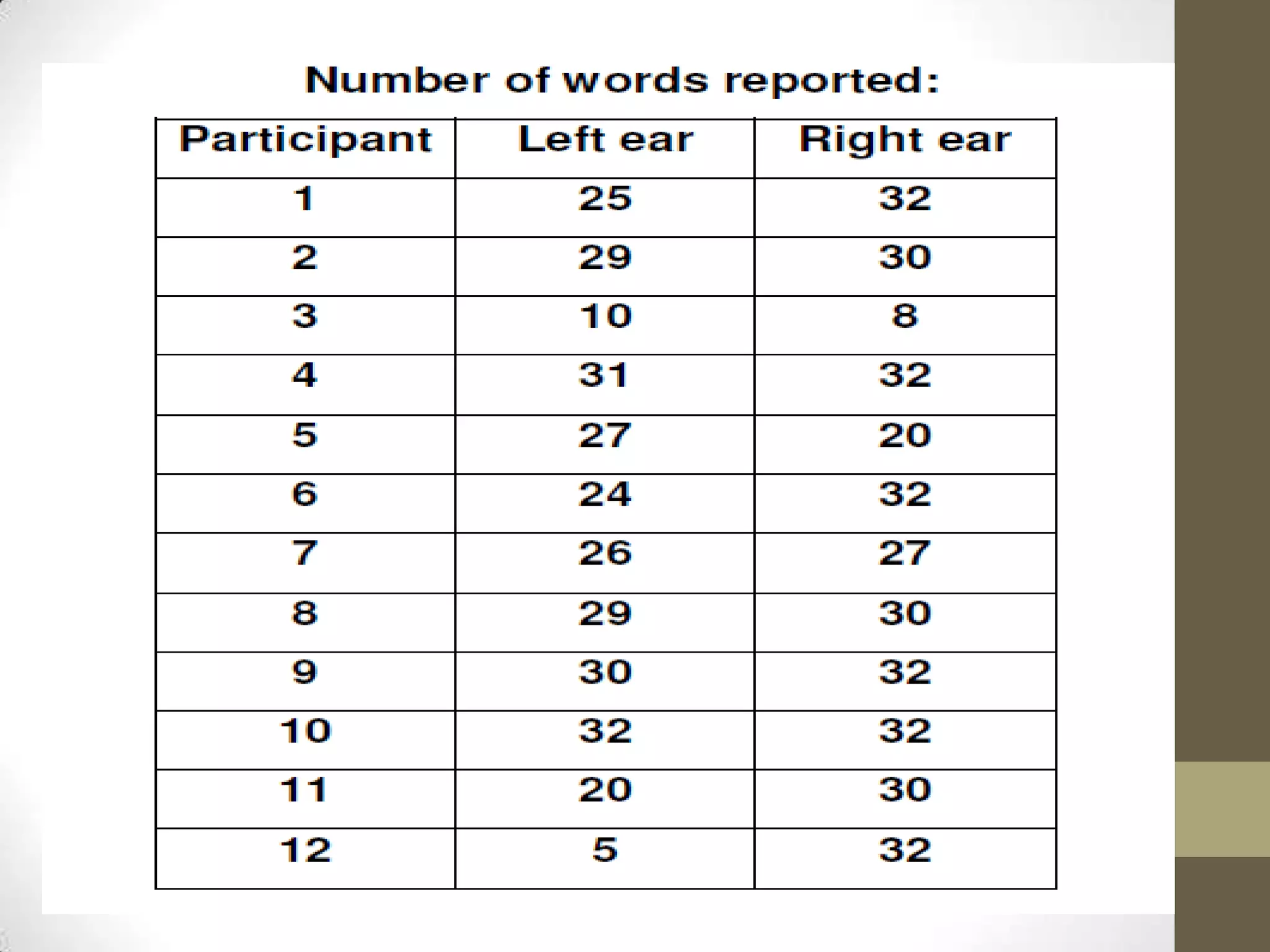
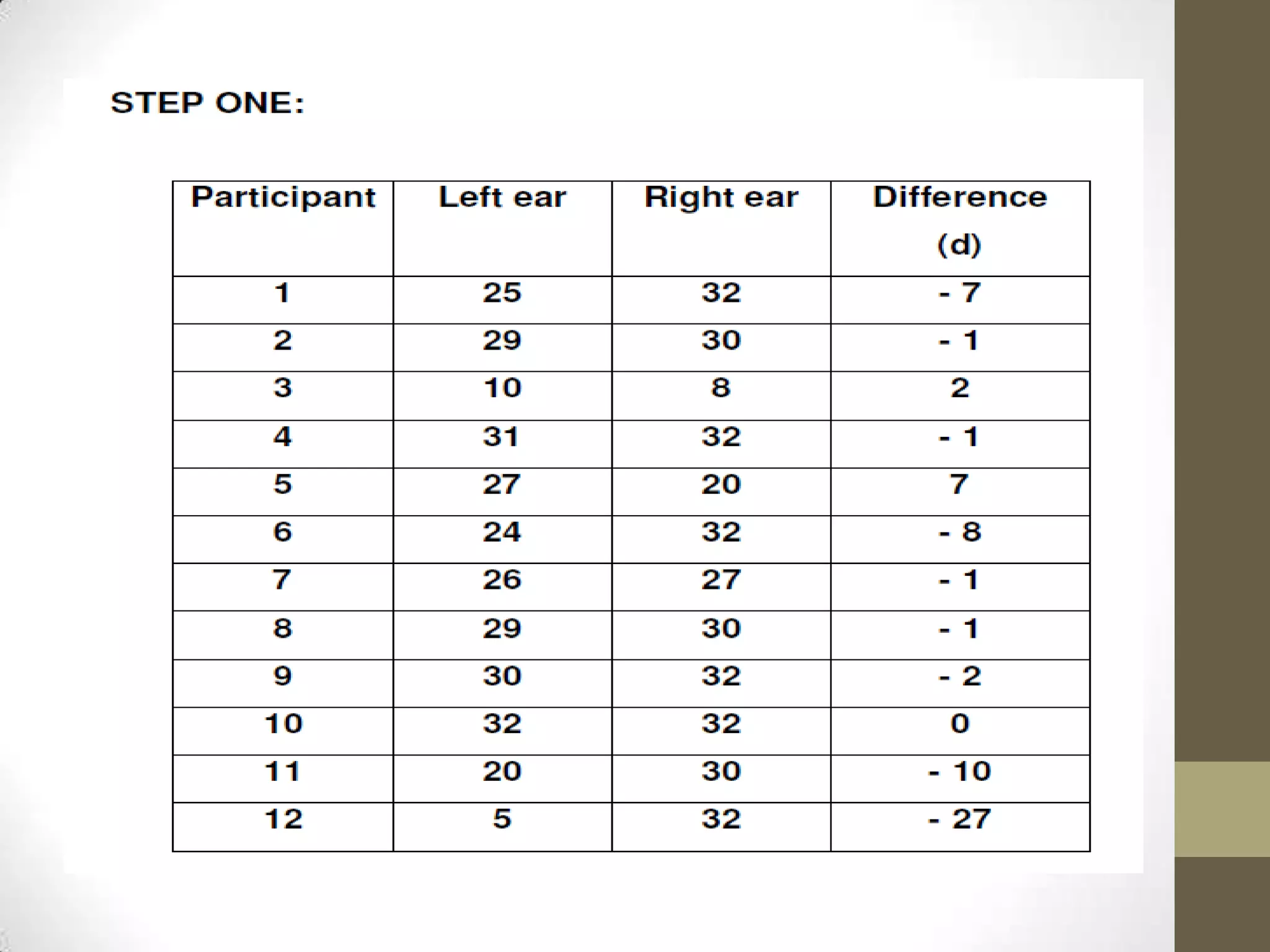
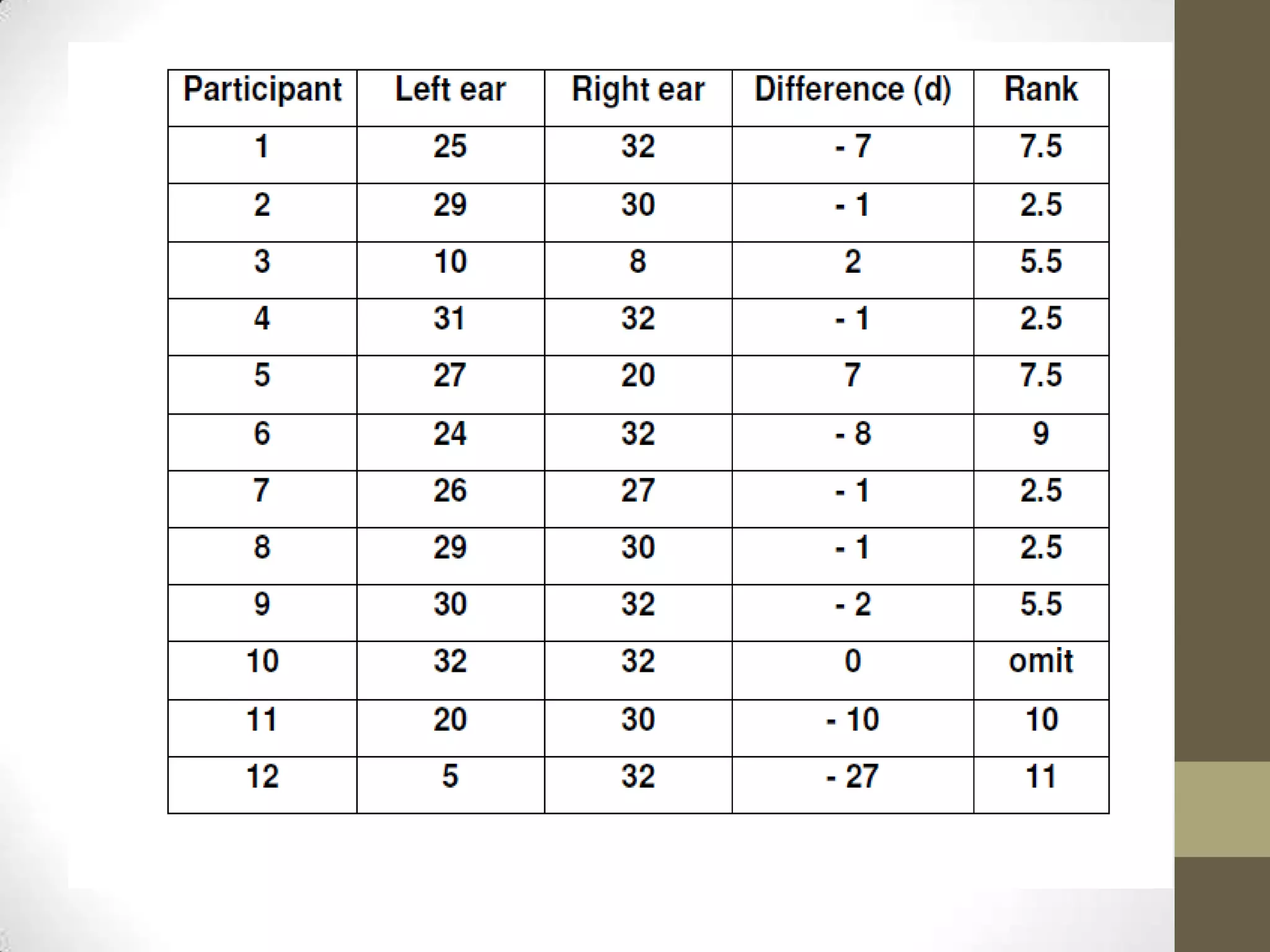
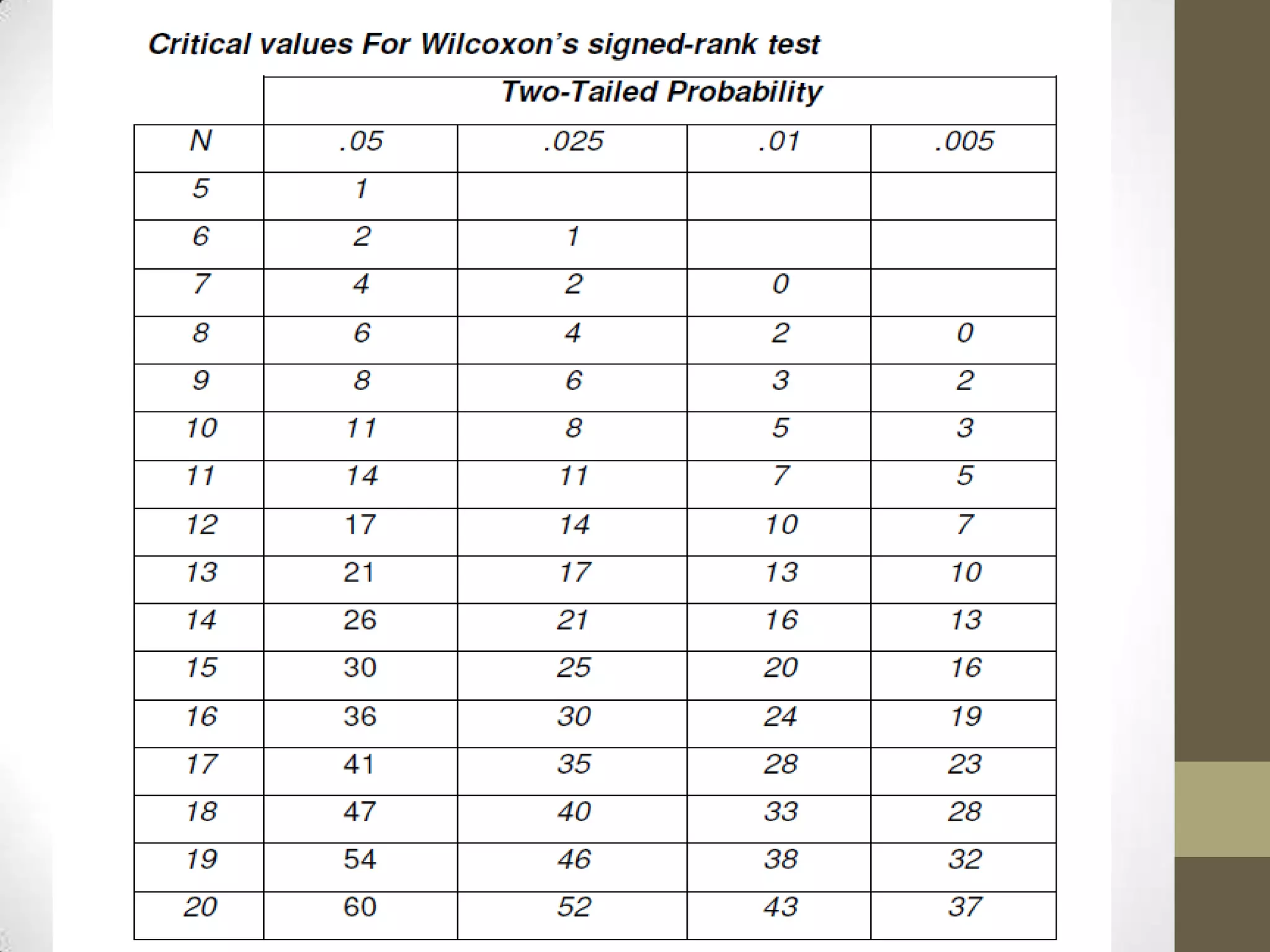
The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is a non-parametric test used to compare two related samples, such as repeated measurements on a single sample, to assess whether their population mean ranks differ. It can be used as a non-parametric alternative to the paired Student's t-test when the population cannot be assumed to be normally distributed. The test involves ranking the differences between pairs of observations and comparing the sum of the ranks of the positive differences to what would be expected if there was no effect. The document provides information on the requirements, formula, and an example application of the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.





![Formula
, the absolute value of the sum of the signed ranks.
1.
As
For
increases, the sampling distribution of
converges to a normal distribution. Thus,
, a z-score can be calculated
as
.
If
then reject
For
,
If
is compared to a critical value from a reference table.[1]
then reject
Alternatively, a p-value can be calculated from enumeration of all possible combinations
of
given
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wilcoxonpowerpoint-140208065322-phpapp02/75/Advance-Statistics-Wilcoxon-Signed-Rank-Test-6-2048.jpg)