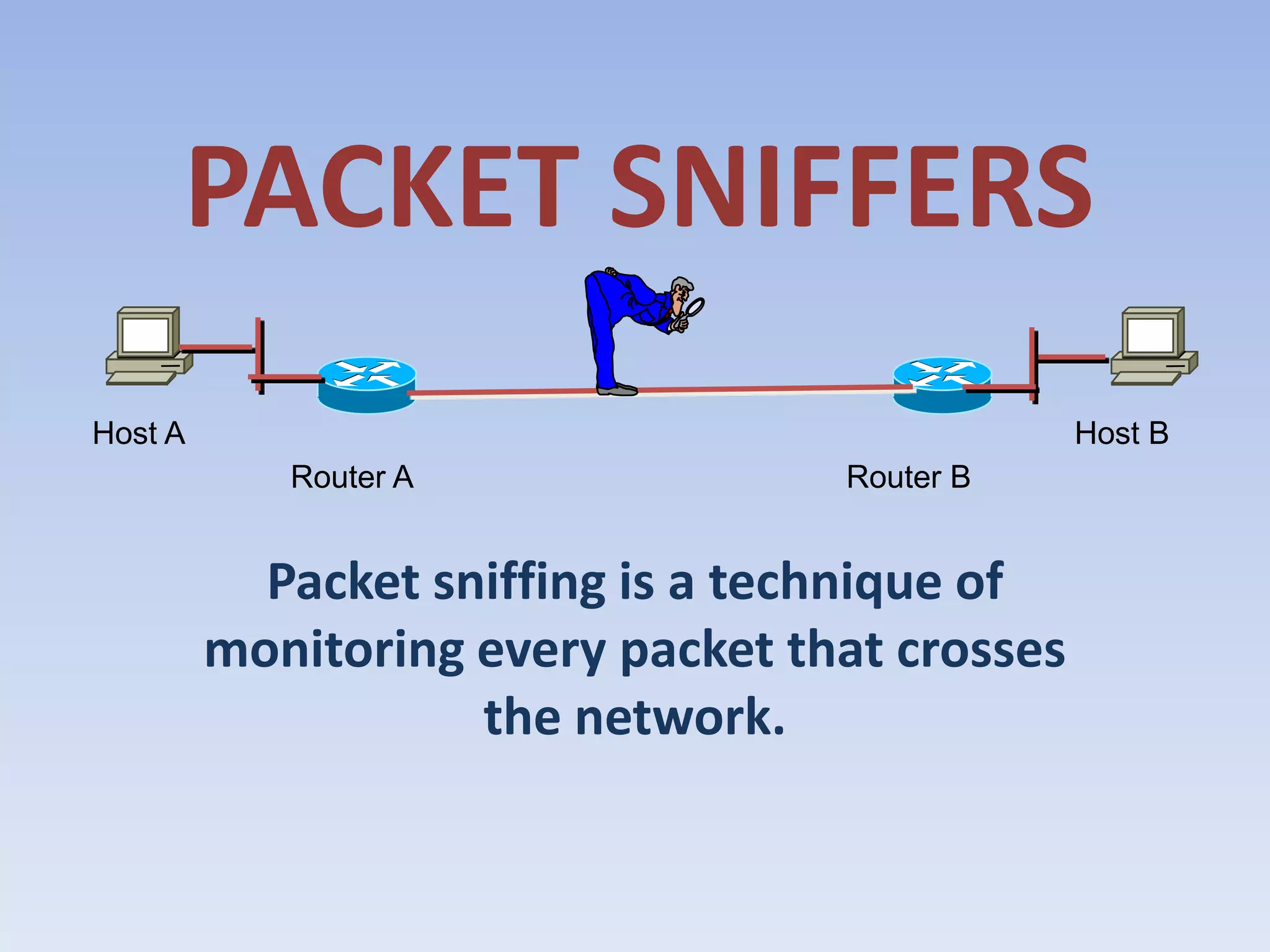
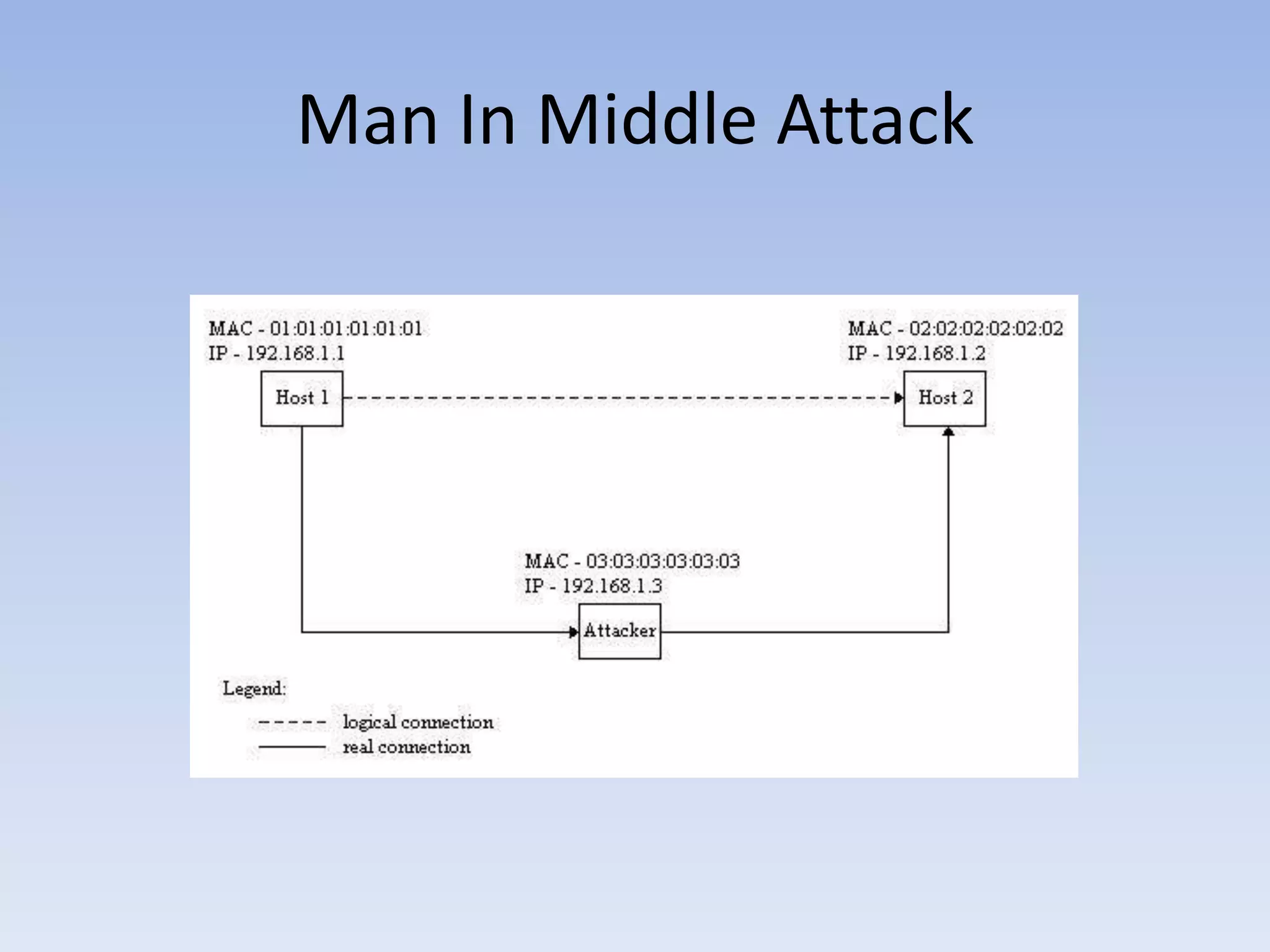
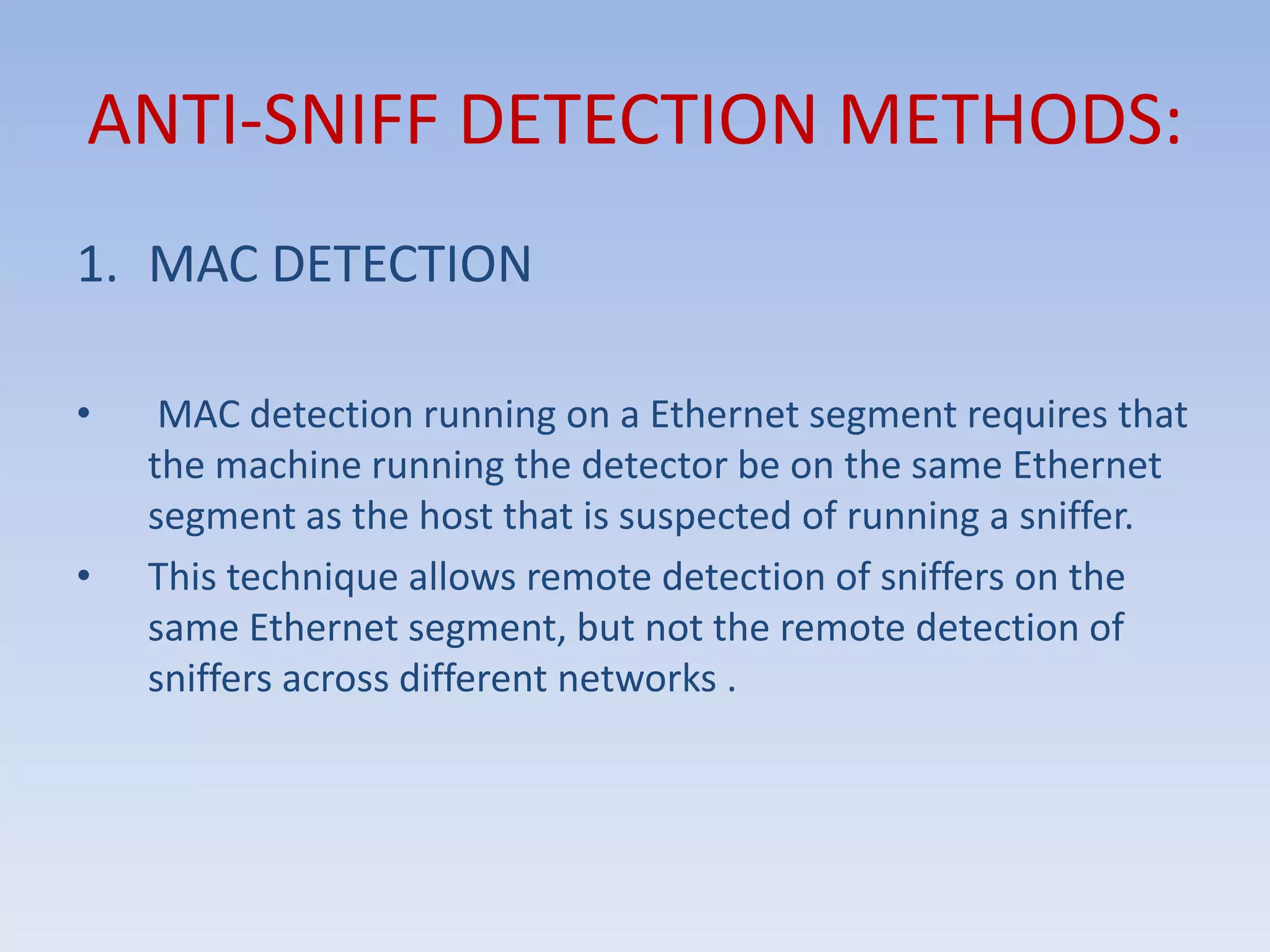
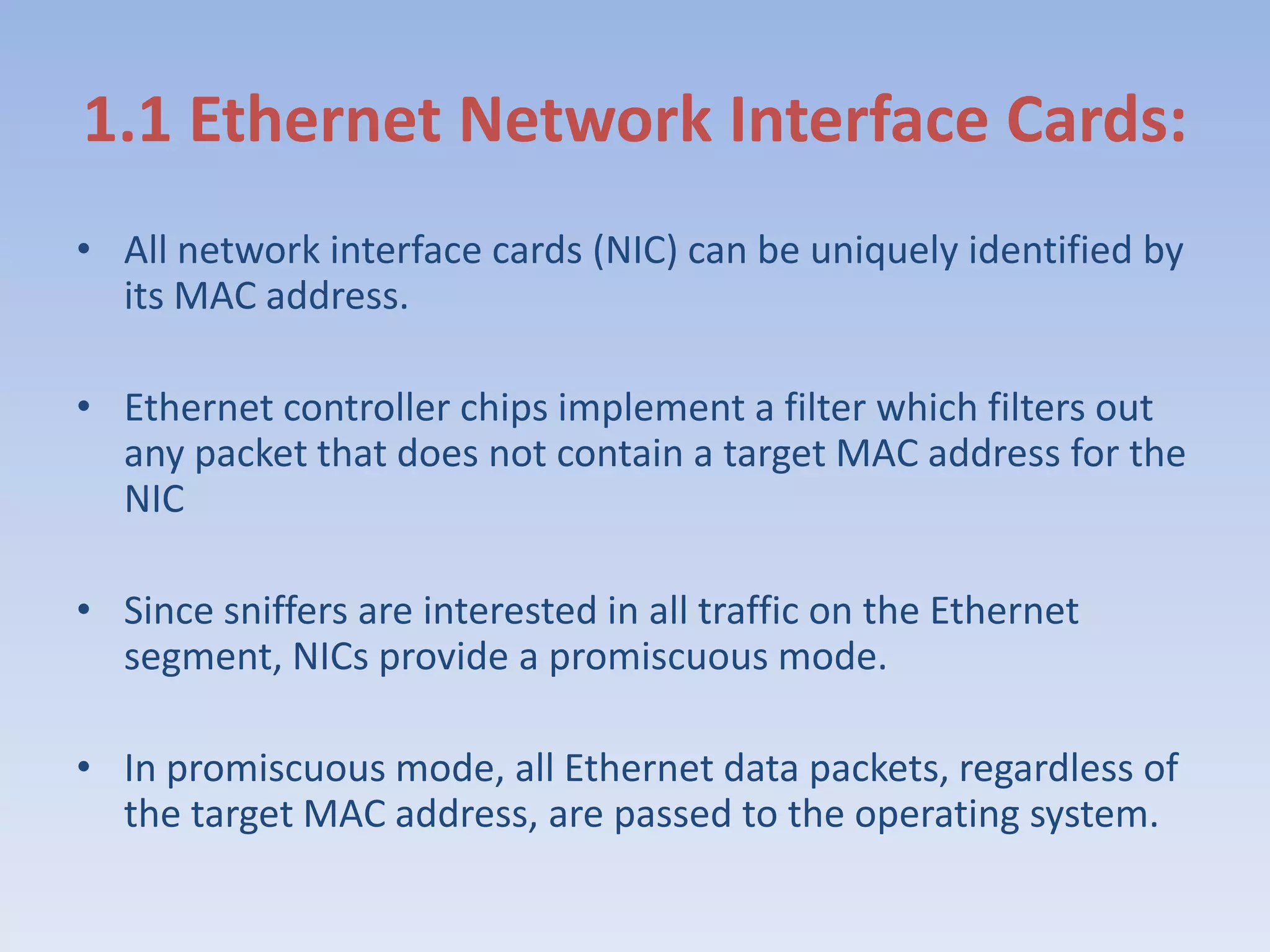
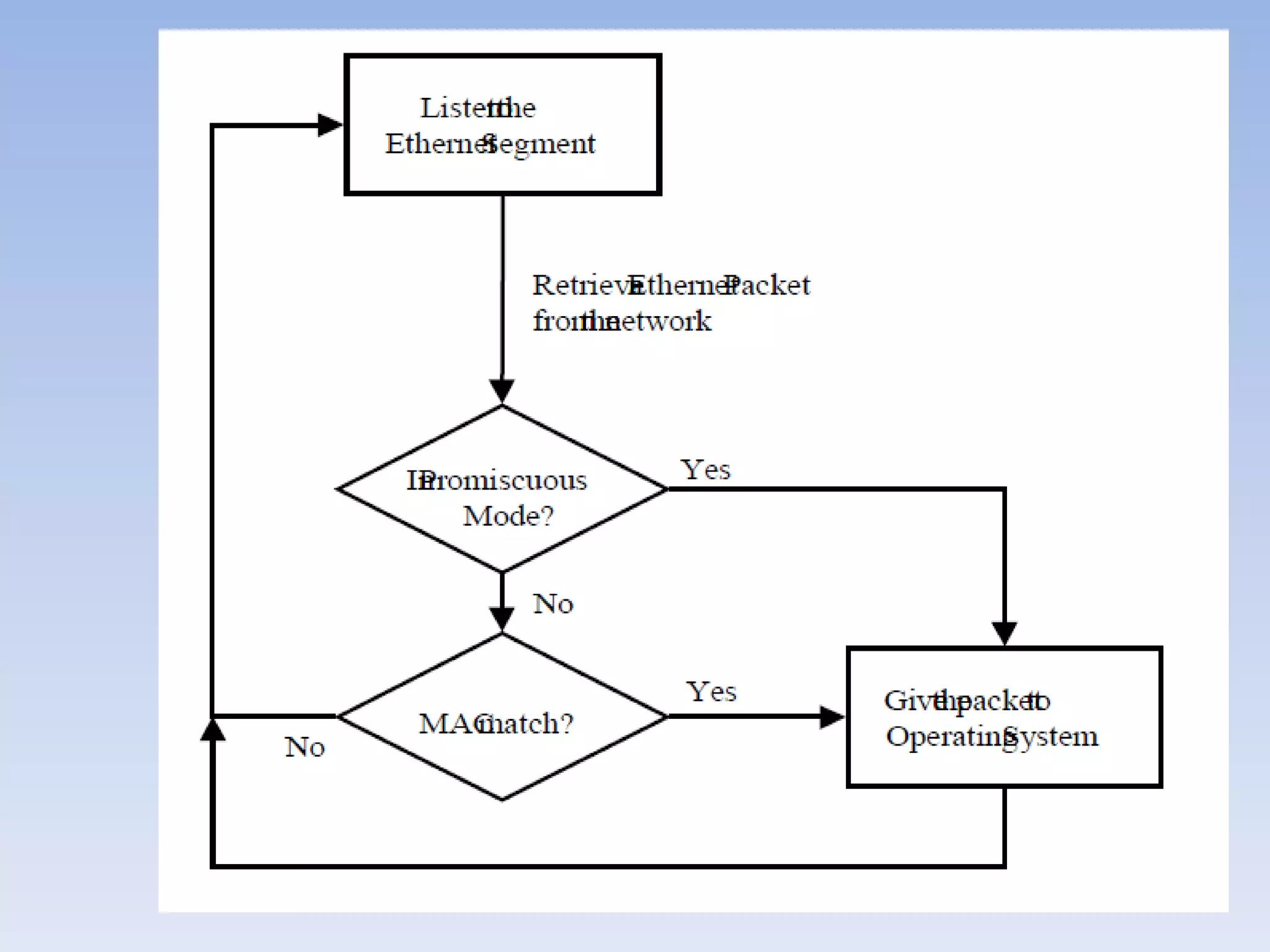
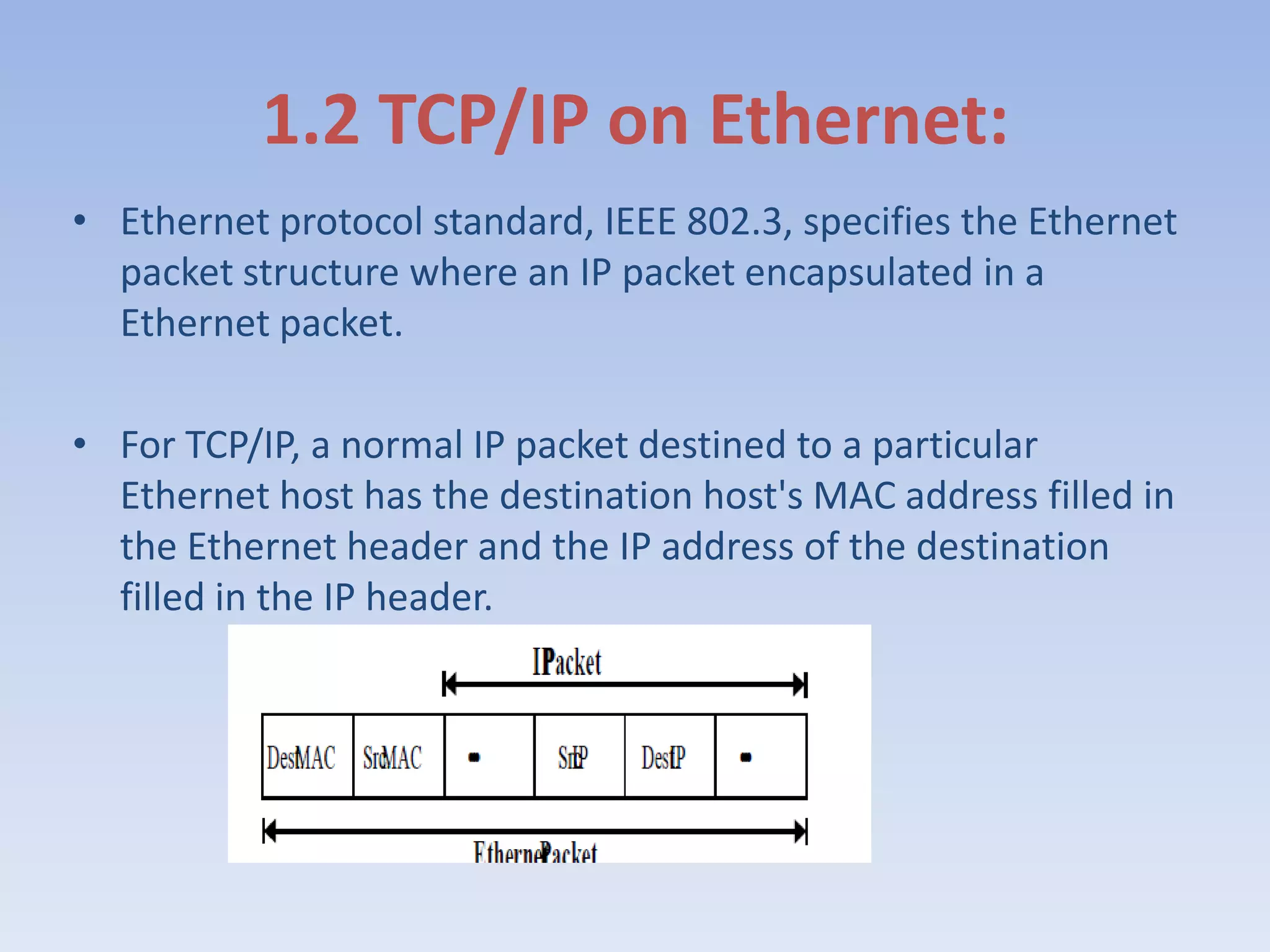
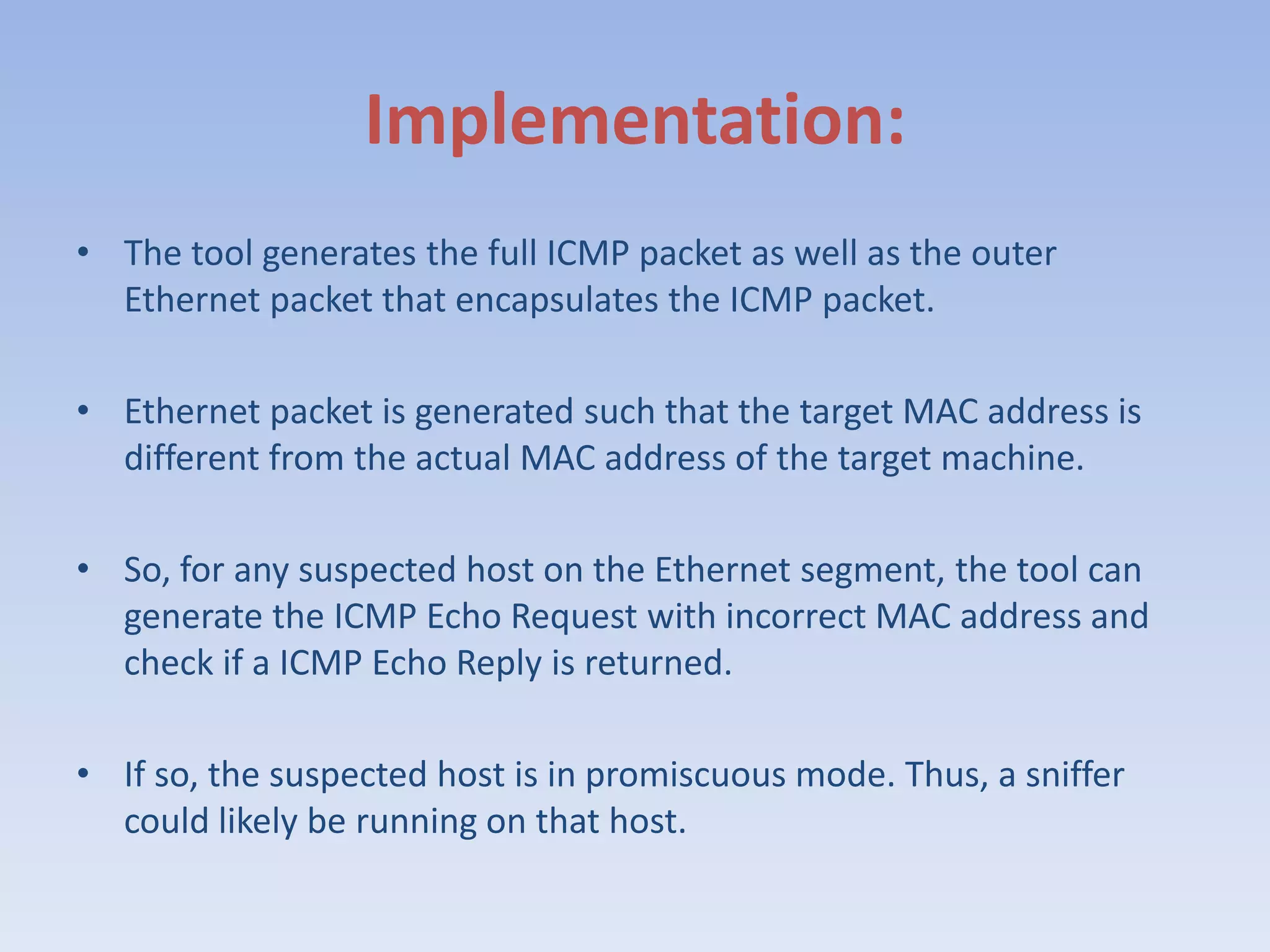
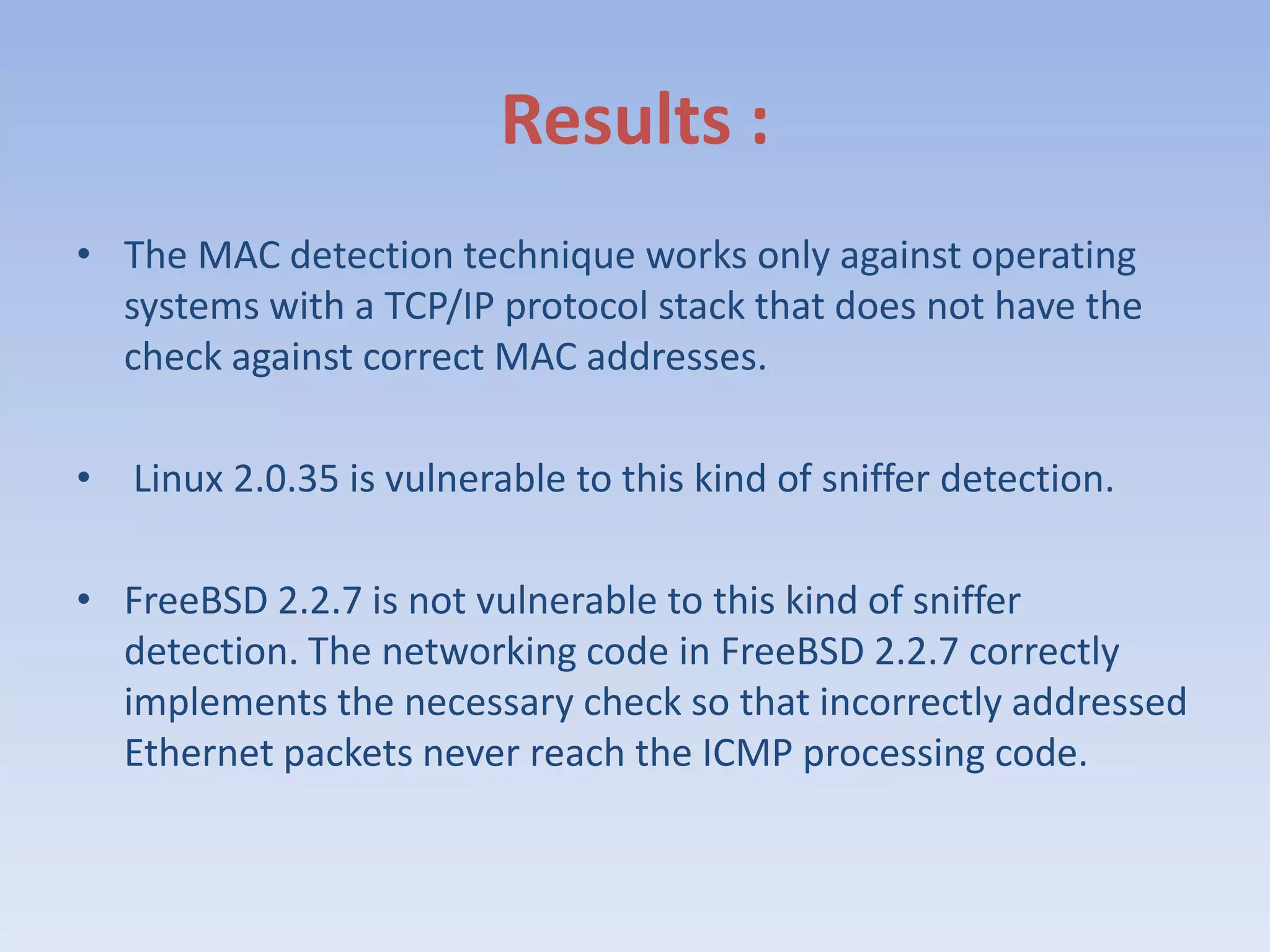
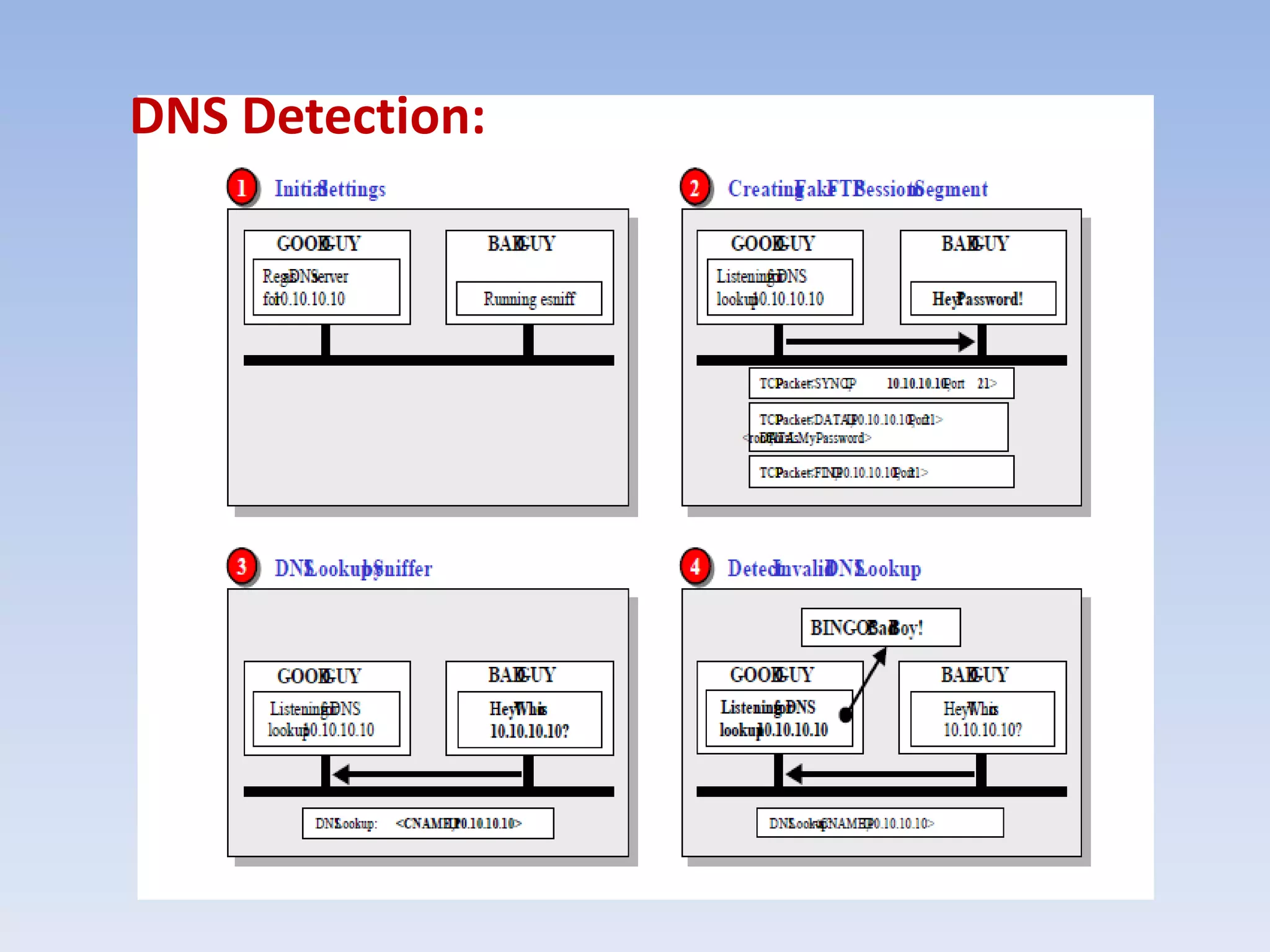
This document discusses packet sniffing and methods for detecting packet sniffers. It defines packet sniffing as monitoring all network packets and describes common packet sniffer tools like tcpdump. It explains that packet sniffers can be used for both legitimate and malicious purposes, such as password theft or network mapping. The document outlines two key methods for detecting packet sniffers - MAC detection and DNS detection. MAC detection works by sending packets with invalid MAC addresses and checking if any hosts respond in promiscuous mode. DNS detection exploits the behavior of sniffers performing DNS lookups on spoofed source IP addresses. Both methods were found to accurately detect the presence of packet sniffers on a network.