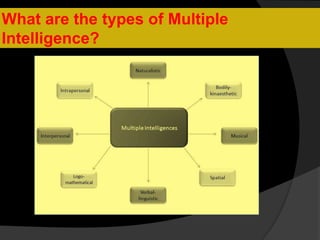
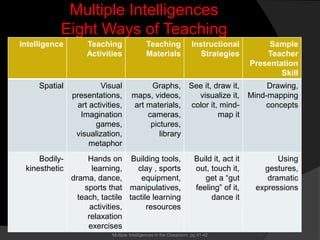
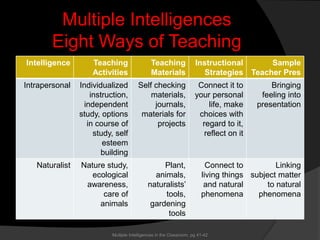
The document discusses Howard Gardner's Theory of Multiple Intelligences, which proposes that intelligence is not a single entity but rather composed of at least eight different intelligences. It outlines each of Gardner's eight intelligences - linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, musical, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalist. For each intelligence, it provides examples of the types of learners that possess that intelligence and sample learning activities and teaching strategies that could benefit those learners. The document advocates assessing students through a variety of methods that engage different intelligences rather than solely through standardized testing.