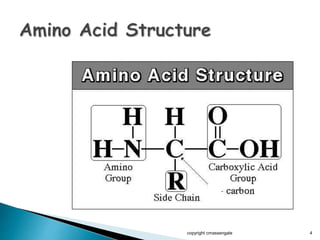
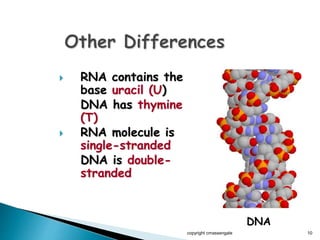
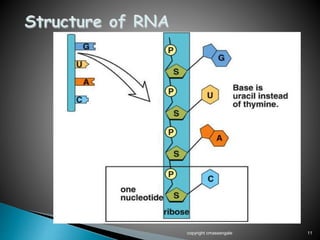
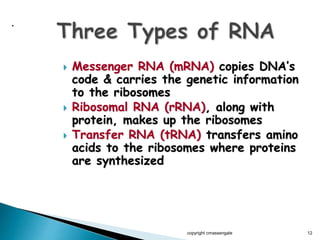
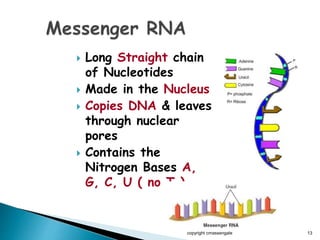
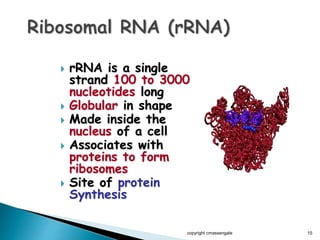
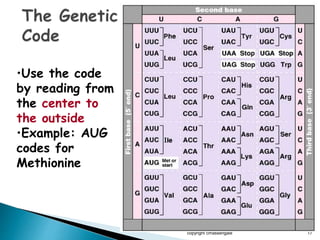
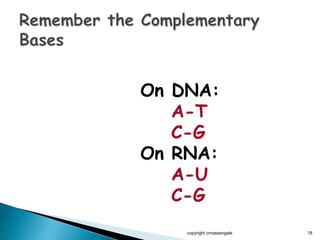
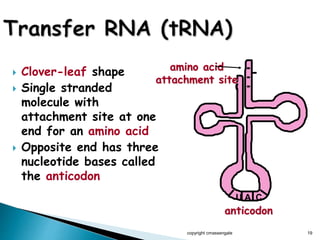
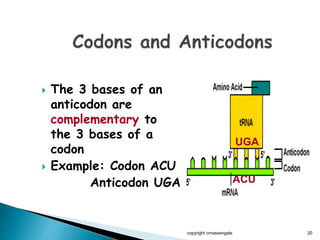
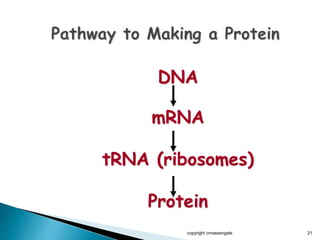
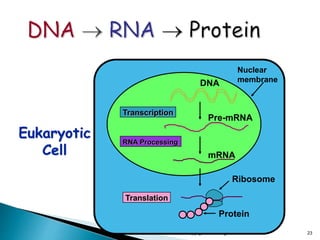
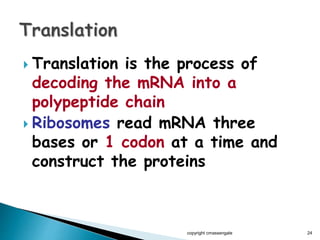
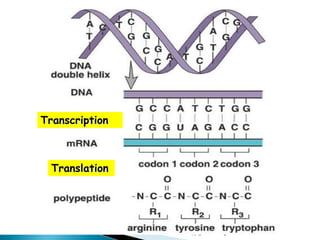
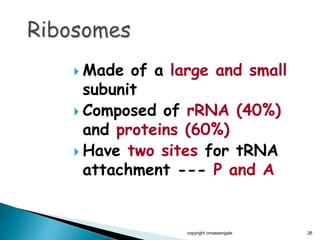
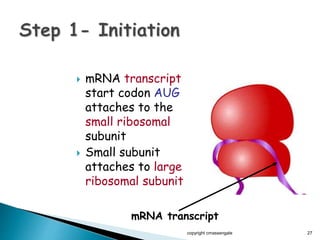
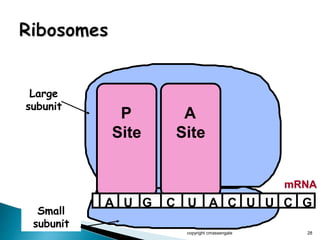
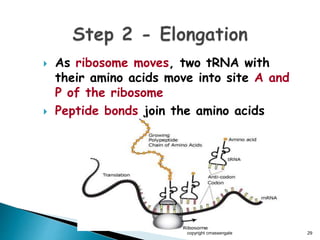
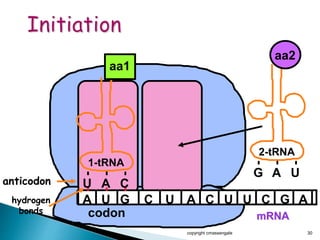
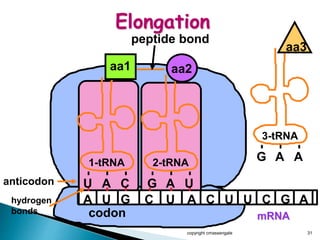
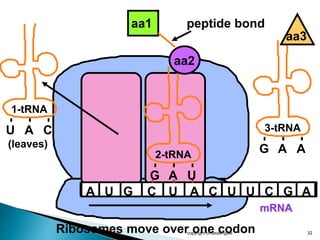
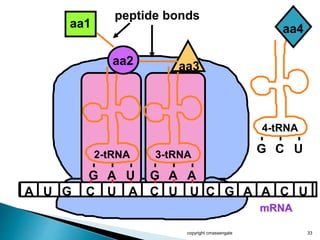
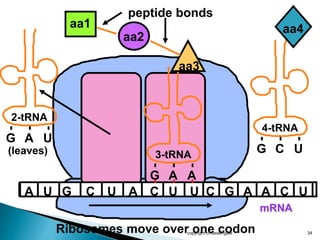
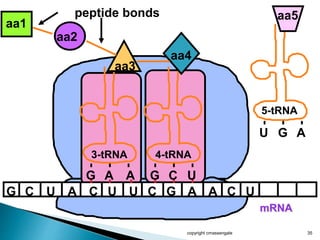
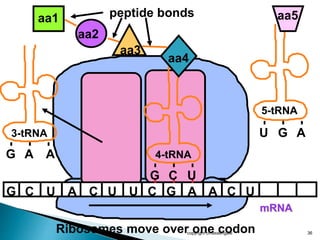
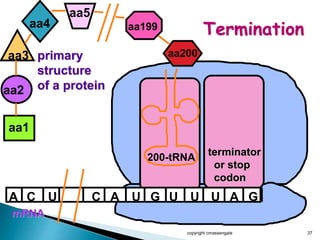
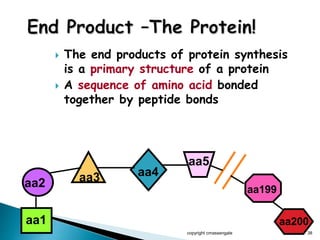
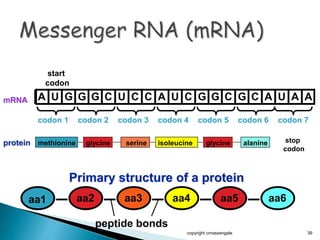
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis which occurs in two main steps: transcription and translation. During transcription, DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the cell nucleus. The mRNA then transports the genetic code to the cytoplasm where ribosomes read the mRNA during translation and assemble amino acids to make a protein based on the code. Transfer RNA molecules deliver amino acids to the ribosome and assemble them into a protein chain based on the mRNA codons.