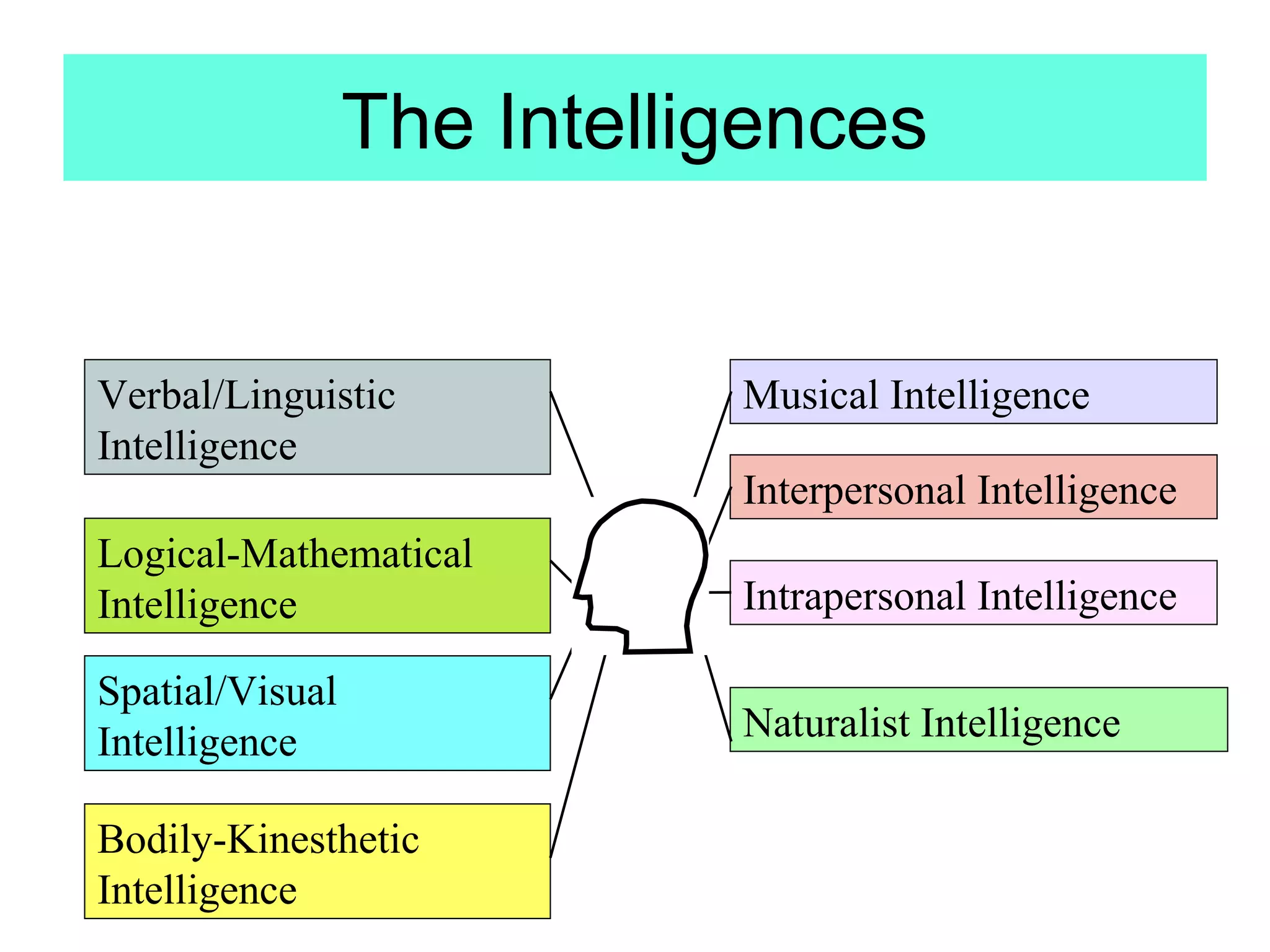
The document outlines Howard Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences, which defines intelligence as the ability to solve problems and create products valued in a particular cultural context. Gardner proposes eight intelligences: linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, musical, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalist. The theory suggests that language learning should incorporate and value all intelligences, not just linguistic skills. Teachers should help students develop their multiple intelligences and see language learning as part of personal development. A variety of activities can be used to engage different intelligences in the language classroom.