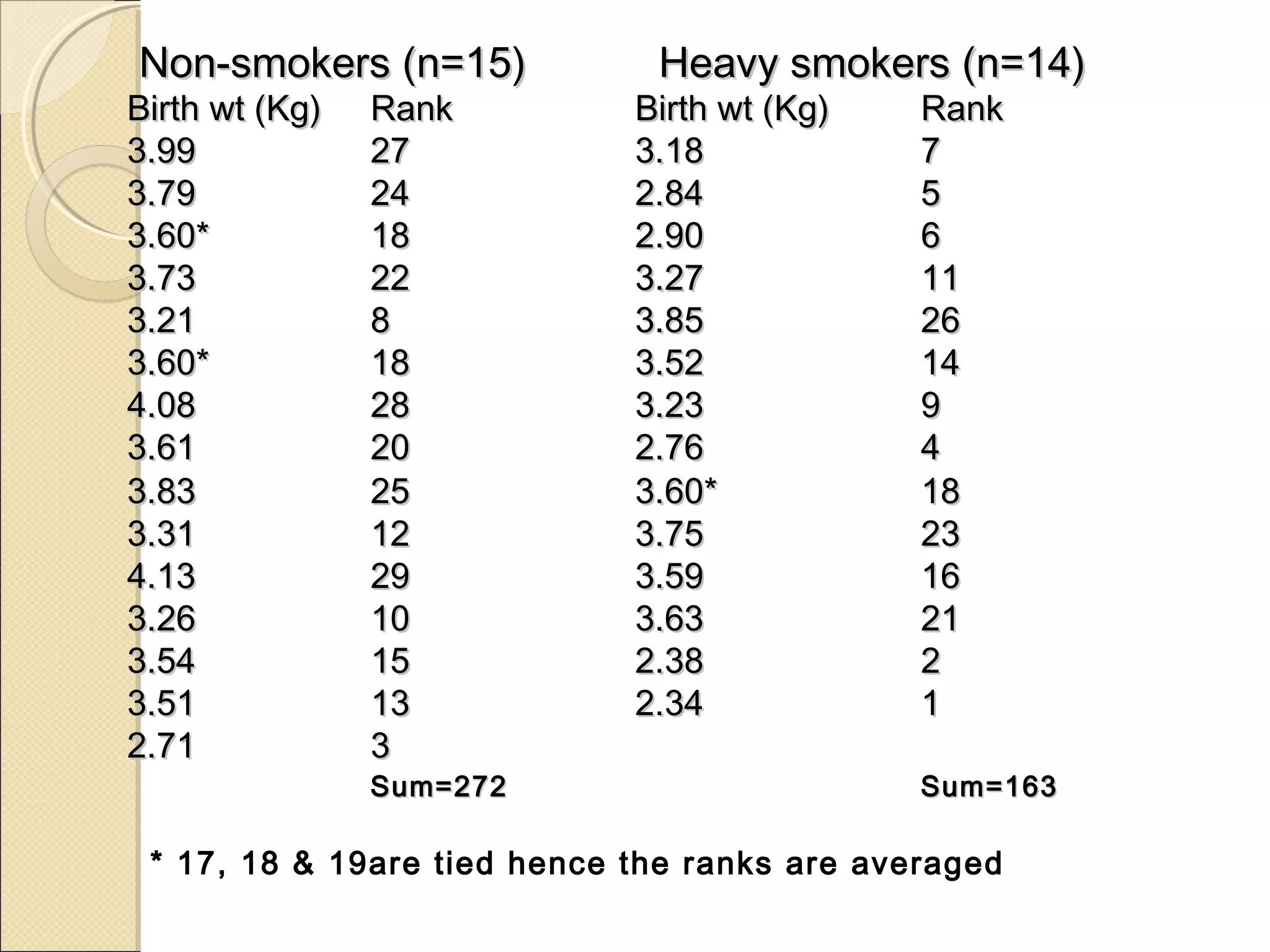
The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is a non-parametric statistical test used to compare two related samples or repeated measurements on a single sample to assess if their population mean ranks differ. It can be used as an alternative to the paired t-test when the population cannot be assumed to be normally distributed. The test involves ranking the differences between paired observations, ignoring the signs of the differences, and comparing the sum of the ranks of the positive or negative differences to critical values to determine if there are statistically significant differences between the samples. A limitation is that observations with a difference of zero are discarded, which can be a concern if samples come from a discrete distribution.

![The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is a non-parametric
statistical hypothesis test used when comparing two related
samples, matched samples, or repeated measurements on a
single sample to assess whether their population mean
ranks differ (i.e. it is a paired difference test). It can be used
as an alternative to the paired Student's t-test, t-test for
matched pairs, or the t-test for dependent samples when
the population cannot be assumed to be normally
distributed.[1]
A Wilcoxon signed-rank test is a
nonparametric test that can be used to determine whether
two dependent samples were selected from populations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mt-180930092153/75/wilcoxon-signed-rank-test-2-2048.jpg)












![Limitation[edit]
As demonstrated in the example, when the
difference between the groups is zero, the
observations are discarded. This is of
particular concern if the samples are taken
from a discrete distribution. In these
scenarios the modification to the Wilcoxon
test by Pratt 1959, provides an alternative
which incorporates the zero differences.[4]
[5]
This modification is more robust for data
on an ordinal scale](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mt-180930092153/75/wilcoxon-signed-rank-test-16-2048.jpg)
