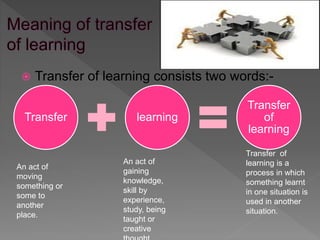
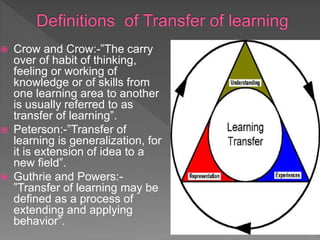
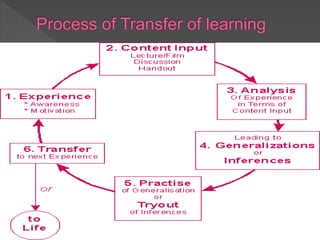
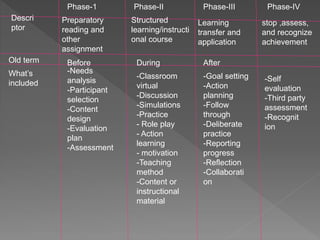
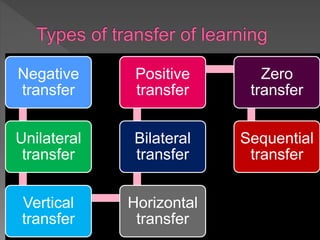
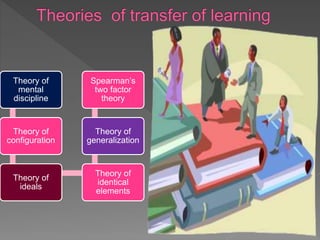
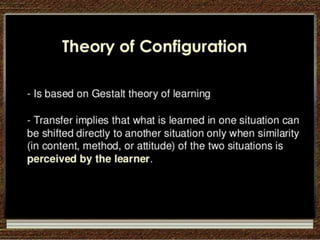
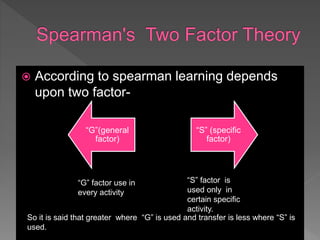
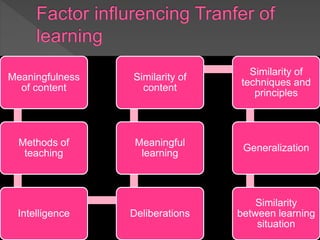
This document discusses transfer of learning, which refers to applying knowledge or skills learned in one context to another new context. It defines transfer of learning and discusses various types of transfer. Theories of transfer from scholars like Crow and Crow, Peterson, and Guthrie are presented. Factors that influence transfer, like curriculum design, teaching methods, learner characteristics, are explained. Implications for teachers and learners are discussed to improve transfer. Theories like identical elements theory and generalization theory are summarized.