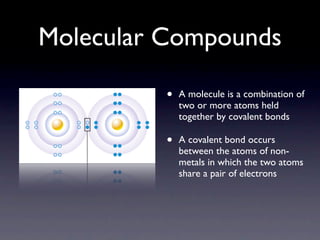
Molecular compounds are formed when two or more different non-metal atoms combine via covalent bonds, sharing electron pairs. Examples include water, which is made of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom. Molecular compounds have properties like being soft and having low melting points. They are named systematically with the first element, the second as an "-ide", and prefixes to indicate atom amounts, like dinitrogen monoxide for N2O.