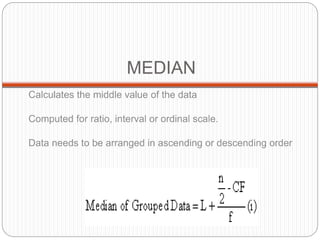
The document discusses various types of data analysis, including univariate, bivariate, and multivariate analysis. It explains descriptive analysis, which summarizes sample data, and inferential analysis, which makes generalizations about a population based on sample results. Additionally, it highlights measures of central tendency and dispersion, as well as methods for analyzing bivariate data such as cross tabulation and correlation coefficients.