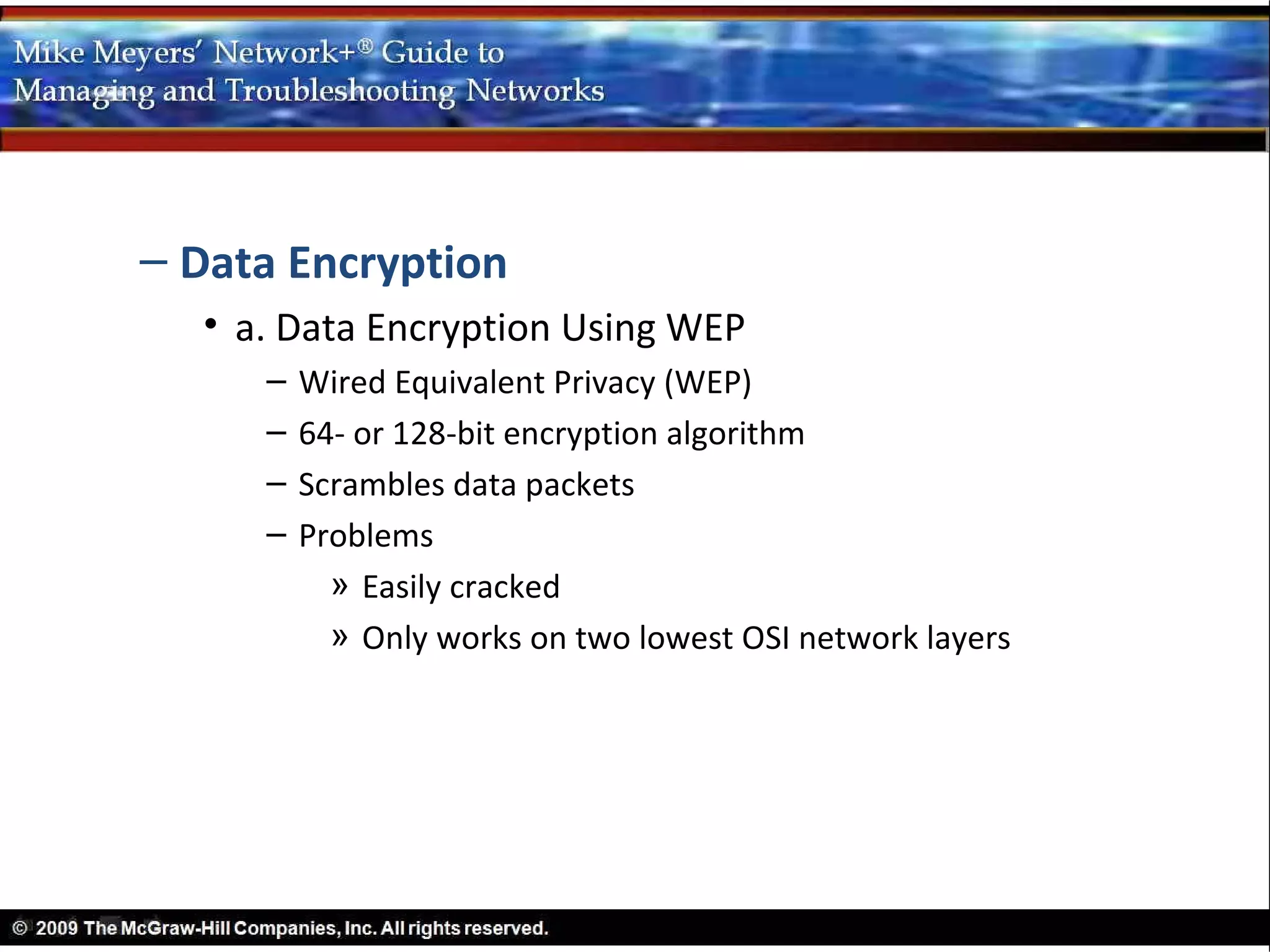
This document provides an overview of wireless networking standards and implementations. It describes how wireless networks use radio waves to communicate and follow the same OSI layers as wired networks. It outlines several IEEE 802.11 wireless standards including 802.11a, b, g, and n. It also discusses how Wi-Fi networks can operate in ad-hoc or infrastructure modes and how CSMA/CA is used to allow multiple devices to share the wireless medium. Finally, it covers common wireless security methods like MAC address filtering, wireless authentication, and data encryption using WEP.


![• Historic/Conceptual
– Wireless network uses radio waves as the media
• Convenient
• Sometimes the only network option
• Same OSI layers as wired networks
• Same [upper layer] protocols
• Different methods for accessing the media
• IEEE 802.11 wireless Ethernet standard
– Wi-Fi
– Most common implementation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/net2eppt16-120801185053-phpapp02/75/Networking-Chapter-16-3-2048.jpg)