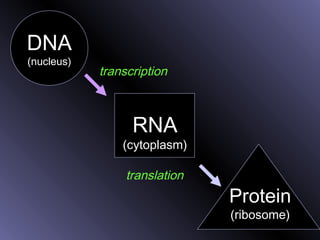
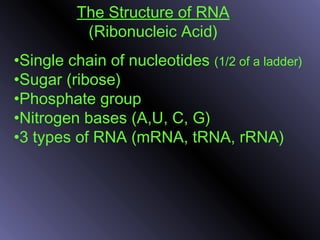
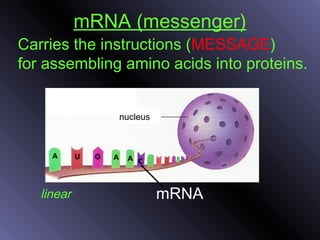
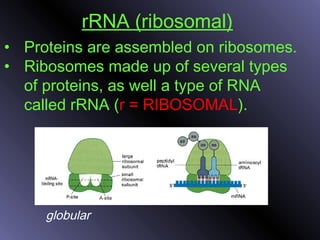
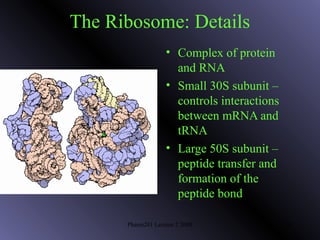
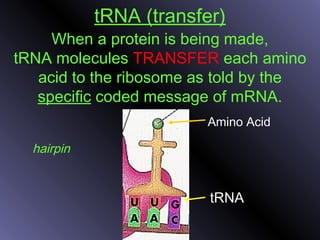
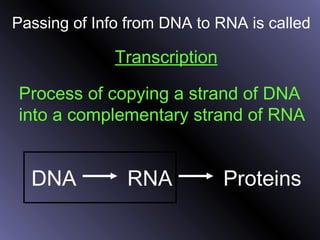
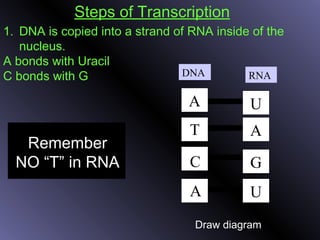
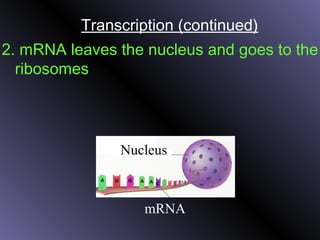
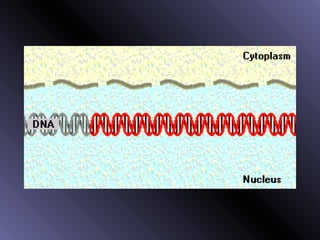
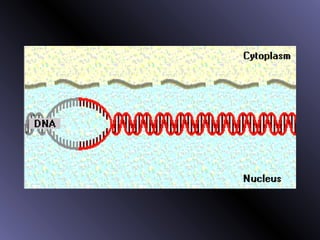
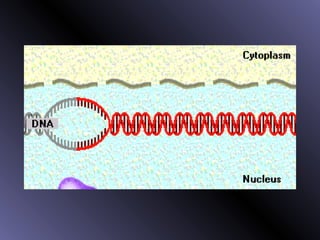
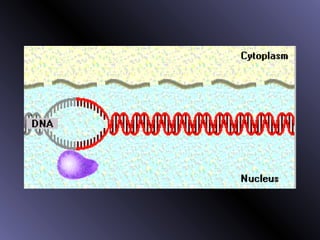
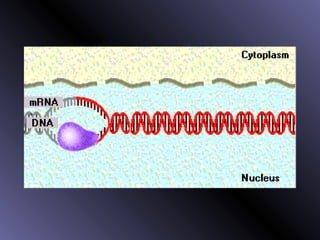
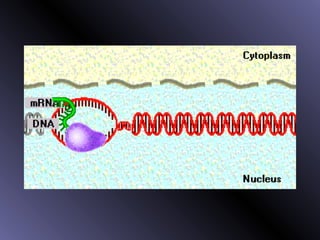
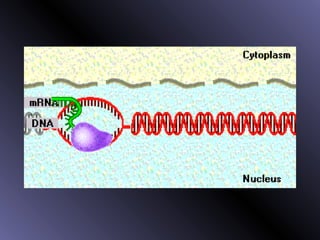
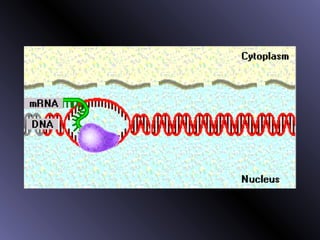
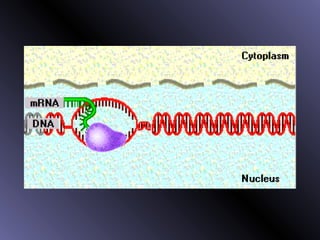
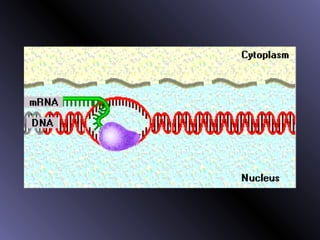
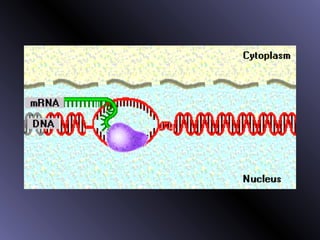
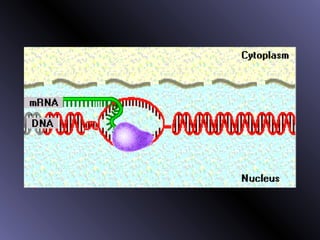
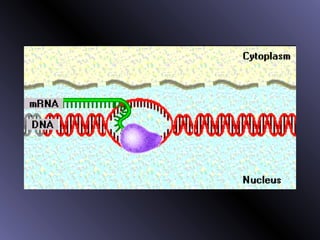
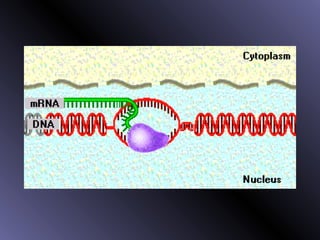
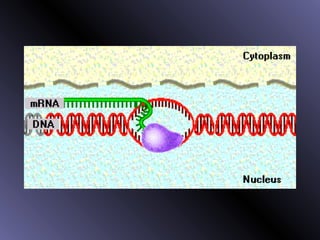
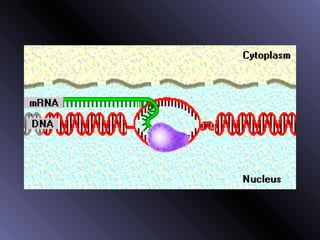
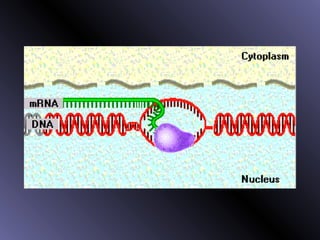
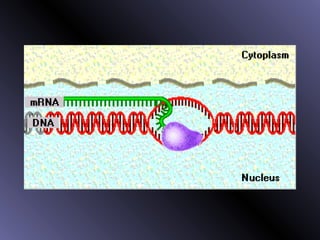
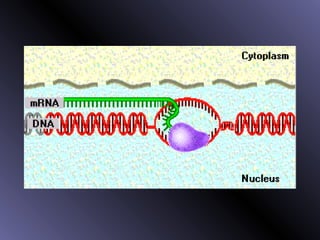
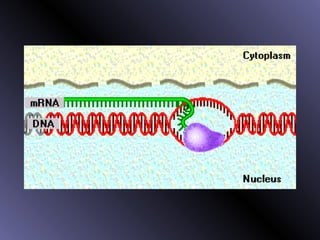
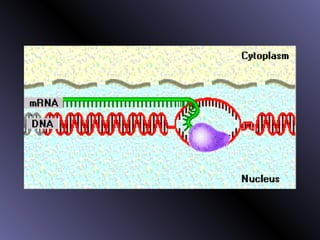
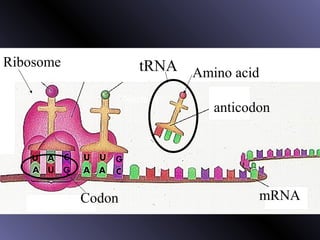
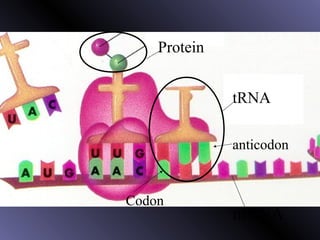
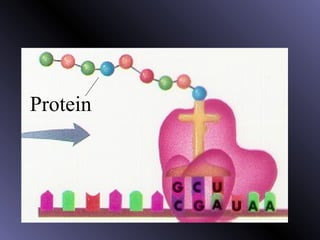
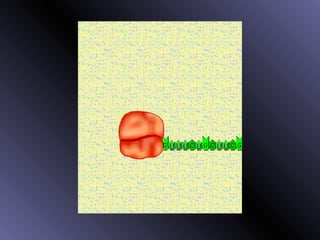
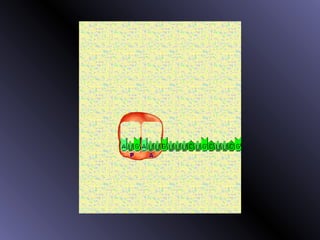
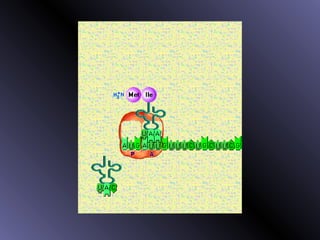
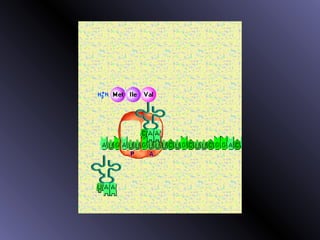
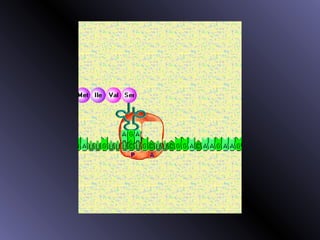
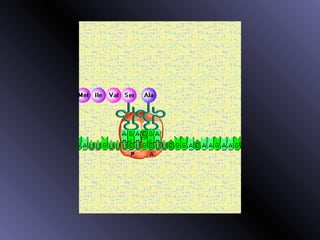
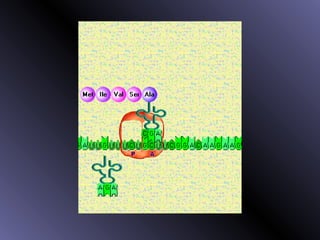
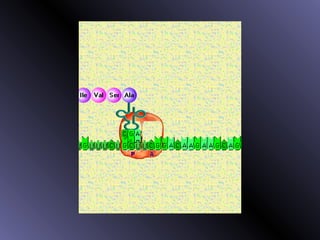
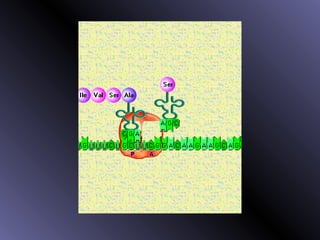
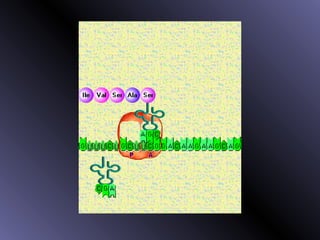
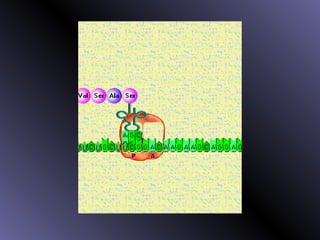
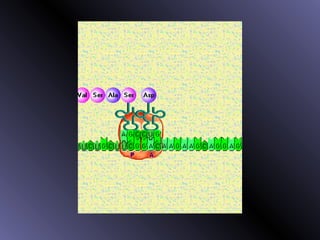
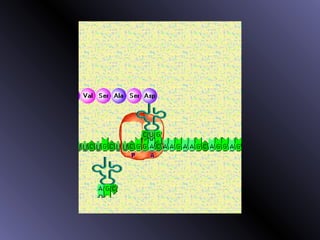
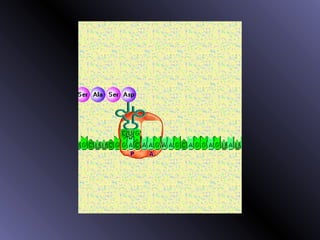
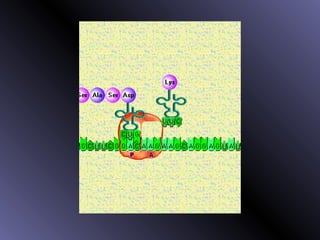
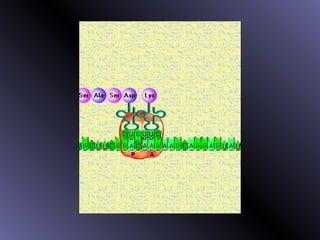
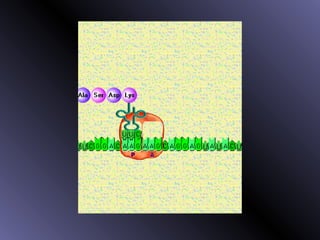
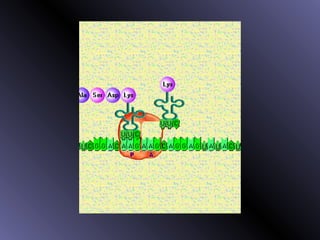
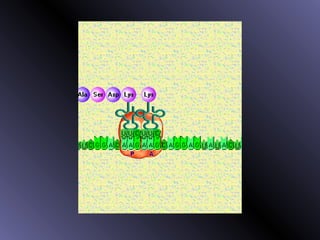
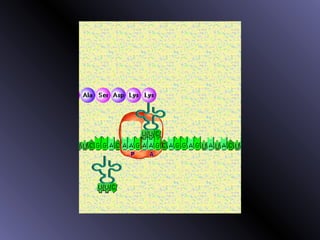
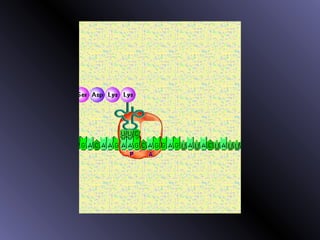
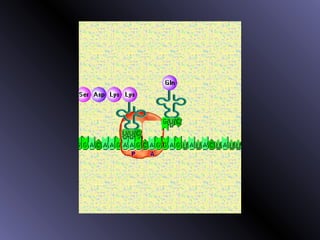
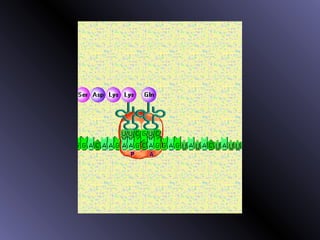
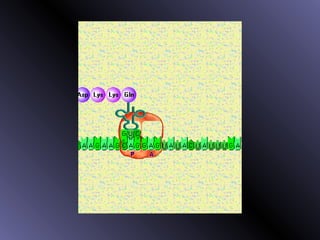
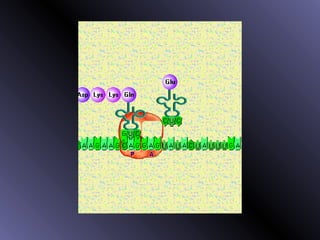
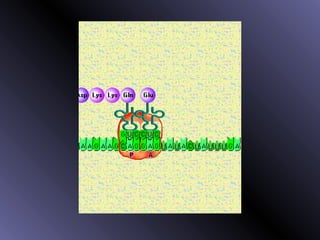
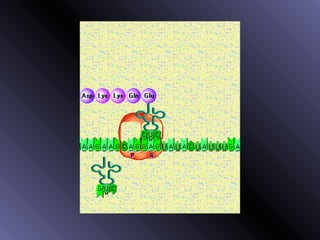
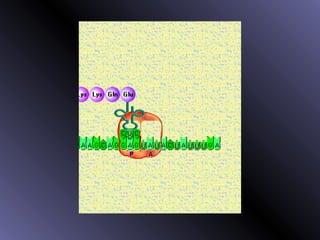
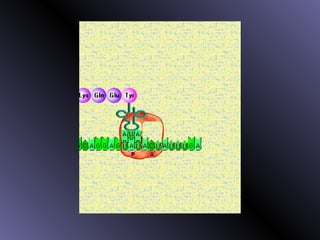
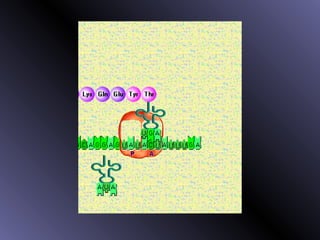
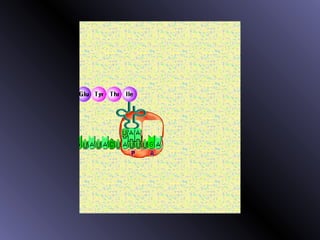
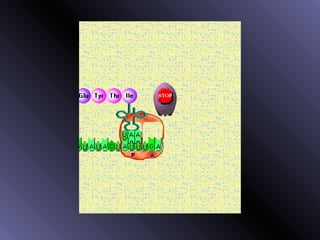
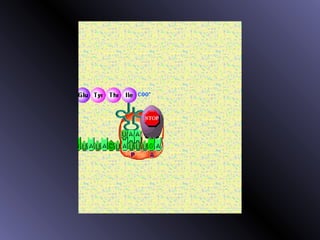
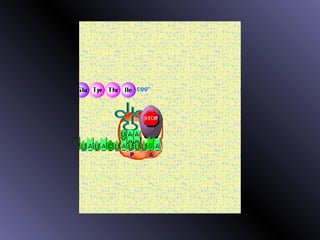
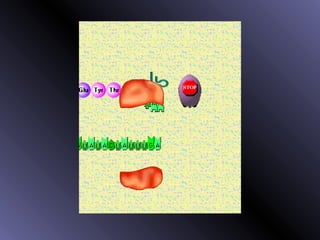
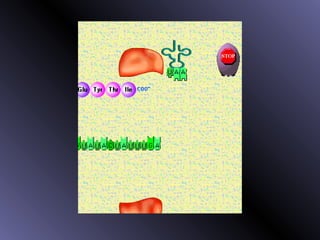
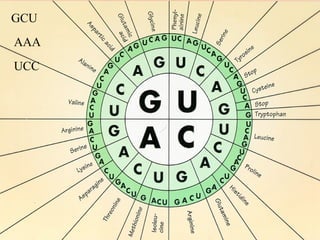
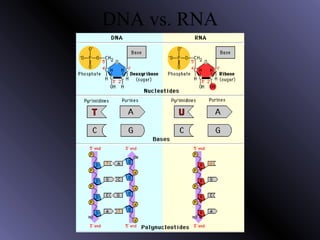
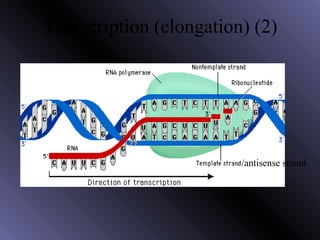
DNA contains genes that code for proteins. During protein synthesis, the DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the cell nucleus. The mRNA then transports the protein coding instructions to the cytoplasm where ribosomes read the mRNA to produce proteins. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules match to the mRNA codons and bring the corresponding amino acids. The amino acids are linked together on the ribosome to form the protein chain according to the mRNA instructions.