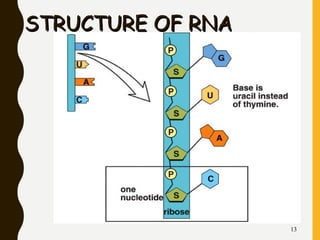
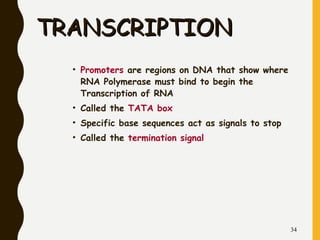
This document explains the process of protein synthesis, detailing how DNA codes for proteins through the intermediary steps of transcription and translation. It describes the roles of various types of RNA, including messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA, as well as the structure of amino acids and the genetic code that translates nucleotide sequences into protein. The document provides a comprehensive overview of how proteins are built from polypeptides and the necessary processes involved in these cellular functions.