This document discusses classifying and naming ionic and covalent compounds, as well as writing their formulas. It provides rules for:
- Classifying compounds as ionic or covalent based on their formula
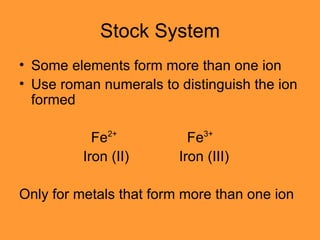
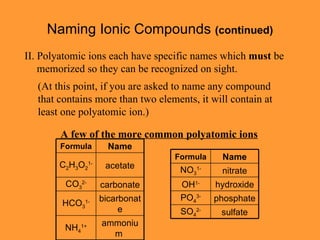
- Naming ionic compounds using stock systems and identifying polyatomic ions
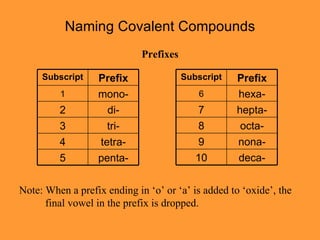
- Naming covalent compounds using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms
- Writing formulas for ionic compounds by balancing charges and for covalent compounds using prefixes
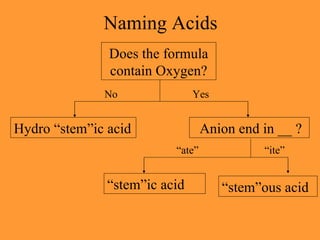
It also discusses acids, bases, and how to name and write formulas for acids based on their anion name endings.