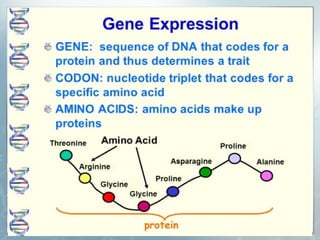
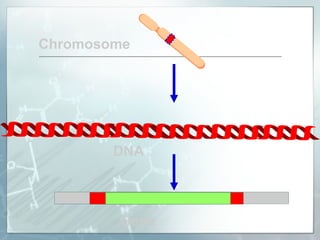
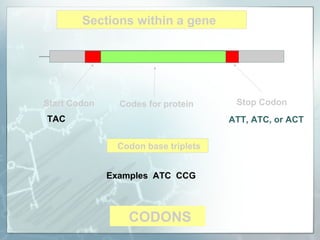
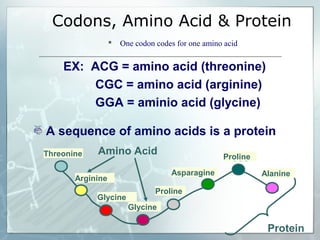
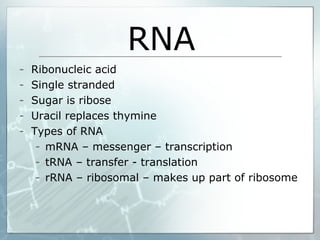
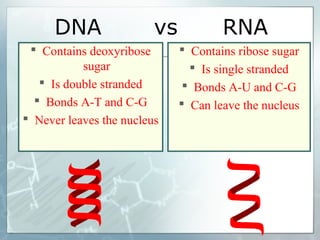
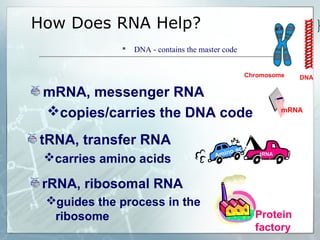
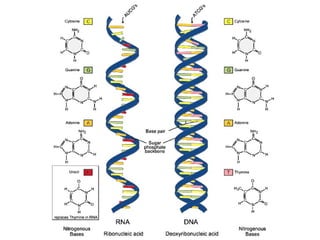
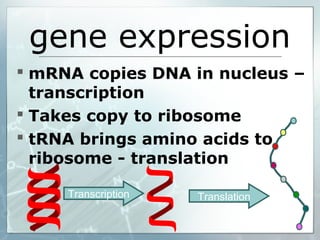
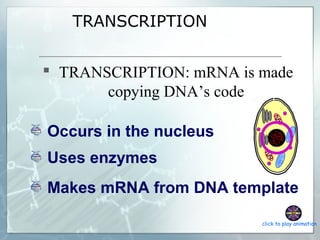
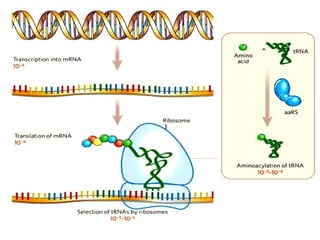
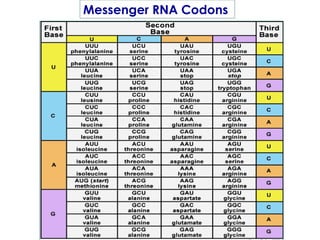
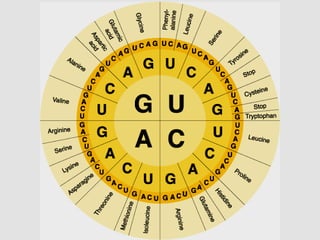
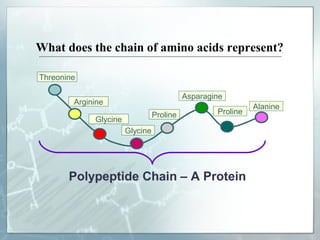
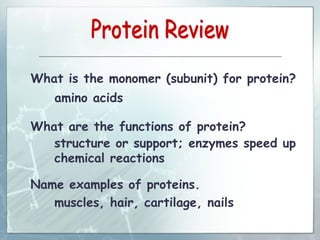
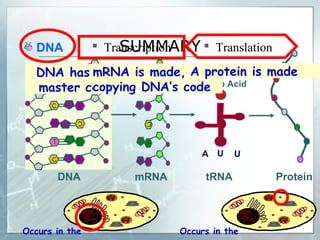
DNA contains genes that code for proteins. During transcription, mRNA is produced by copying DNA in the nucleus. The mRNA then transports the genetic code to the cytoplasm for translation at the ribosome. Translation is the process where tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codons to produce a protein, consisting of a chain of amino acids specified by the DNA.