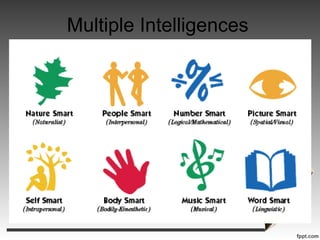
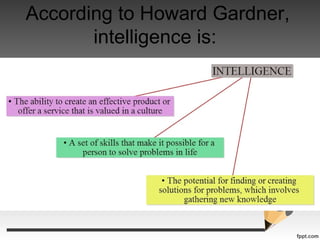
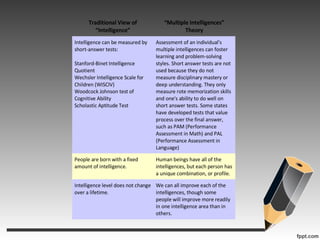
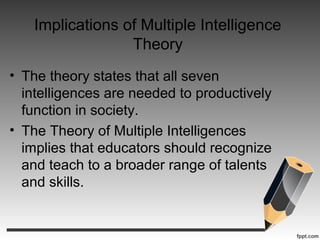
Howard Gardner developed the theory of multiple intelligences which challenged traditional views of intelligence. According to Gardner, intelligence is not a single general capacity but rather consists of at least nine distinct intelligences. These include logical-mathematical, linguistic, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, musical, interpersonal, intrapersonal, naturalist, and existential intelligences. Gardner's theory has implications for education, suggesting teachers structure lessons to engage multiple intelligences and recognize different strengths and styles of learning in students. Critics argue the theory is not well defined and may not encourage core knowledge, while supporters believe it leads to more authentic, strengths-based learning.