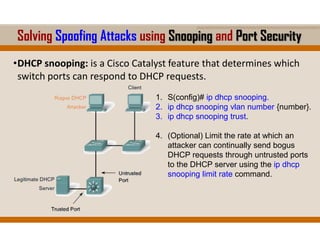
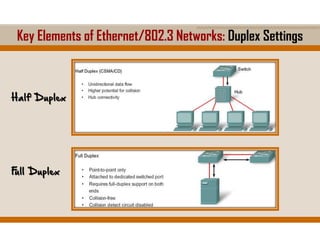
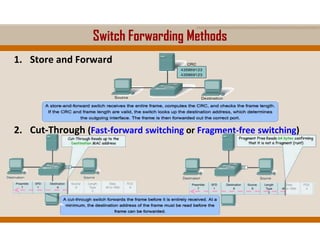
The document covers key elements of Ethernet/802.3 networks, including communication standards, switch port configurations, and design considerations for network performance such as bandwidth and latency. It discusses security measures against common attacks like MAC flooding and spoofing, and explains how to configure port security and DHCP snooping. Additionally, it provides insights into switch management, including configuration, restoring settings, and backing up configurations.


























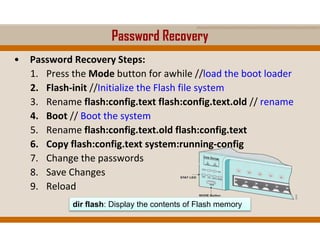
![Back up Configuration Files to a TFTP Server
• Backing Up Configuration
1.switch#copy system:running-config
tftp:[[[//location]/directory]/filename]
2.or switch#copy nvram:startup-config
tftp:[[[//location]/directory]/filename].
• Restoring Configuration
1.Switch#copy tftp:[[[//location]/directory]/filename]
system:running-config
2.or switch#copy tftp:[[[//location]/directory]/filename]
nvram:startup-config.
Ex: S1# copy running-config tftp://192.168.1.1/abdo-config](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02basicswitchconceptsandconfiguration-140823180242-phpapp01/85/LAN-Switching-and-Wireless-Ch2-Basic-Switch-Concepts-and-Configuration-30-320.jpg)