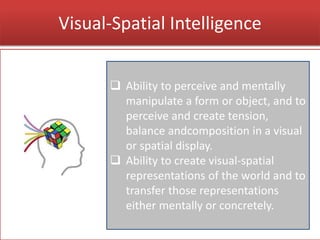
The document discusses Howard Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences, which proposes that intelligence is comprised of at least nine distinct types rather than a single general ability. It defines each type of intelligence, including logical-mathematical, intrapersonal, interpersonal, linguistic, bodily-kinesthetic, visual-spatial, musical, naturalist, and existential. The theory argues that people possess different combinations of these intelligences and can strengthen each one. It aims to categorize talents and skills in a way that allows for diverse teaching methods rather than a single approach.