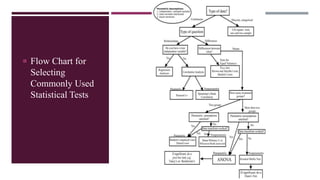
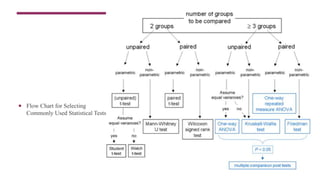
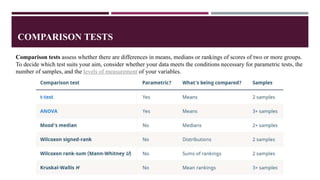
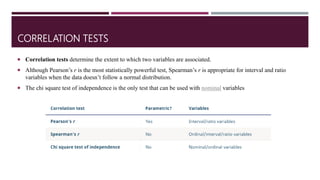
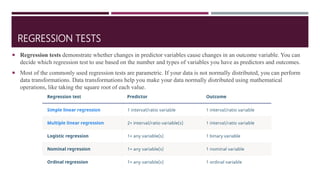
This document provides information about inferential statistics presented by Dr. Hina Jalal. It defines inferential statistics as using data from a sample to make inferences about the larger population from which the sample was taken. It discusses key areas of inferential statistics like estimating population parameters and testing hypotheses. It also explains the importance of inferential statistics in research for making conclusions from samples, comparing models, and enabling inferences about populations based on sample data. Flow charts are presented for selecting common statistical tests for comparisons, correlations, and regression.