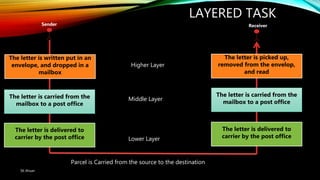
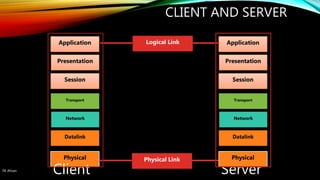
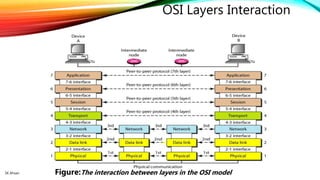
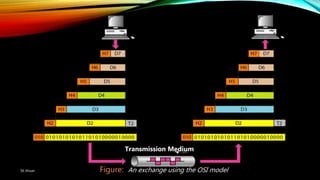
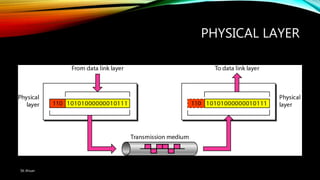
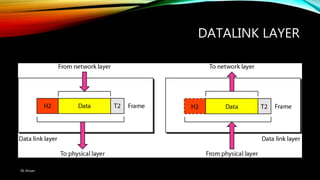
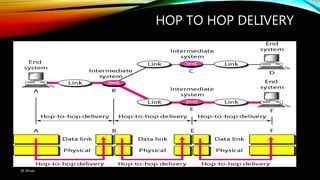
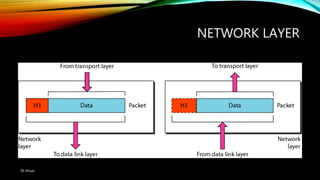
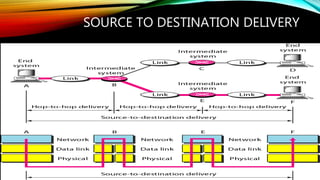
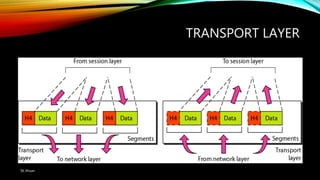
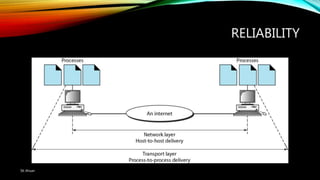
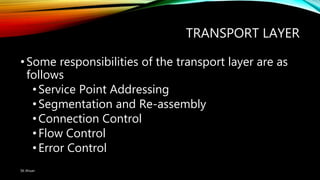
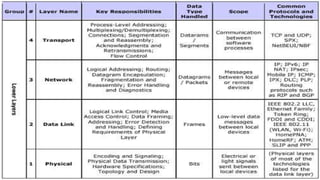
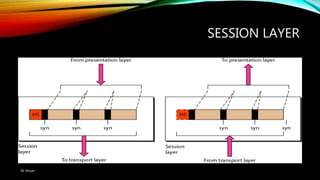
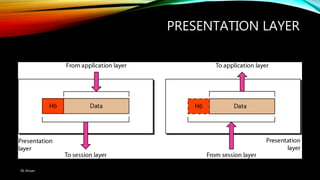
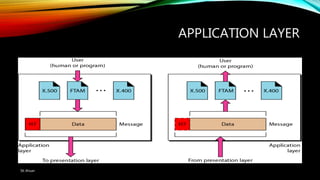
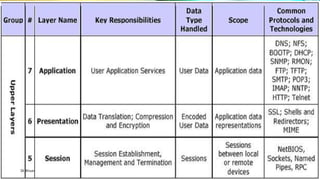
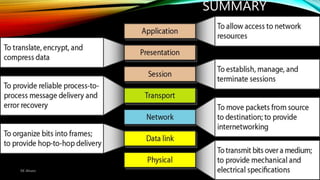
The document discusses the OSI model and its seven layers, detailing how different protocols work together to facilitate network communication. It explains the roles and responsibilities of each layer, ranging from the physical layer that handles raw bit transmission to the application layer that provides services to end-user applications. The content emphasizes the importance of layered architecture in simplifying communication processes and interoperability between different systems.