Embed presentation


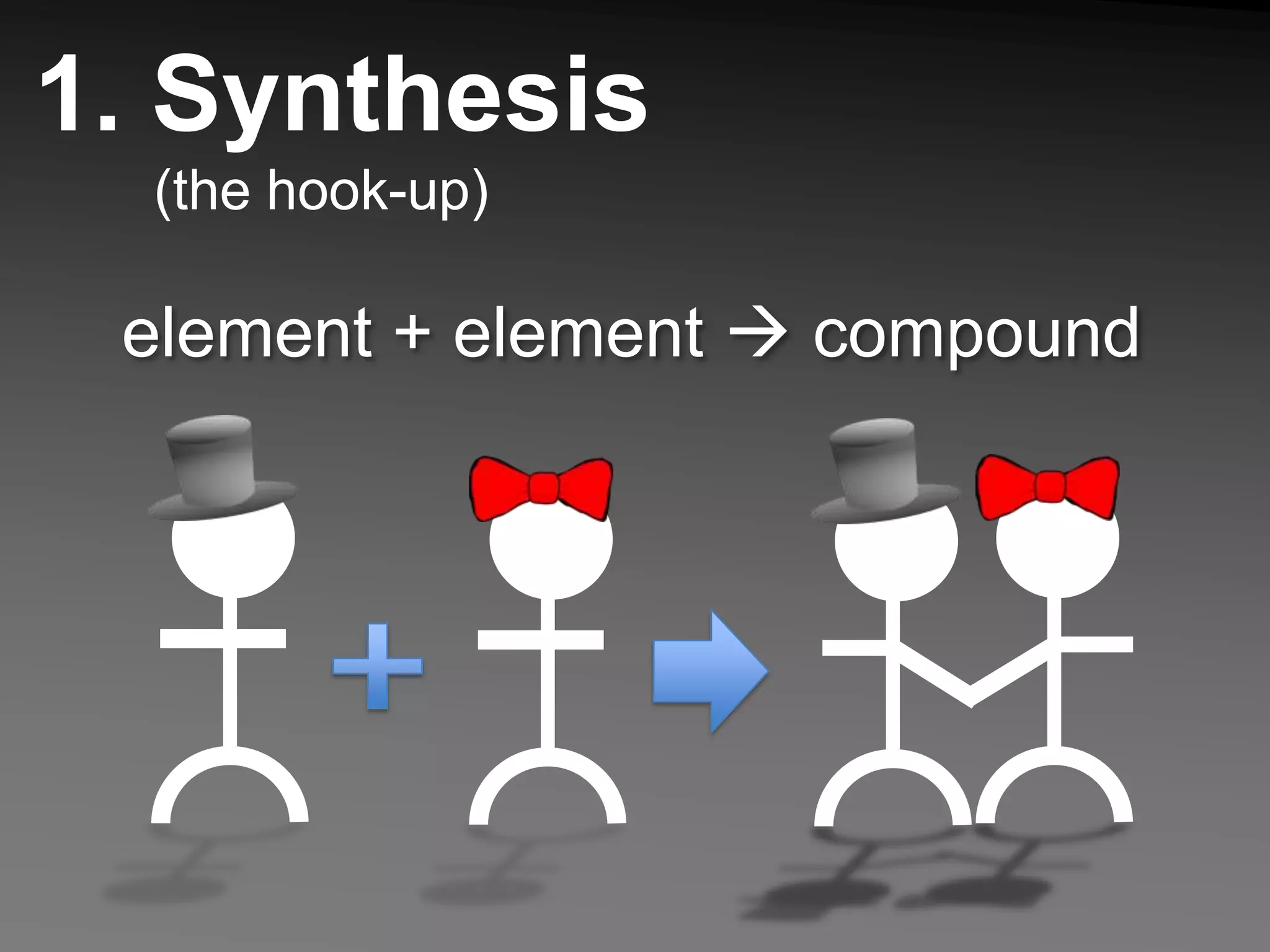





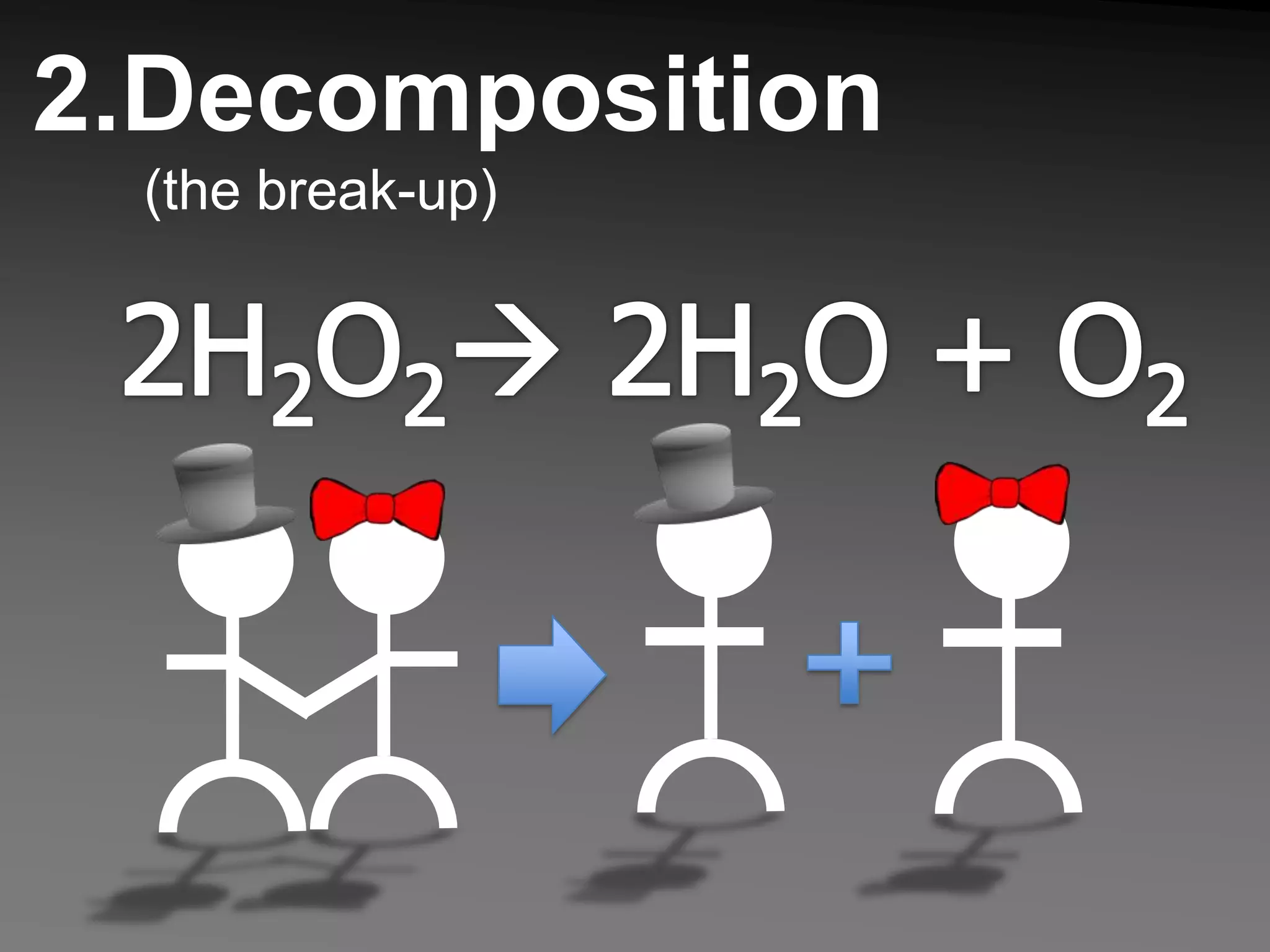

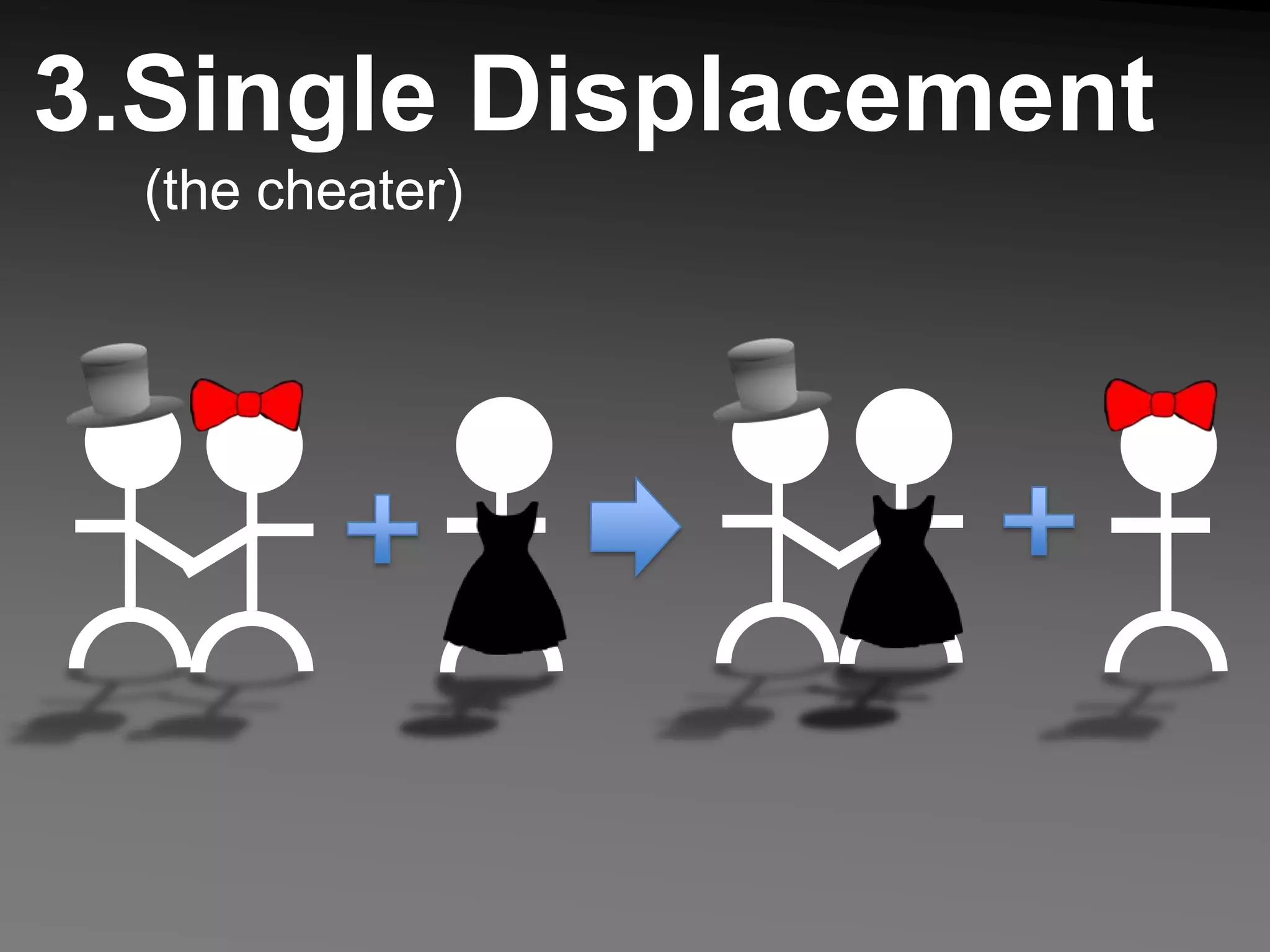

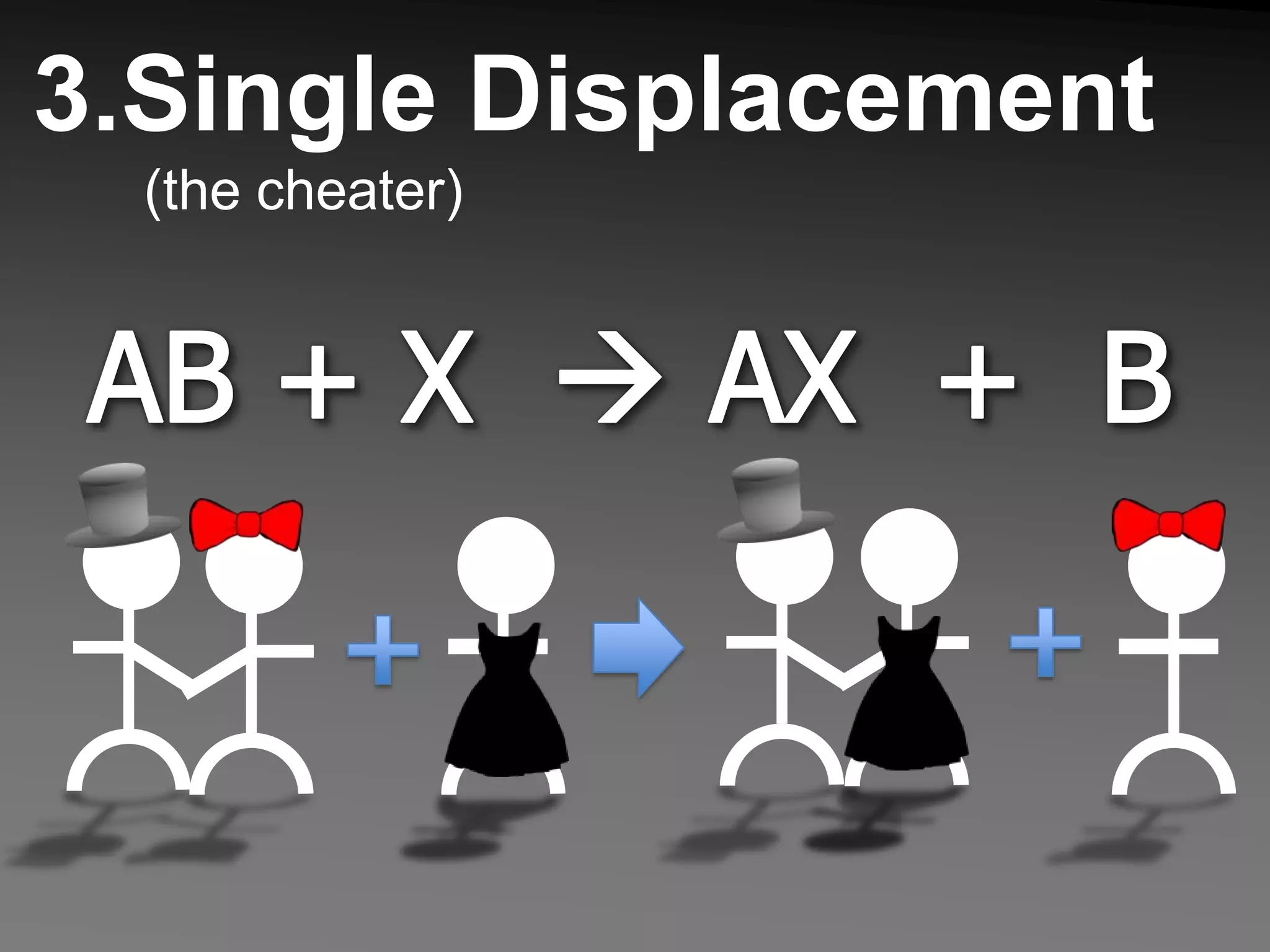



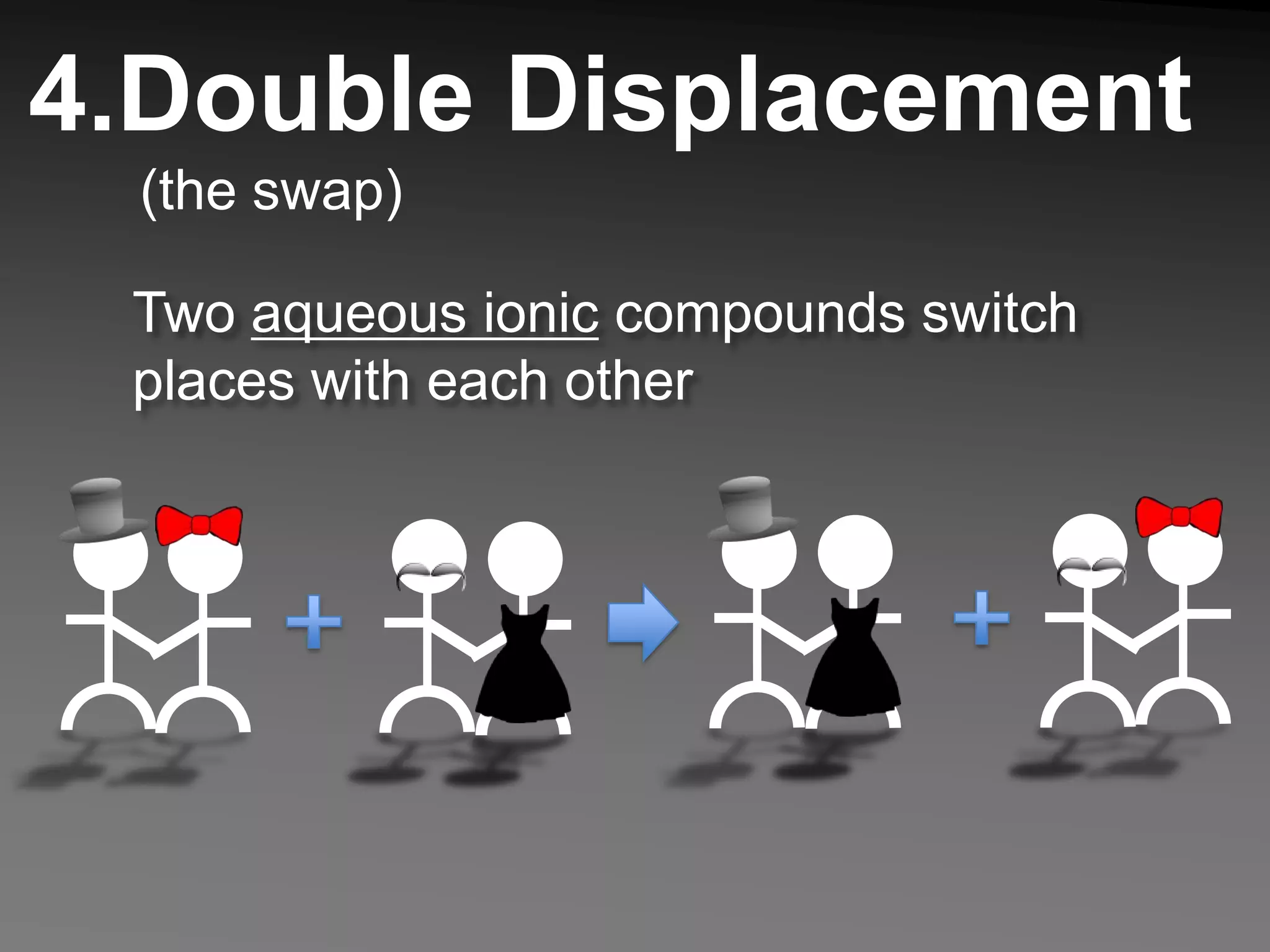





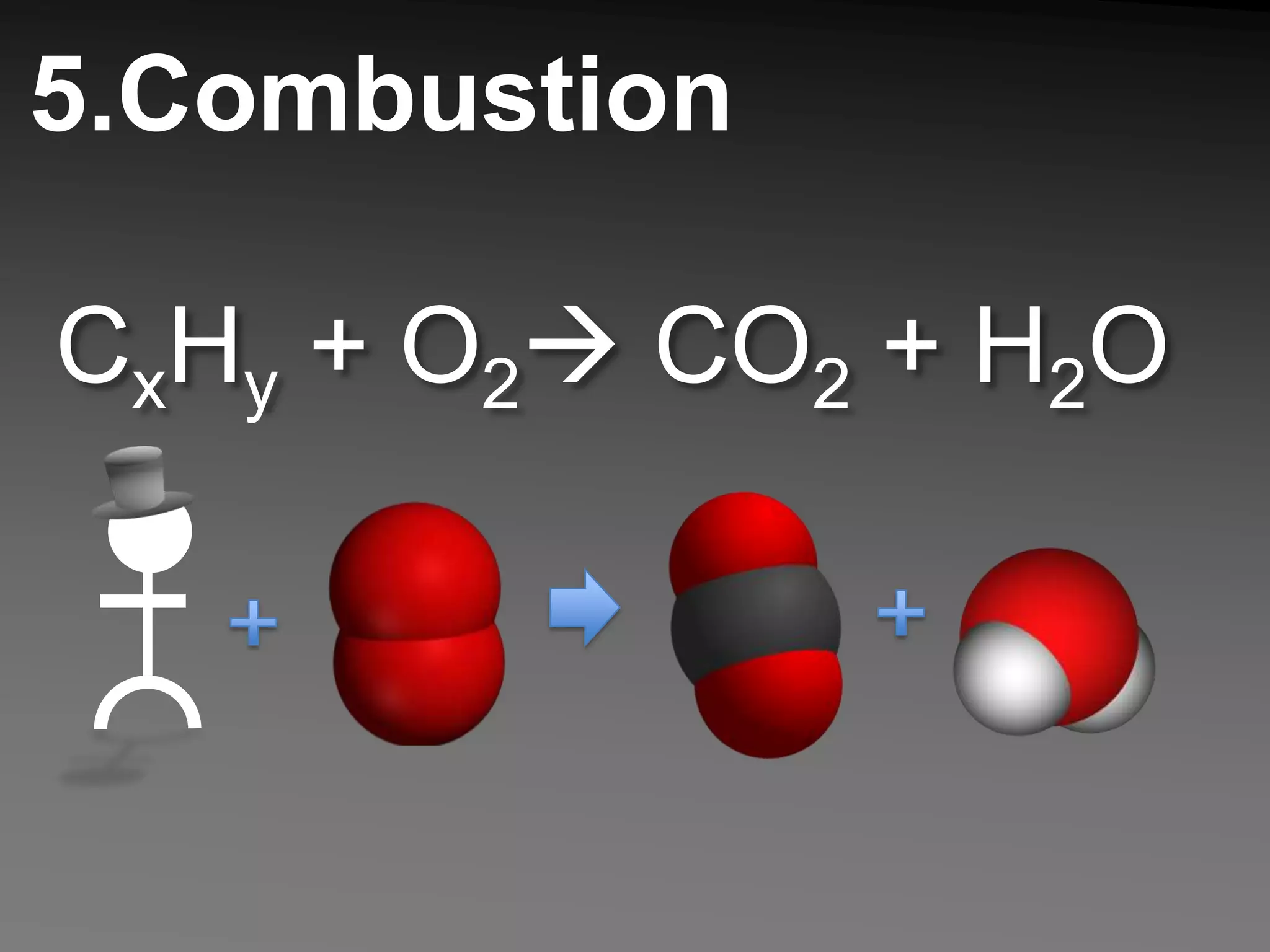



The document describes 5 types of chemical reactions: 1. Synthesis reactions combine elements to form compounds. 2. Decomposition reactions break compounds down into their constituent elements. 3. Single displacement reactions occur when one element displaces another in a compound. 4. Double displacement reactions involve the switching of ions between two ionic compounds in aqueous solution. 5. Combustion reactions involve the burning of hydrocarbons in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
























