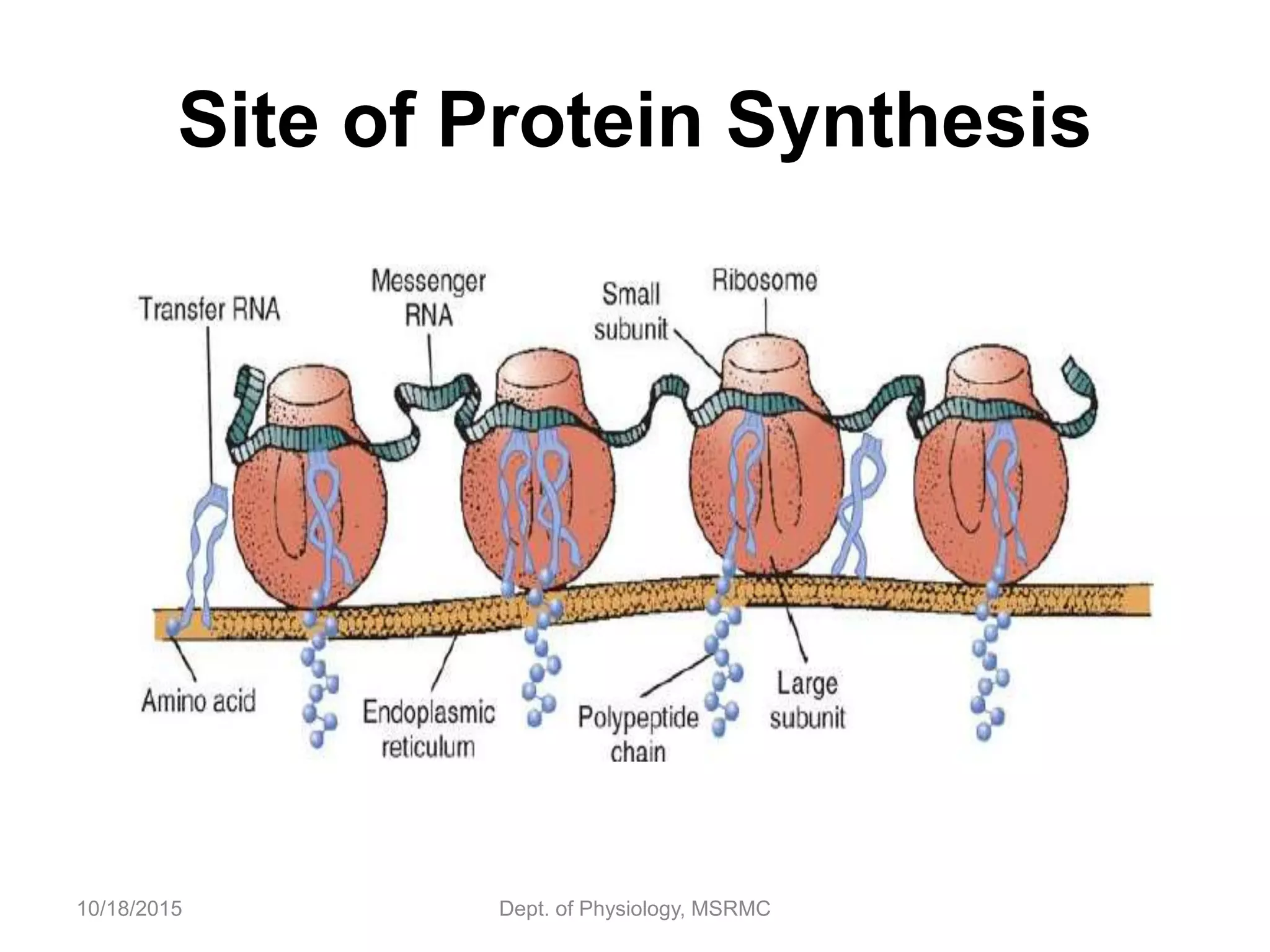
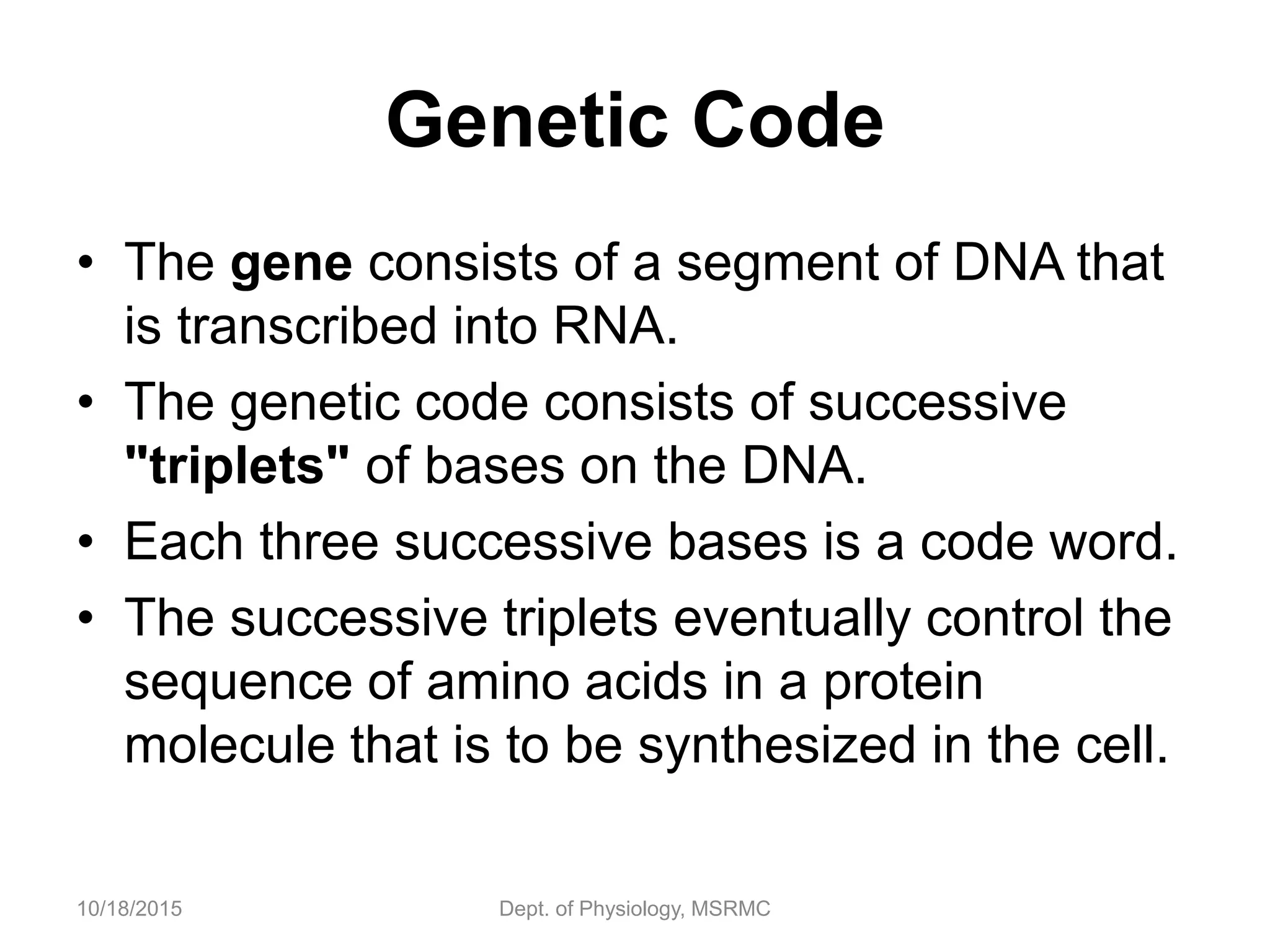
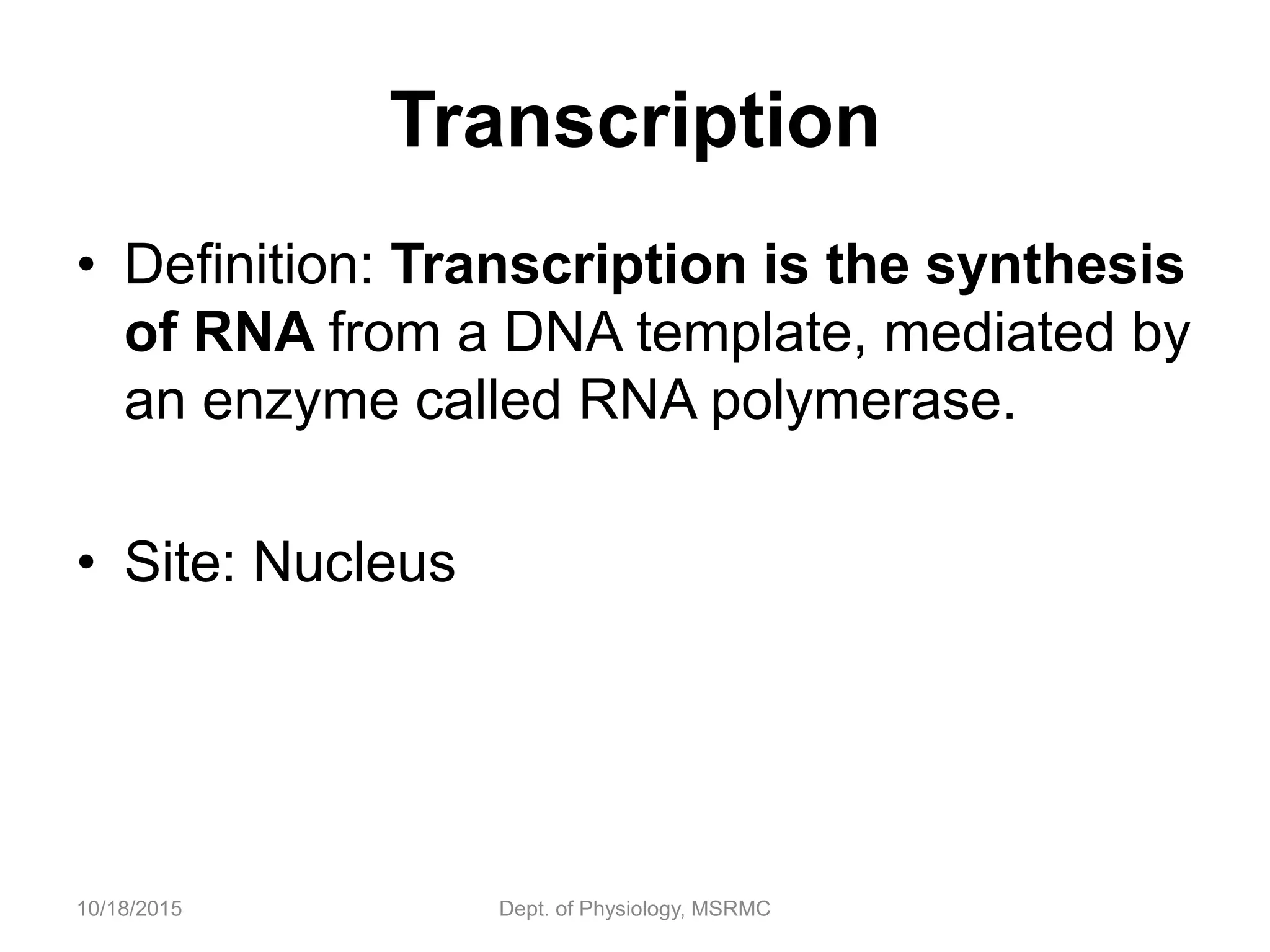
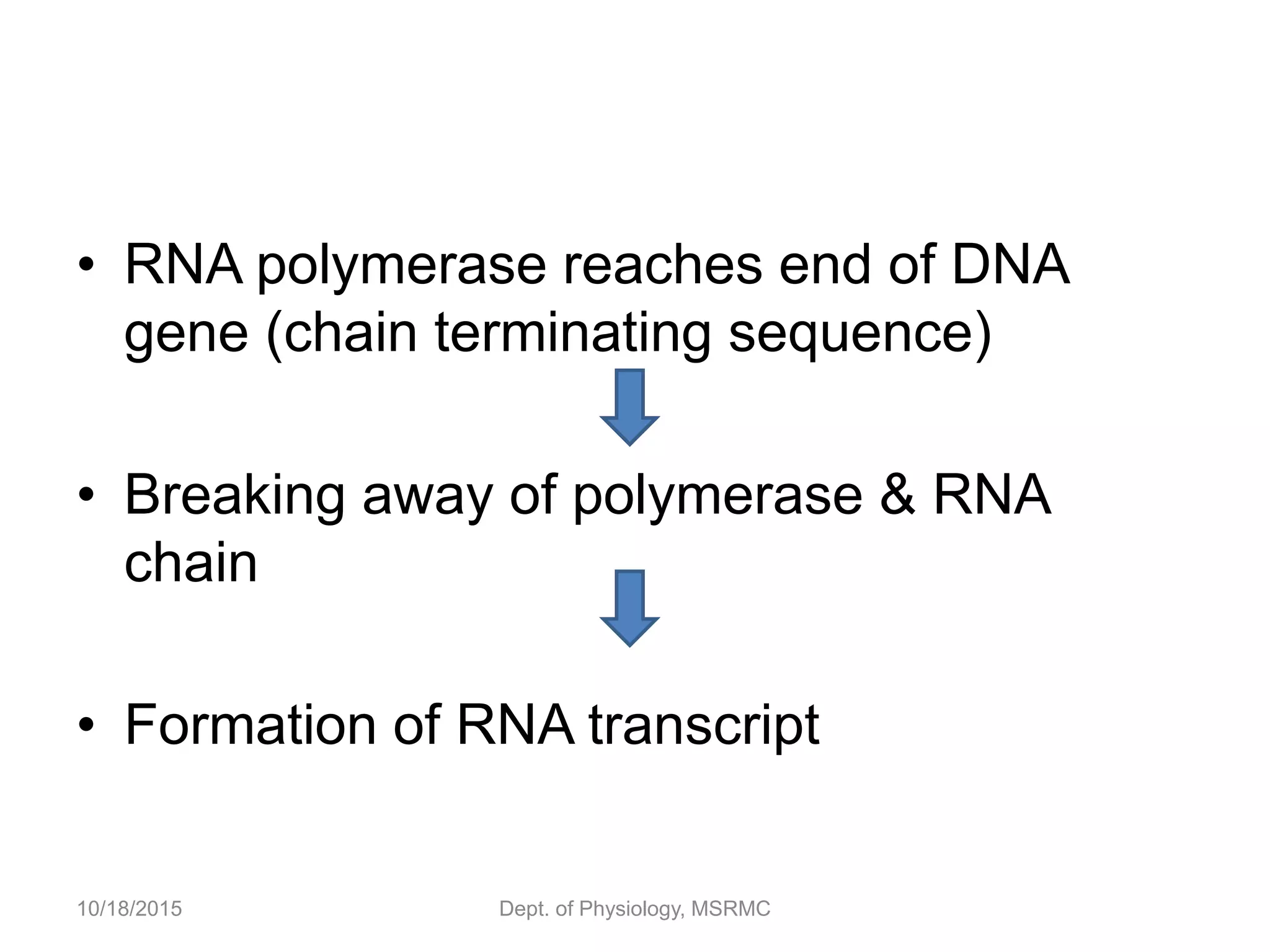
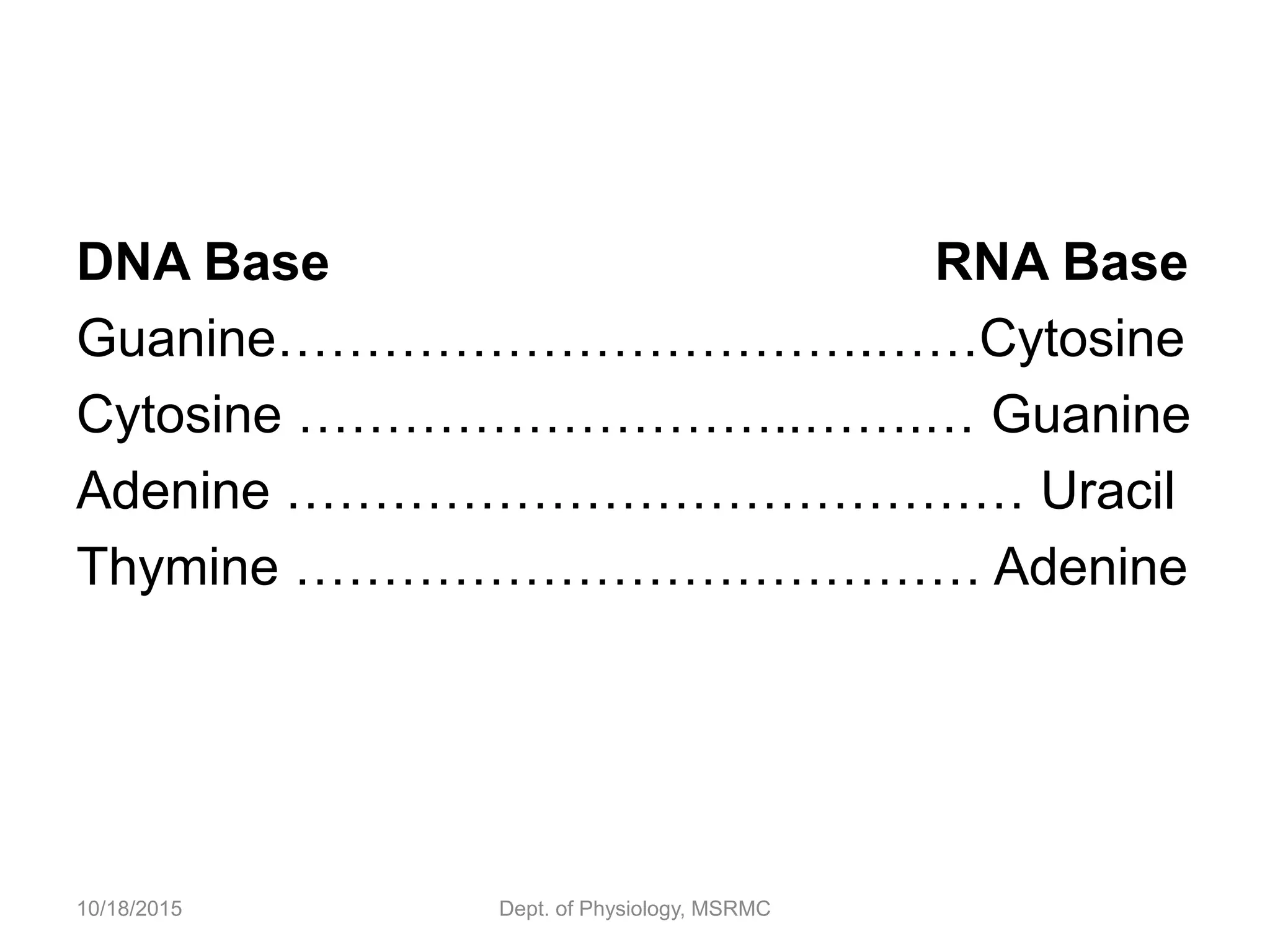
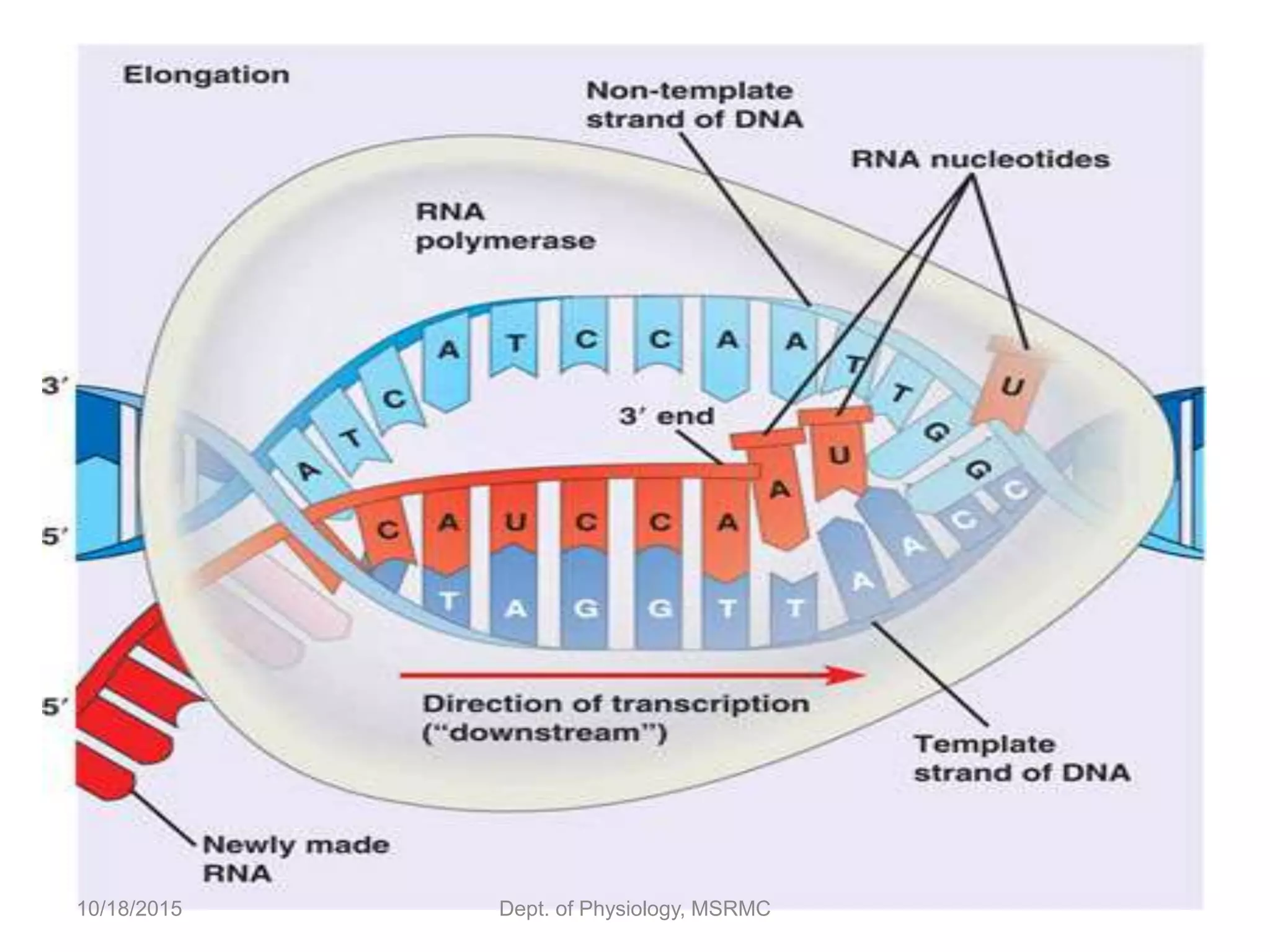
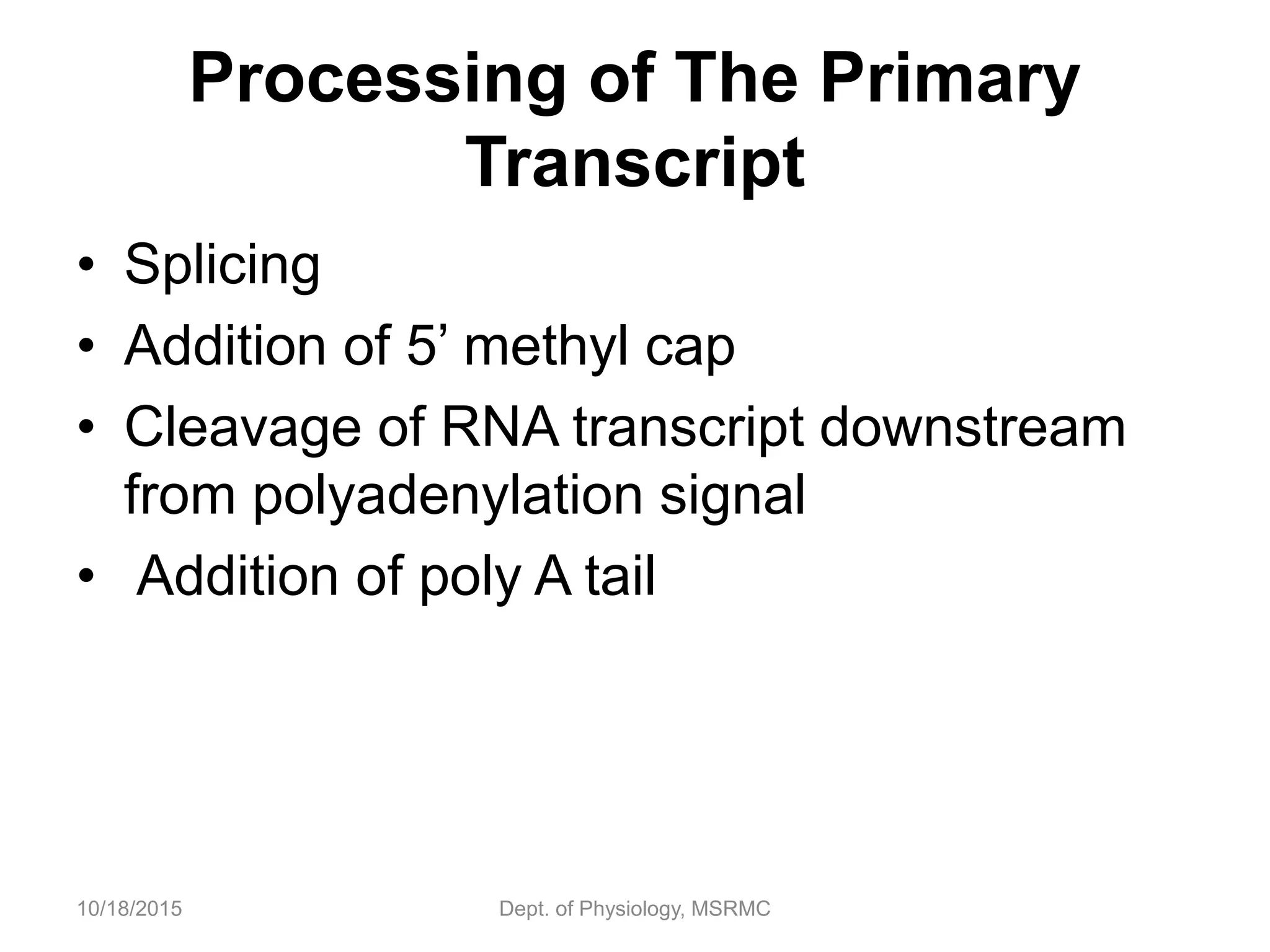
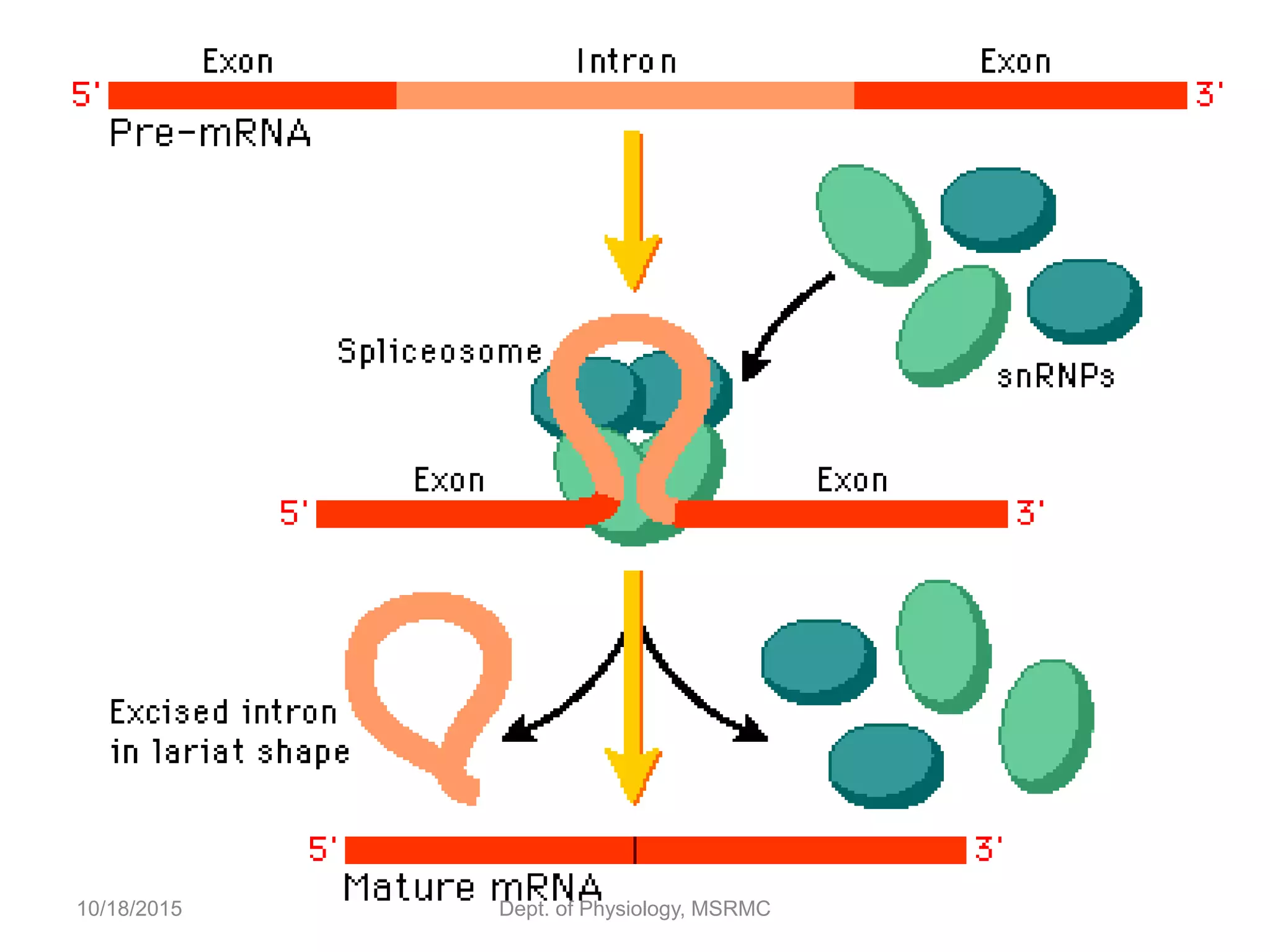
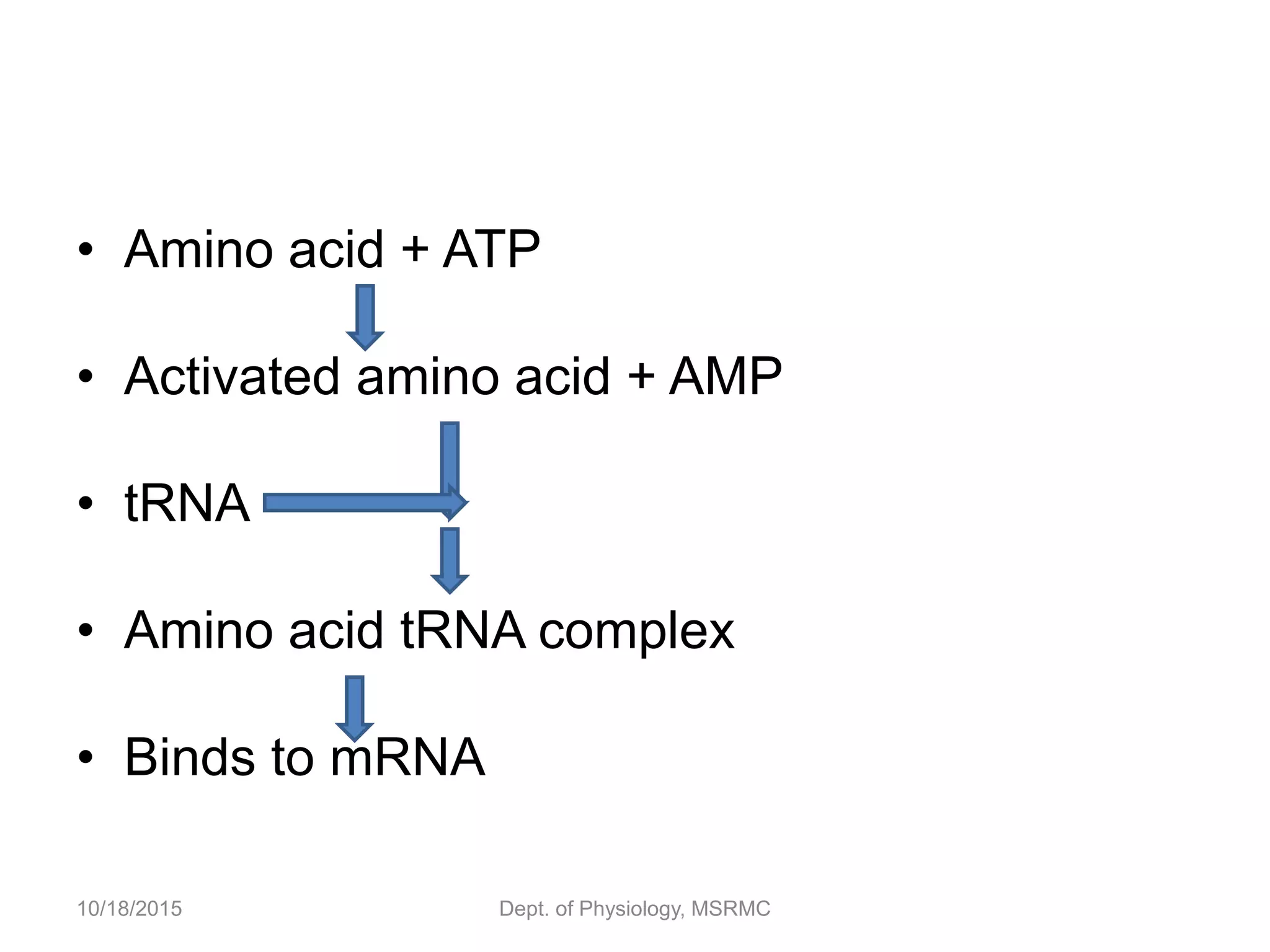
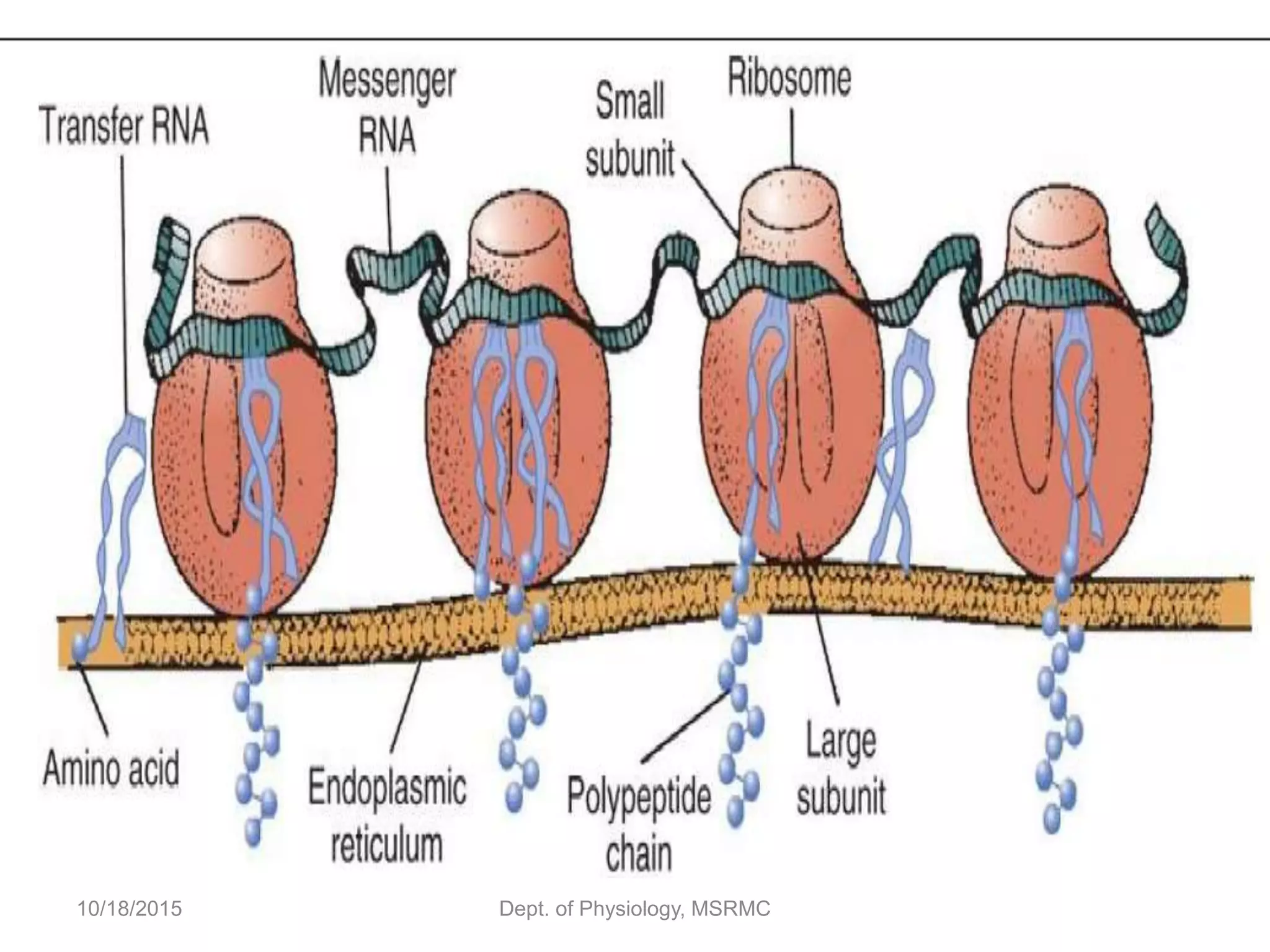
Proteins are essential functional units in cells that are synthesized through a multi-step process involving transcription of DNA in the nucleus to mRNA, which is then transported to the cytoplasm and translated by ribosomes to produce a protein. During translation, tRNA molecules carry amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codon sequence to form the polypeptide chain. The protein then undergoes post-translational modifications to achieve its functional structure before carrying out important cellular roles such as enzymatic reactions, transport, structure, and signaling. Regulation of protein synthesis ensures only necessary proteins are produced at the right times and places in the cell.