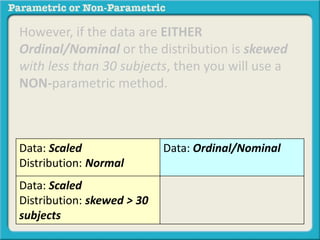
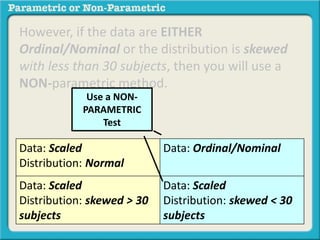
This presentation discusses parametric and non-parametric methods for analyzing relationships between variables. Parametric methods can be used when sample data is normally distributed and scaled, representing population parameters. They involve examining relationships between variables like death anxiety and religiosity through statistical tests. Non-parametric methods do not require normal distribution or scaling and can be used as an alternative.