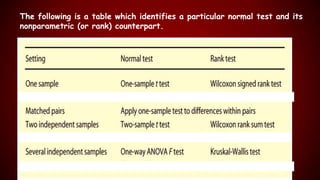
This document discusses non-parametric statistical tests, which make few assumptions about the distribution of the underlying population. It provides examples of non-parametric tests like the sign test, Wilcoxon rank sum test, and Kruskal-Wallis test. These tests involve ranking all observations from different groups together and applying statistical tests to the ranks rather than the original values. Non-parametric tests are useful when assumptions of parametric tests may not hold but lack power with small samples.