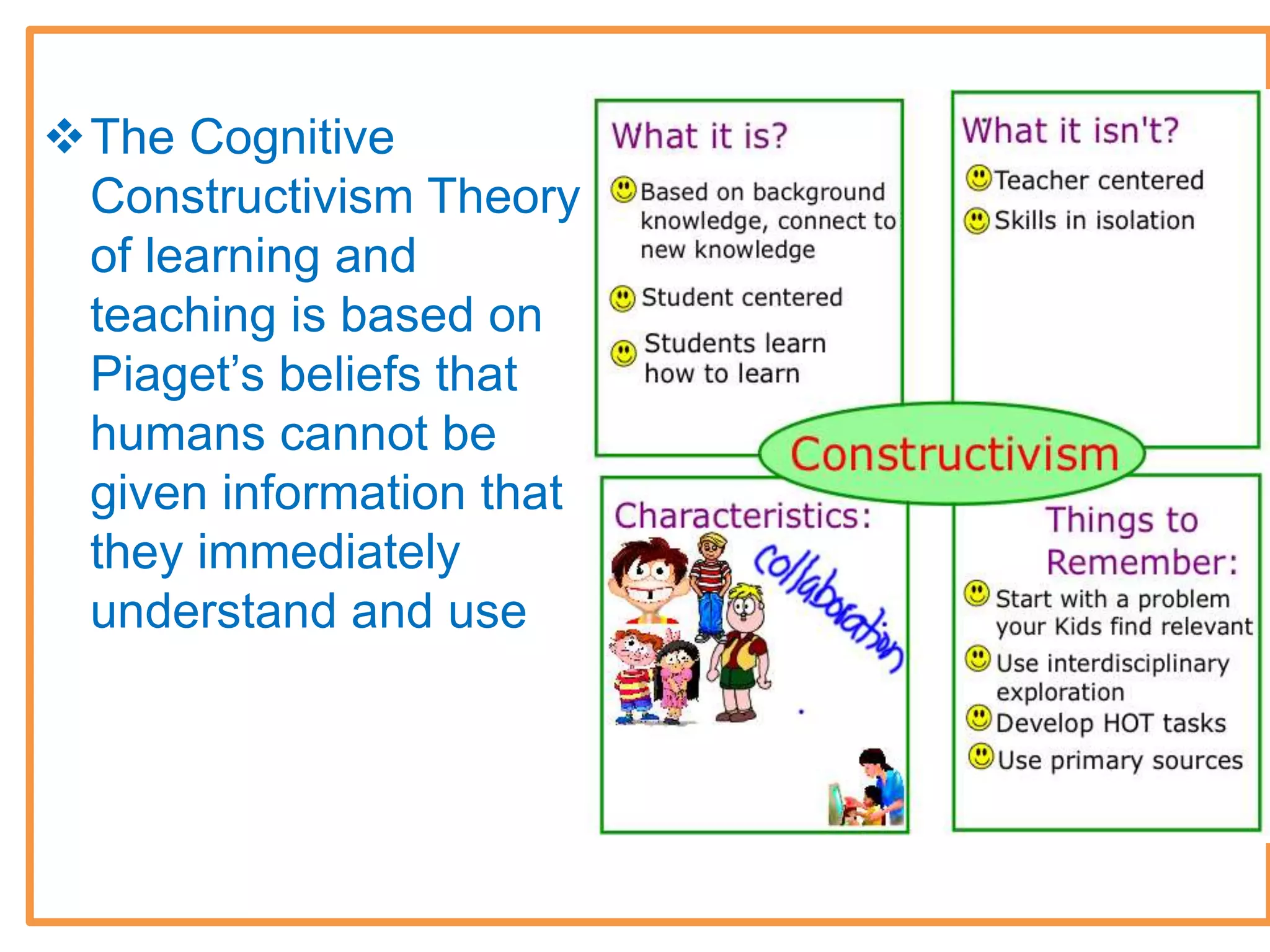
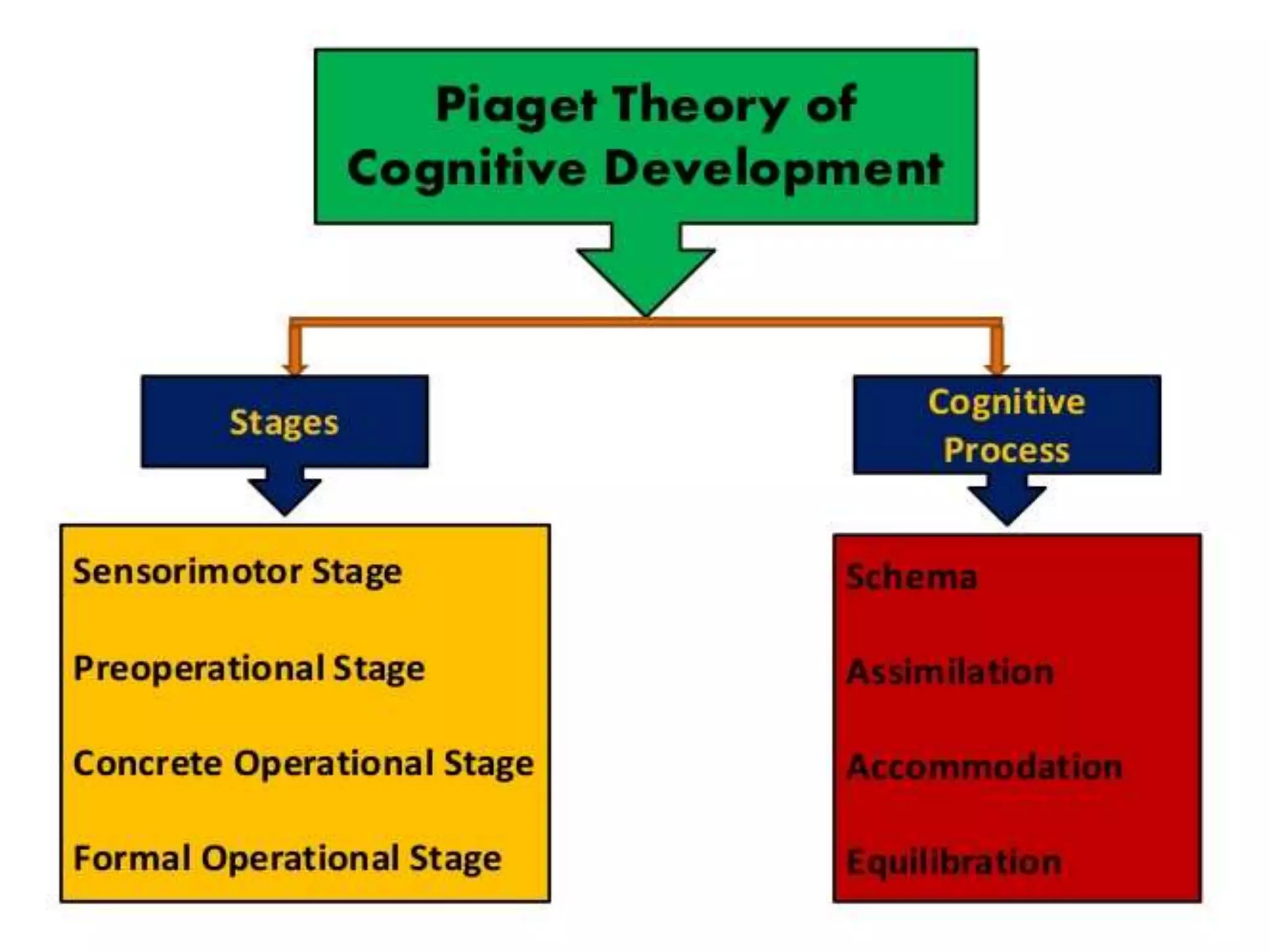
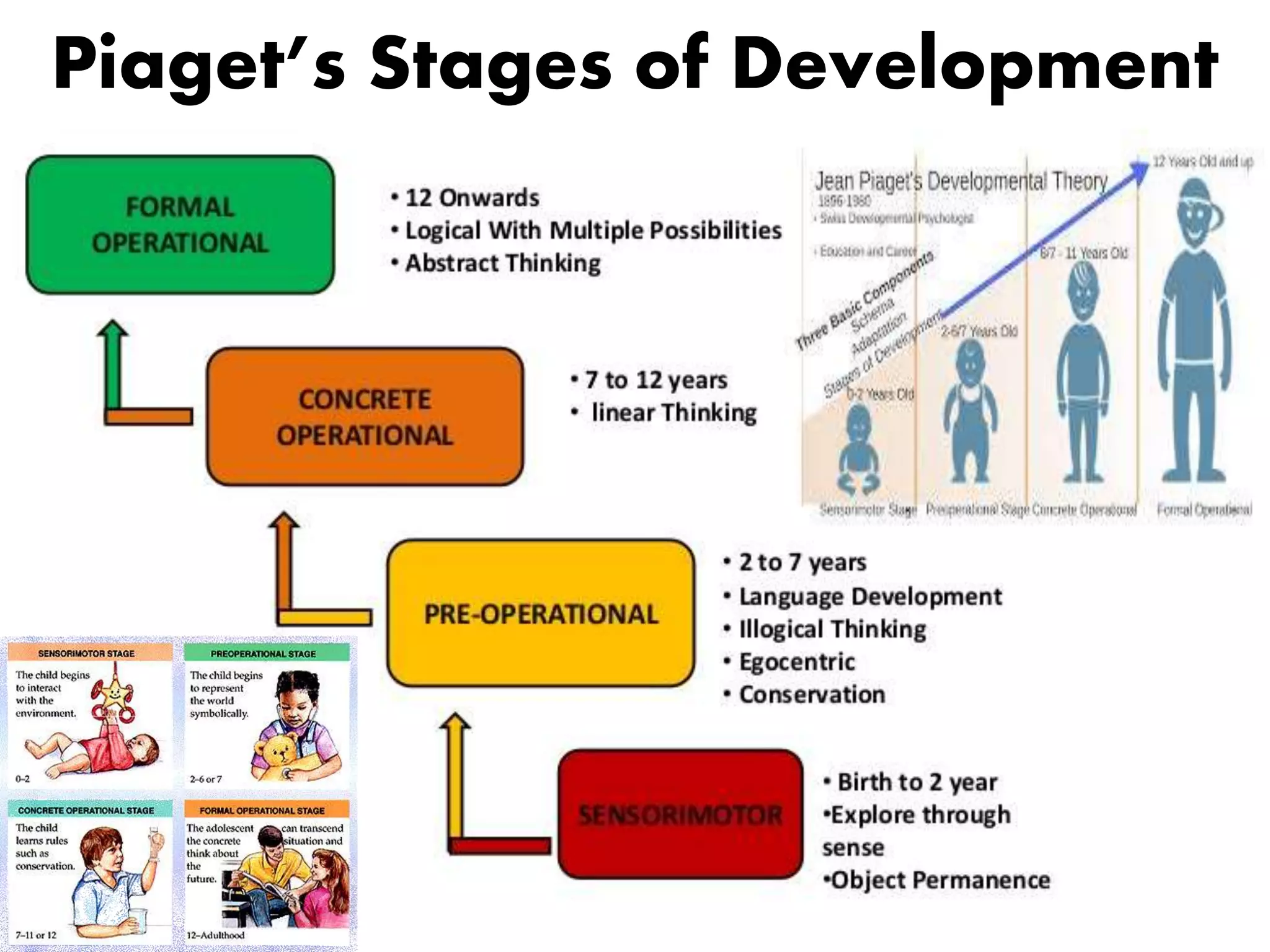
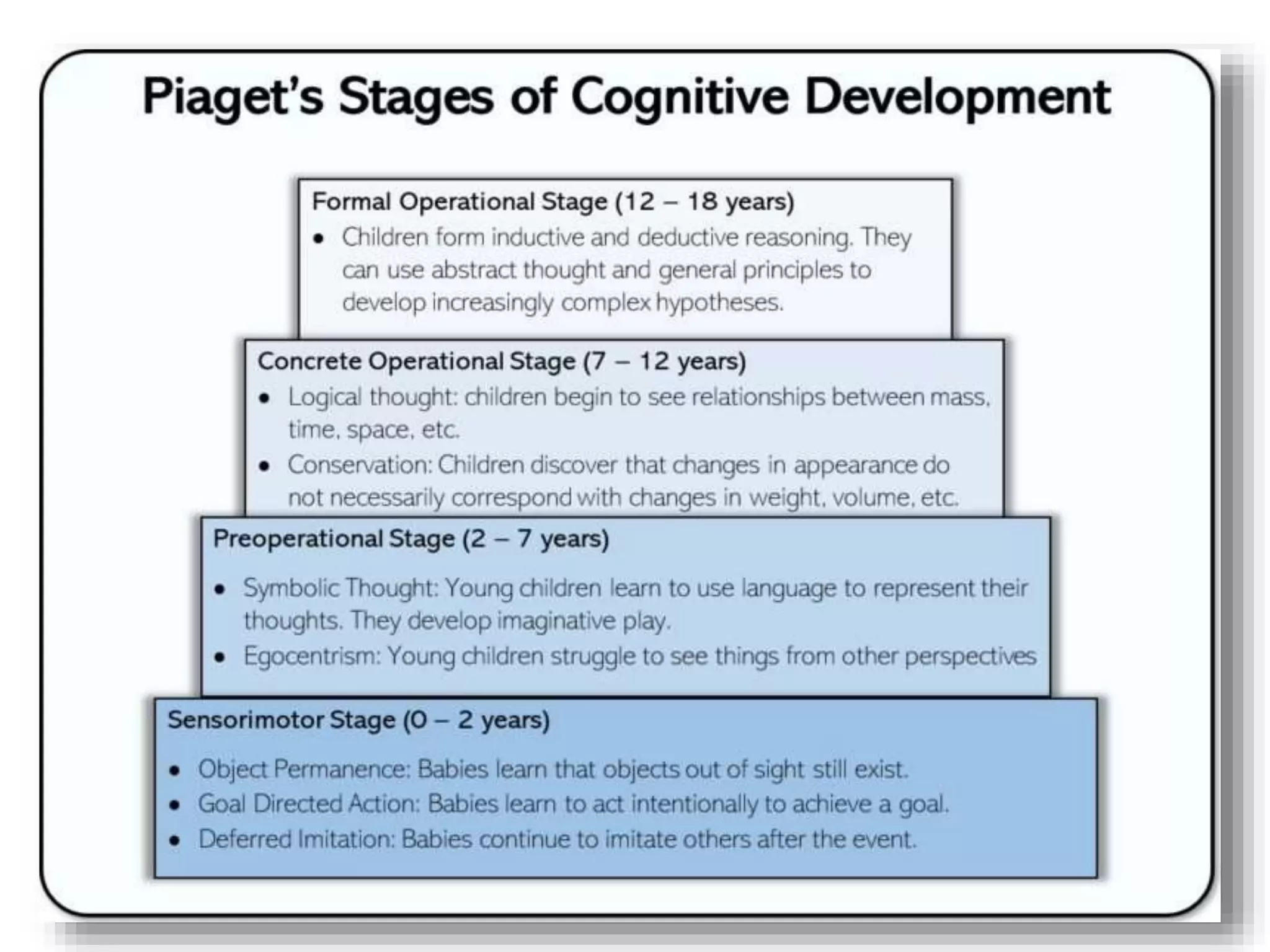
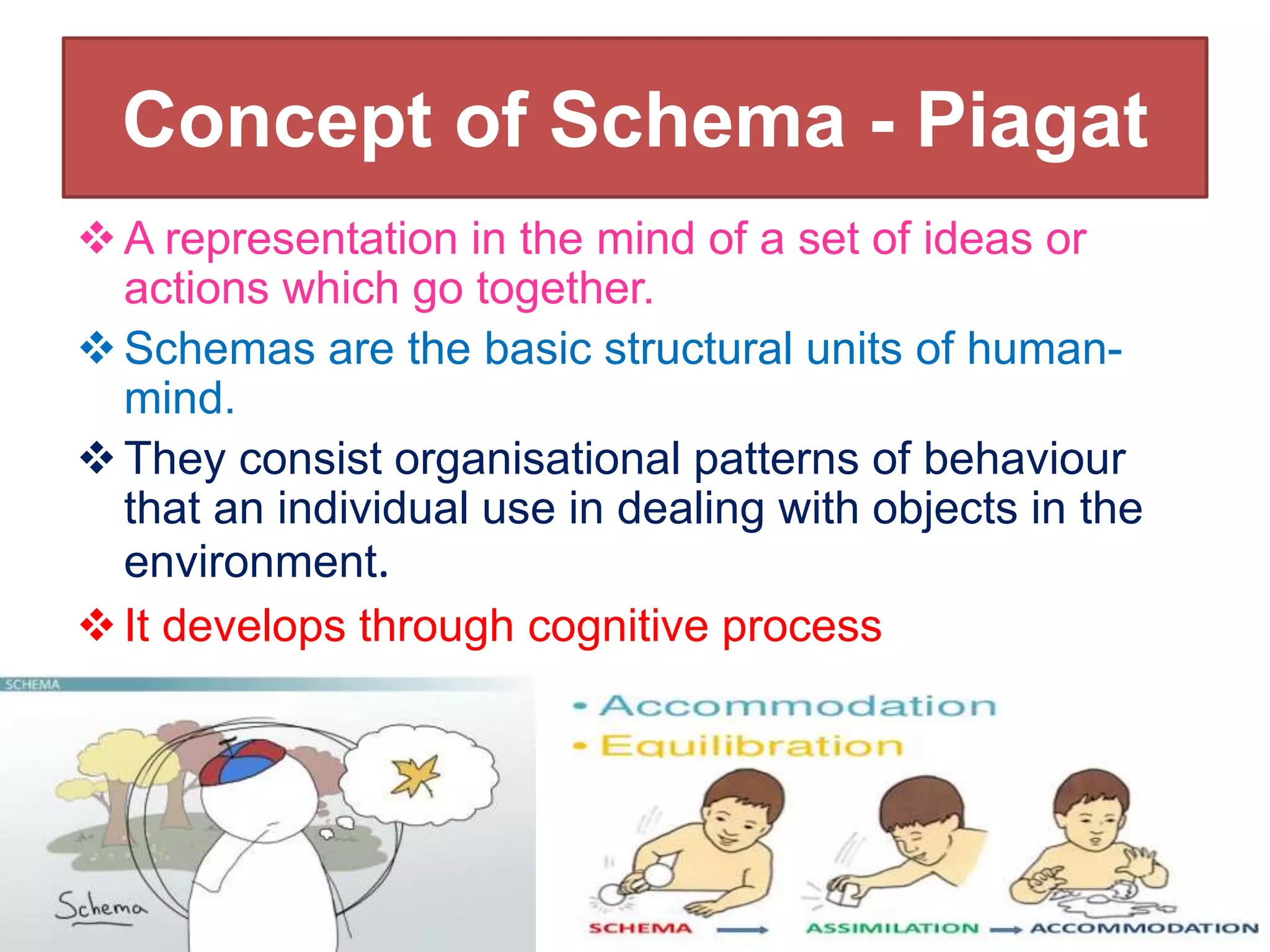
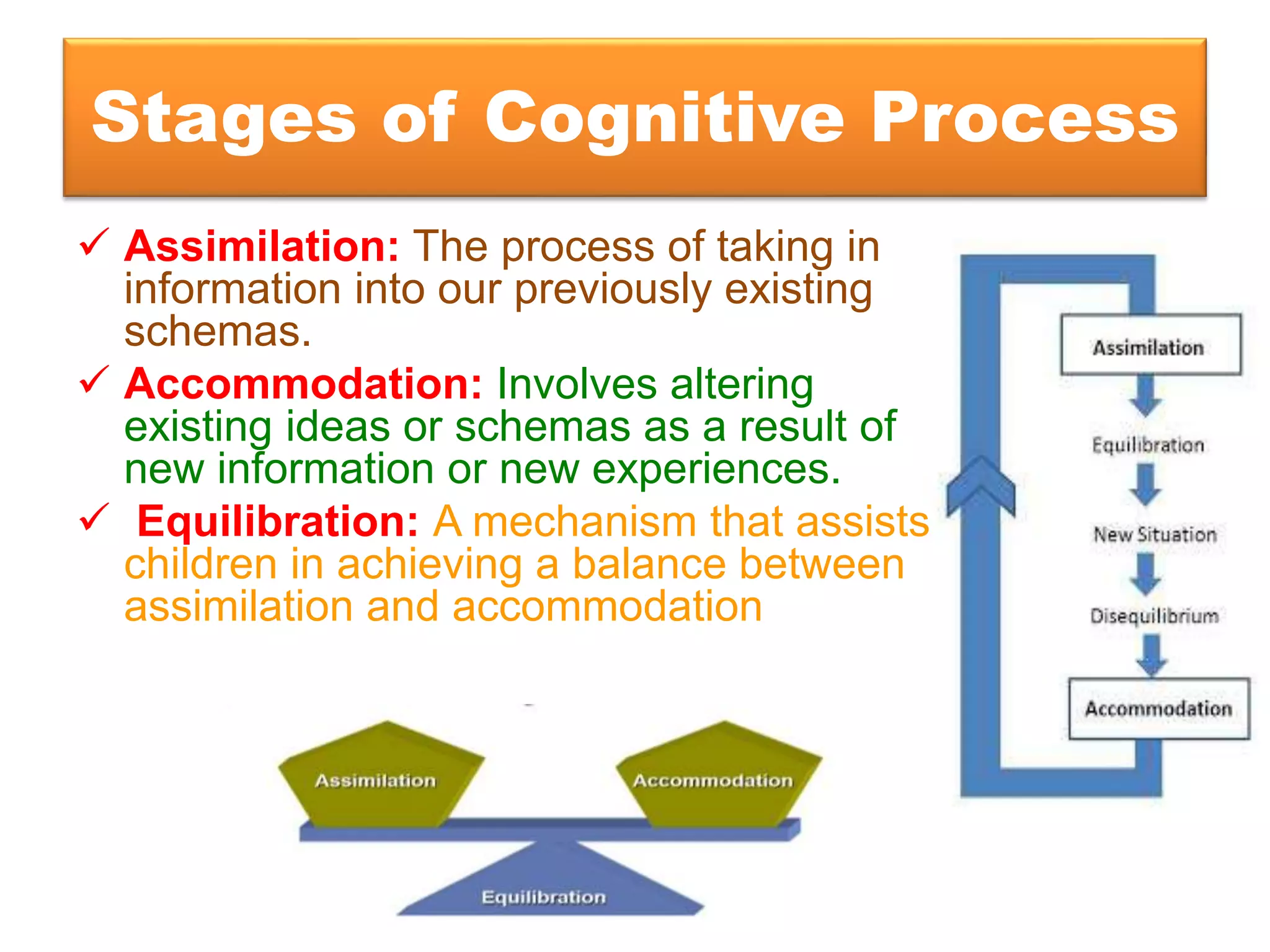
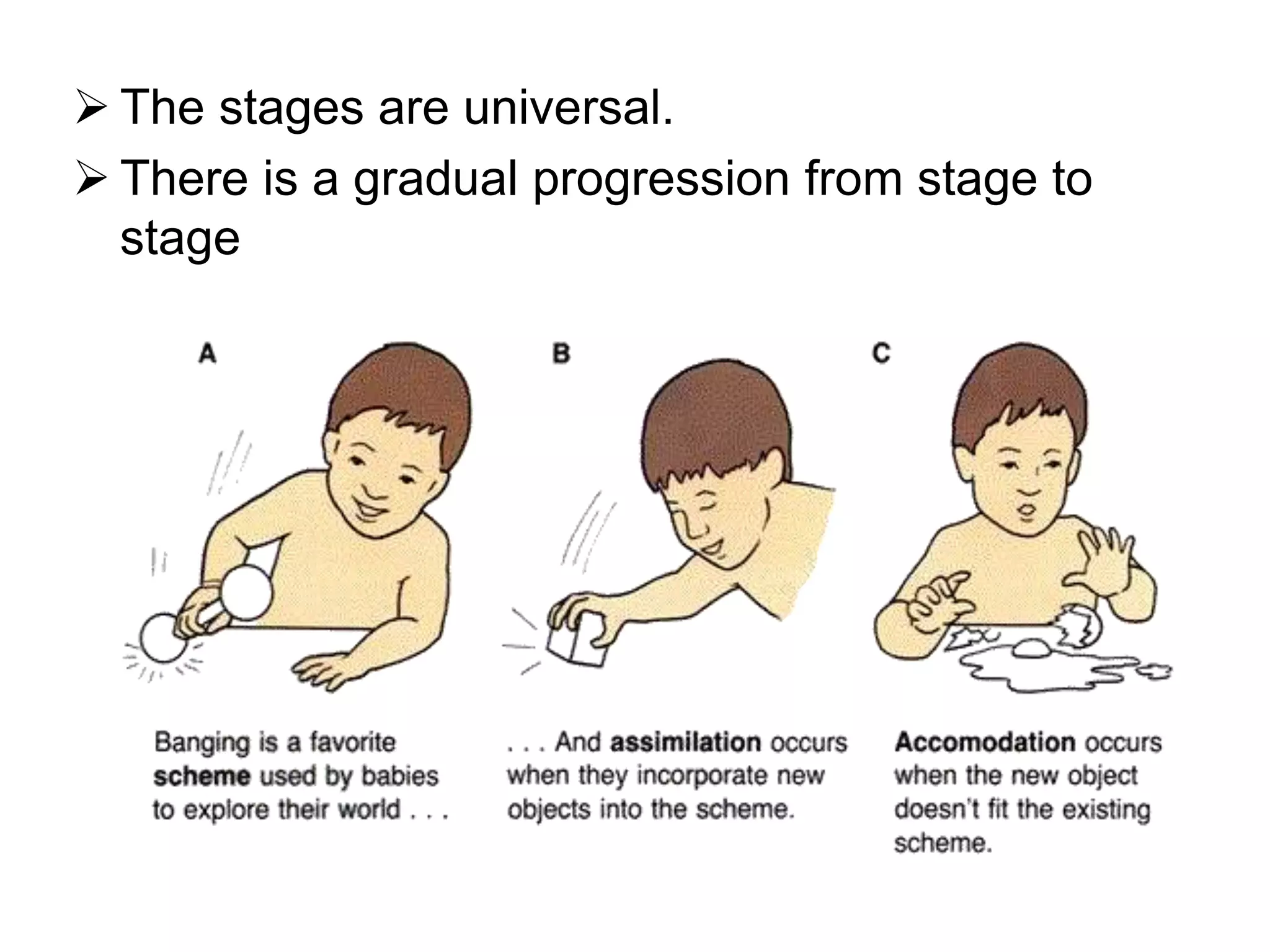
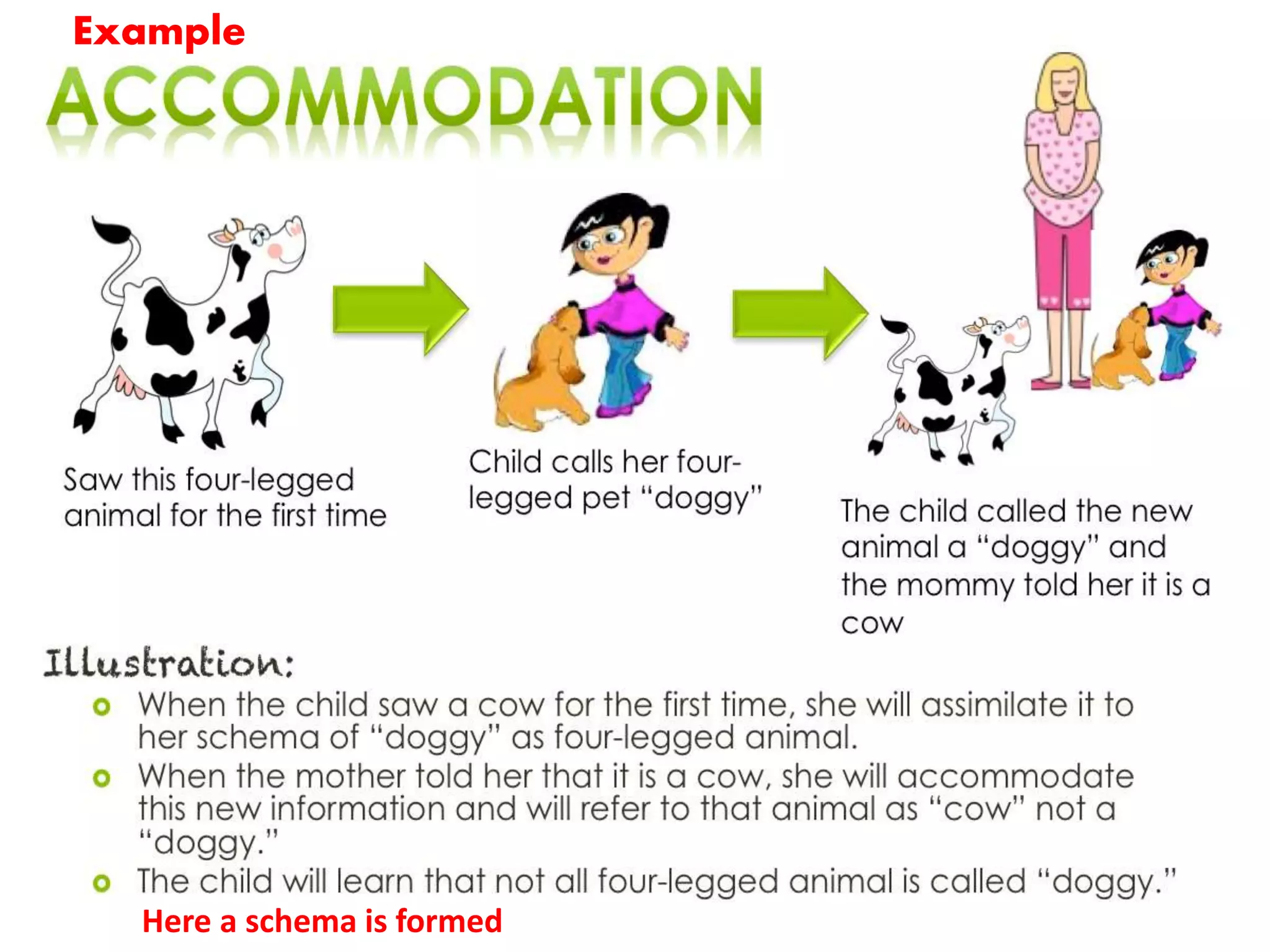
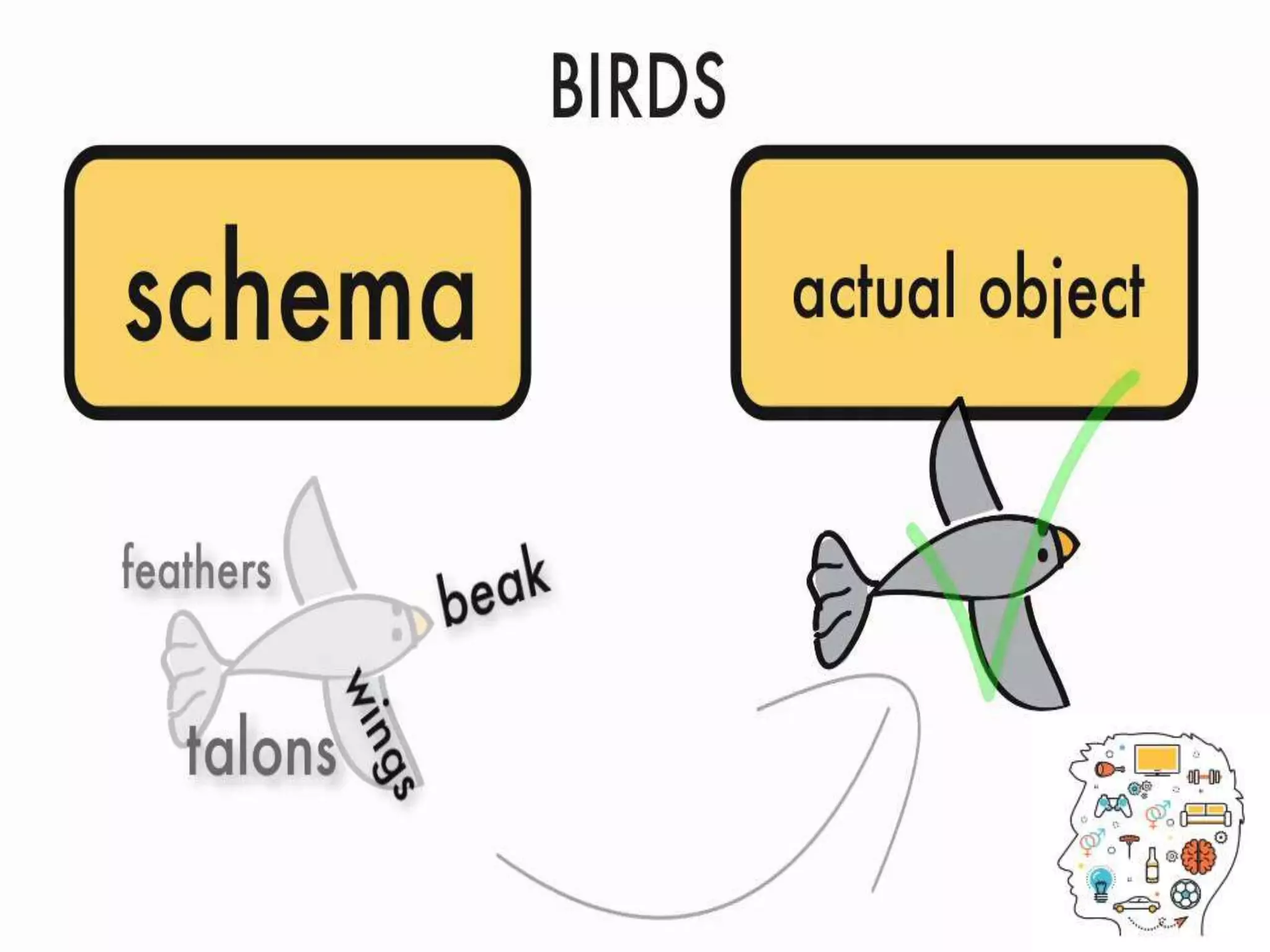
The document outlines Jean Piaget's cognitive constructivism theory, which posits that individuals construct knowledge through experiences and that understanding is influenced by prior knowledge. It details Piaget's four stages of cognitive development: sensorimotor, pre-operational, concrete operational, and formal operational, highlighting how intelligence and thought processes evolve through these stages. Additionally, it explains key concepts within cognitive constructivism, such as schemas, assimilation, accommodation, and equilibration.