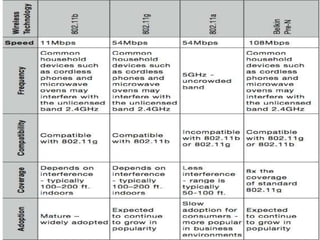
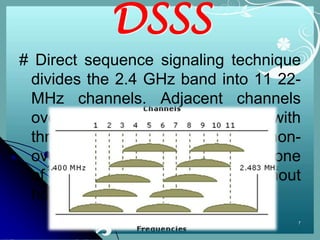
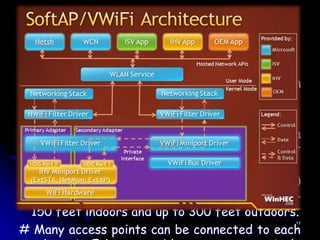
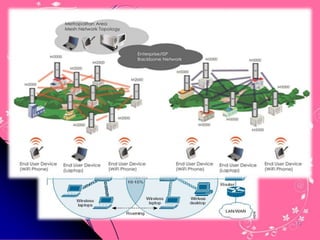
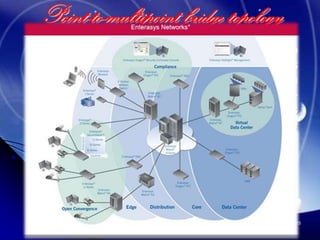
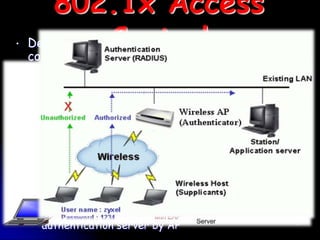
Wi-Fi is a wireless technology standard that allows electronic devices to connect to the internet or communicate with each other wirelessly. The presentation discusses Wi-Fi technologies like 802.11b, 802.11a, and 802.11g. It explains the basic components of a Wi-Fi network including access points, Wi-Fi cards, and security measures. It also covers Wi-Fi configurations, applications, security techniques and topologies like AP-based, peer-to-peer, and point-to-multipoint bridge.