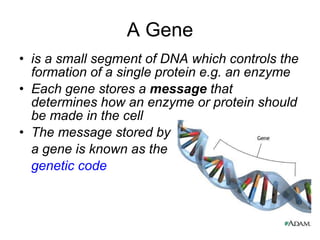
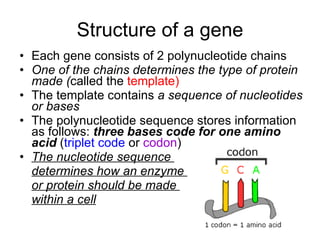
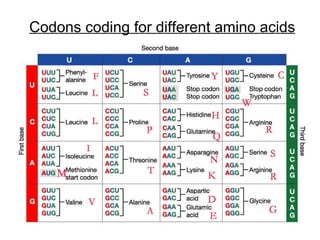
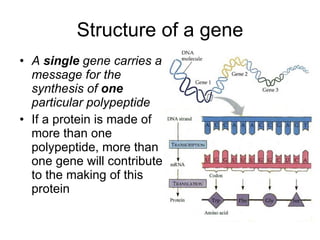
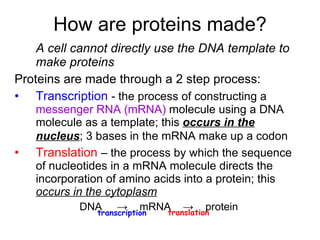
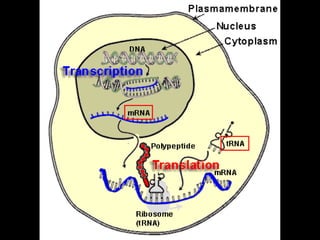
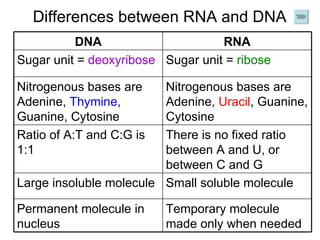
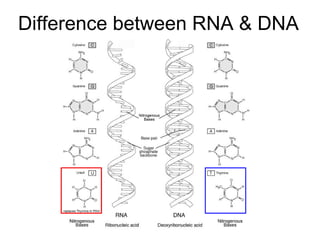
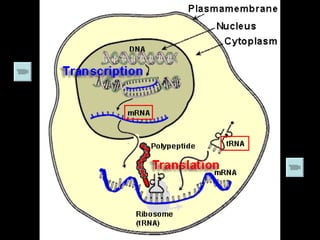
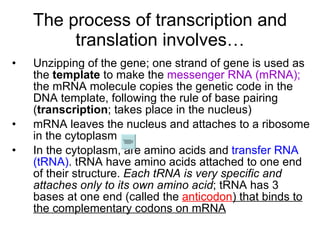
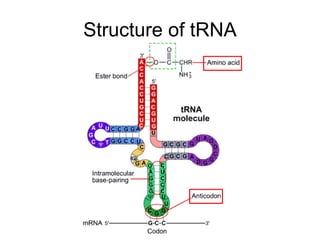
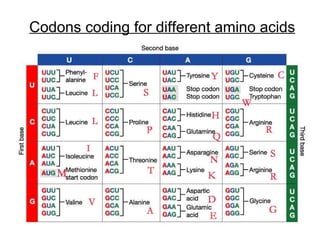
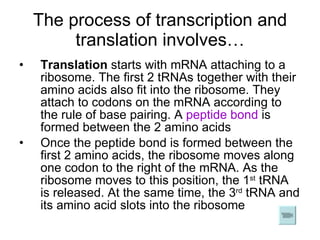
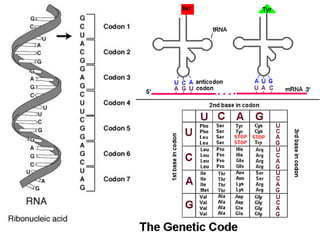
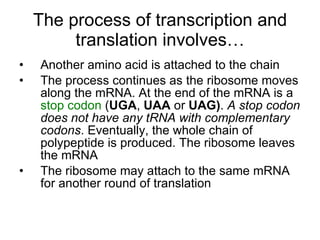
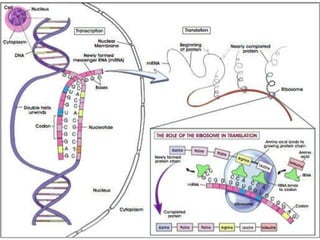
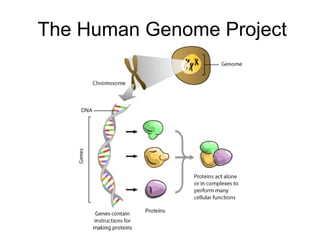
The document discusses how genes control the formation of proteins through transcription and translation. A gene is a segment of DNA that stores instructions to make a specific protein. During transcription, the DNA sequence is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the nucleus. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome, where translation occurs. During translation, transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codon sequence. This results in a polypeptide chain that folds into a protein.