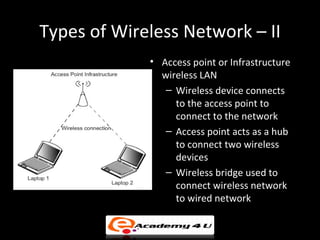
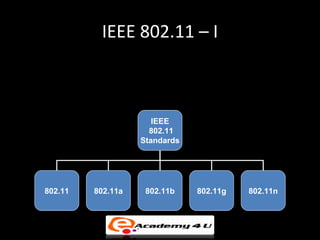
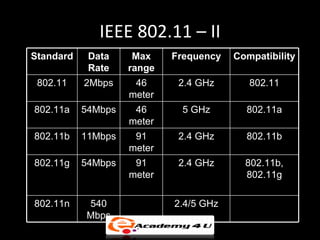
Wireless networking allows devices to connect to a network without cables by using technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and HomeRF. Common types of wireless networks include peer-to-peer networks connecting devices directly and infrastructure networks with an access point connecting devices to a larger network. Key components of setting up a wireless network include wireless adapters, access points, antennas, and configuring standards and security protocols like WEP, WPA, and MAC address filtering.