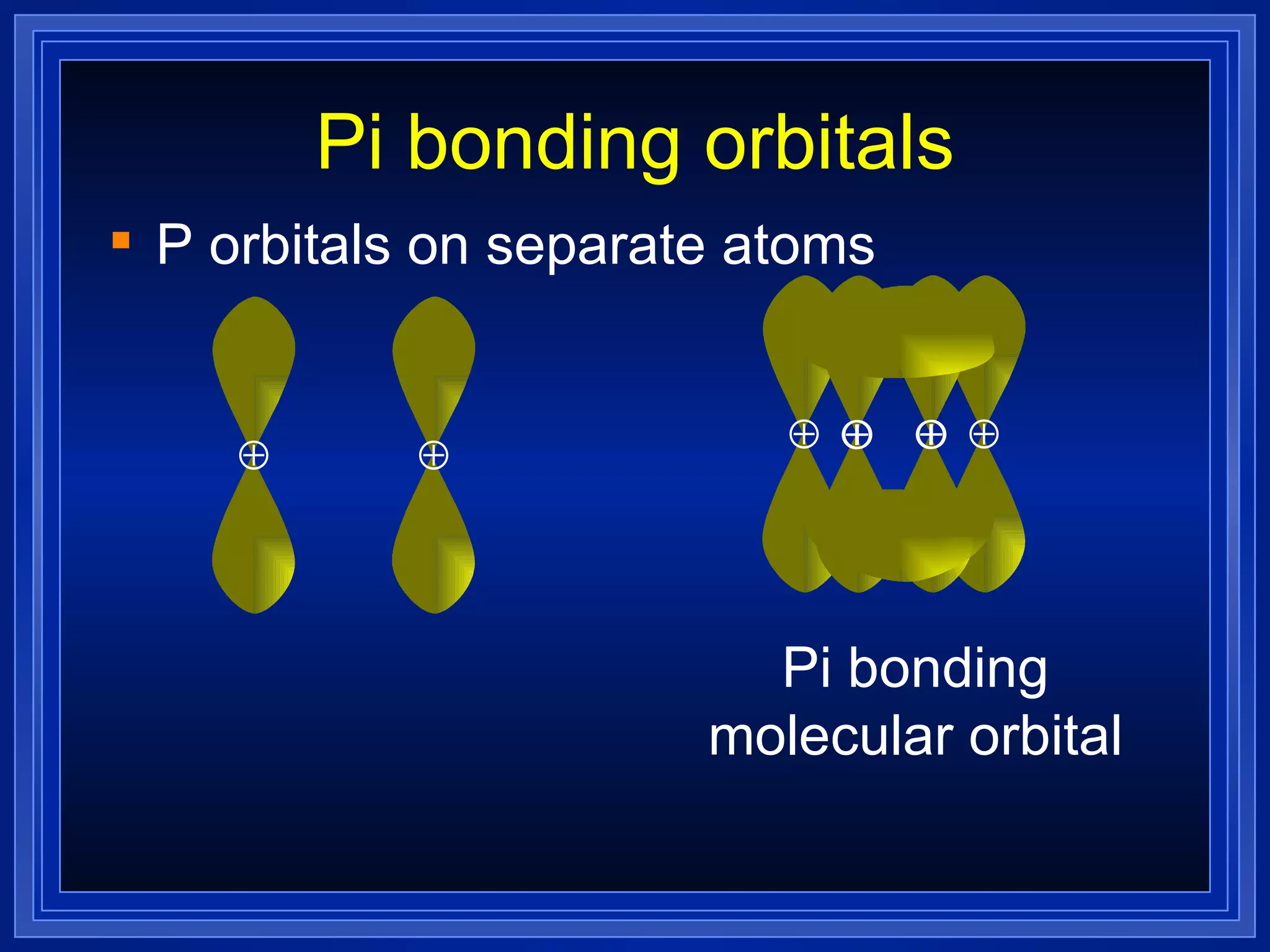
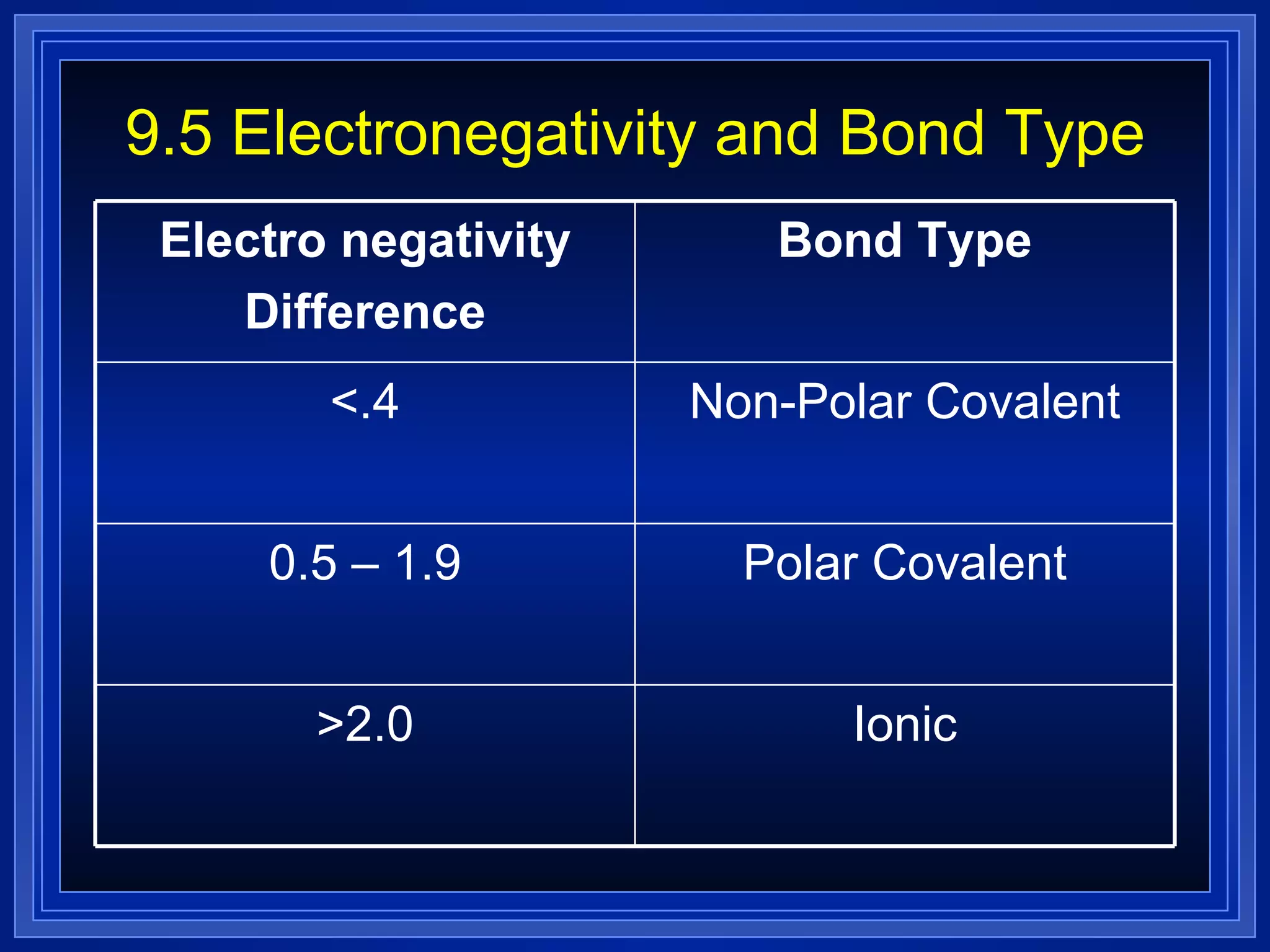
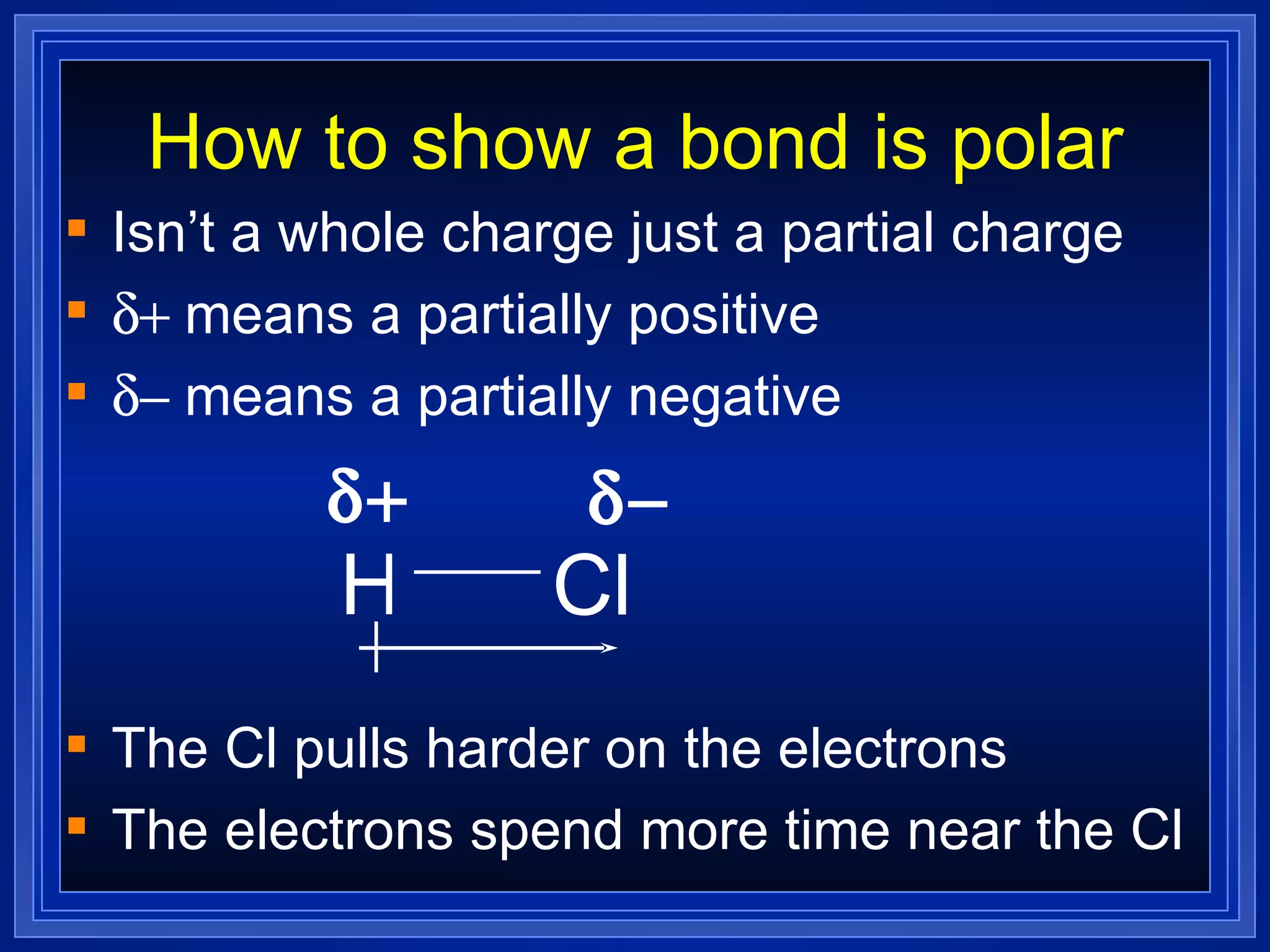
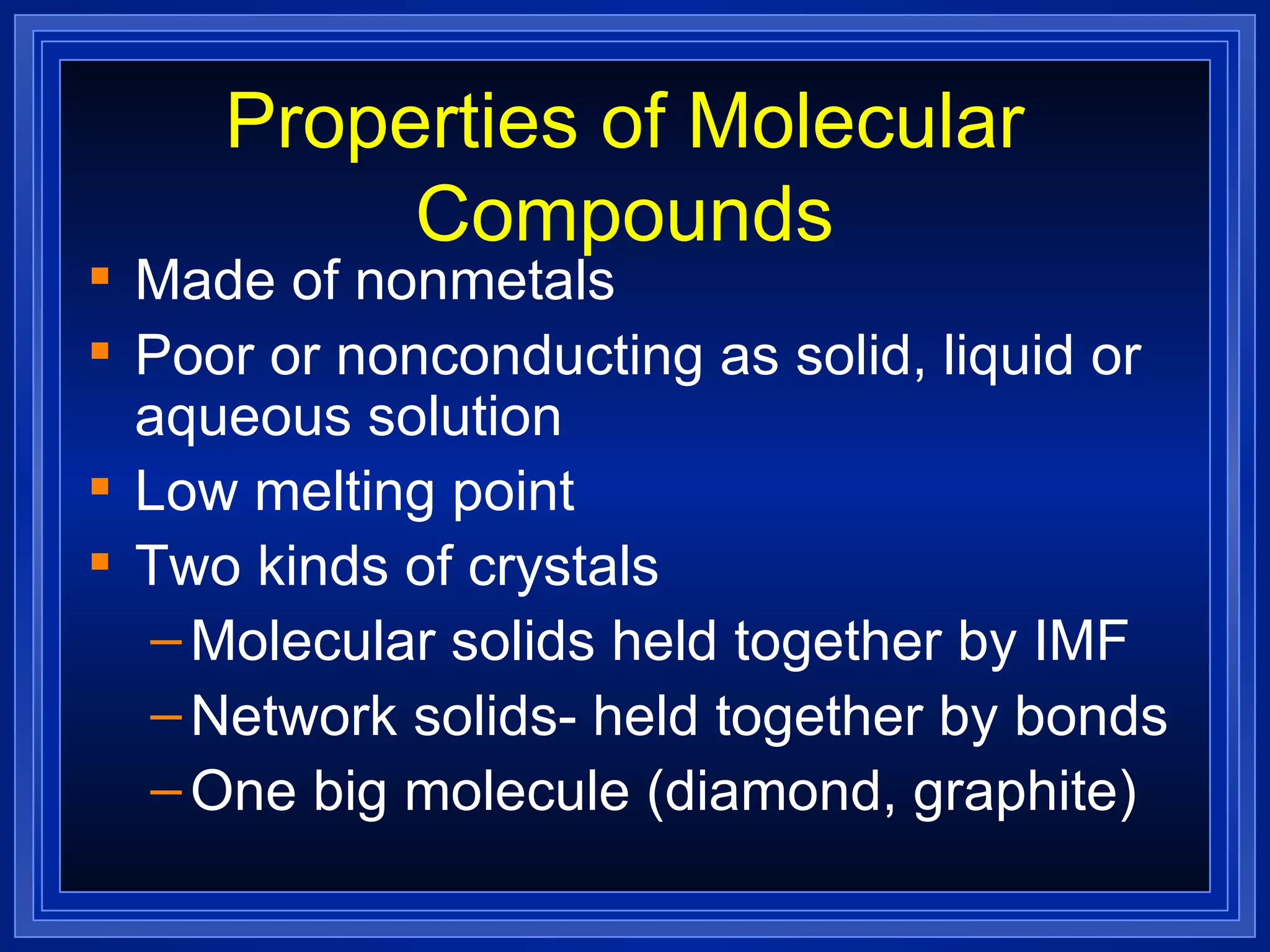
This document provides a summary of covalent bonding and molecular compounds in 3 paragraphs:
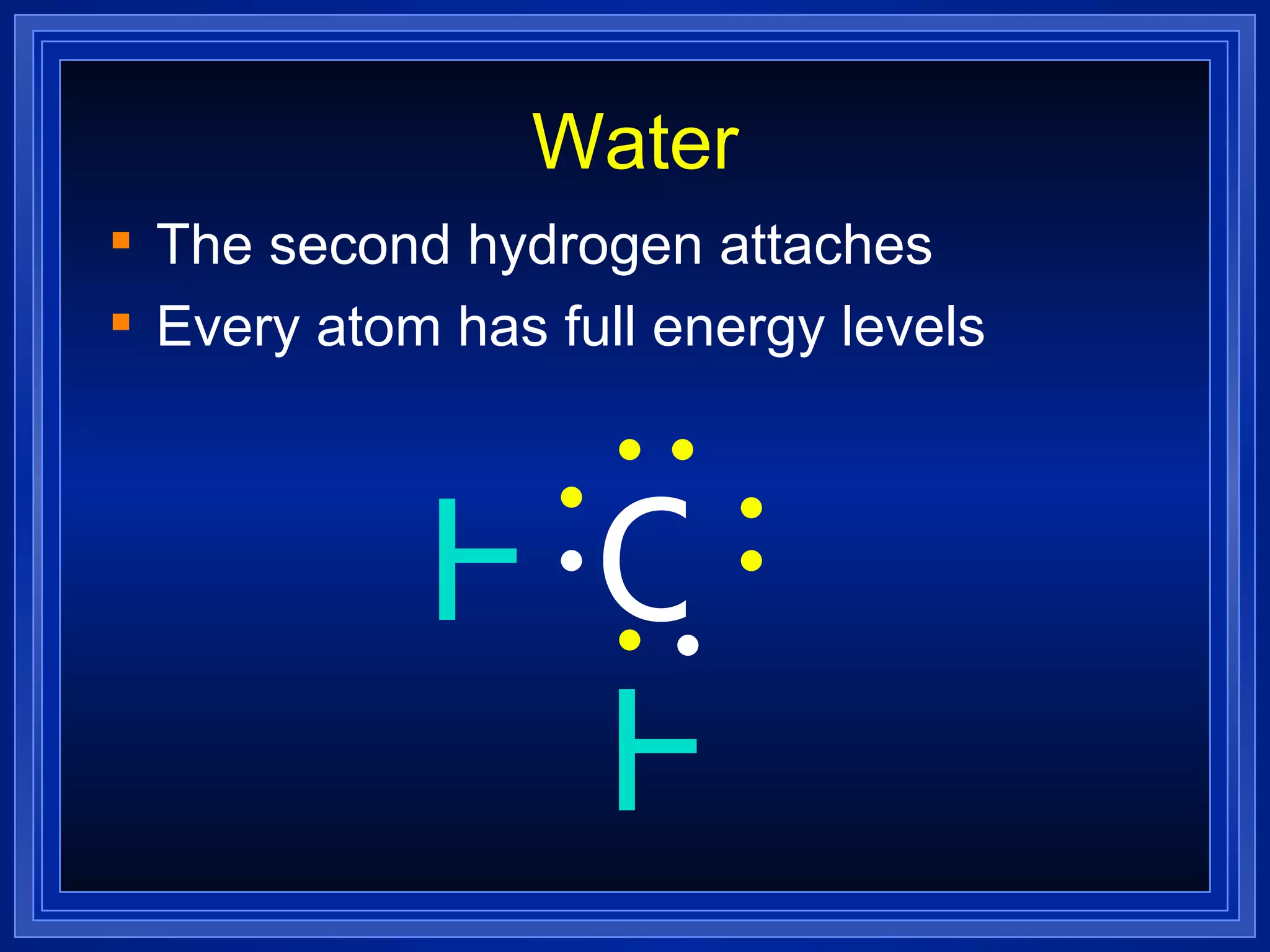
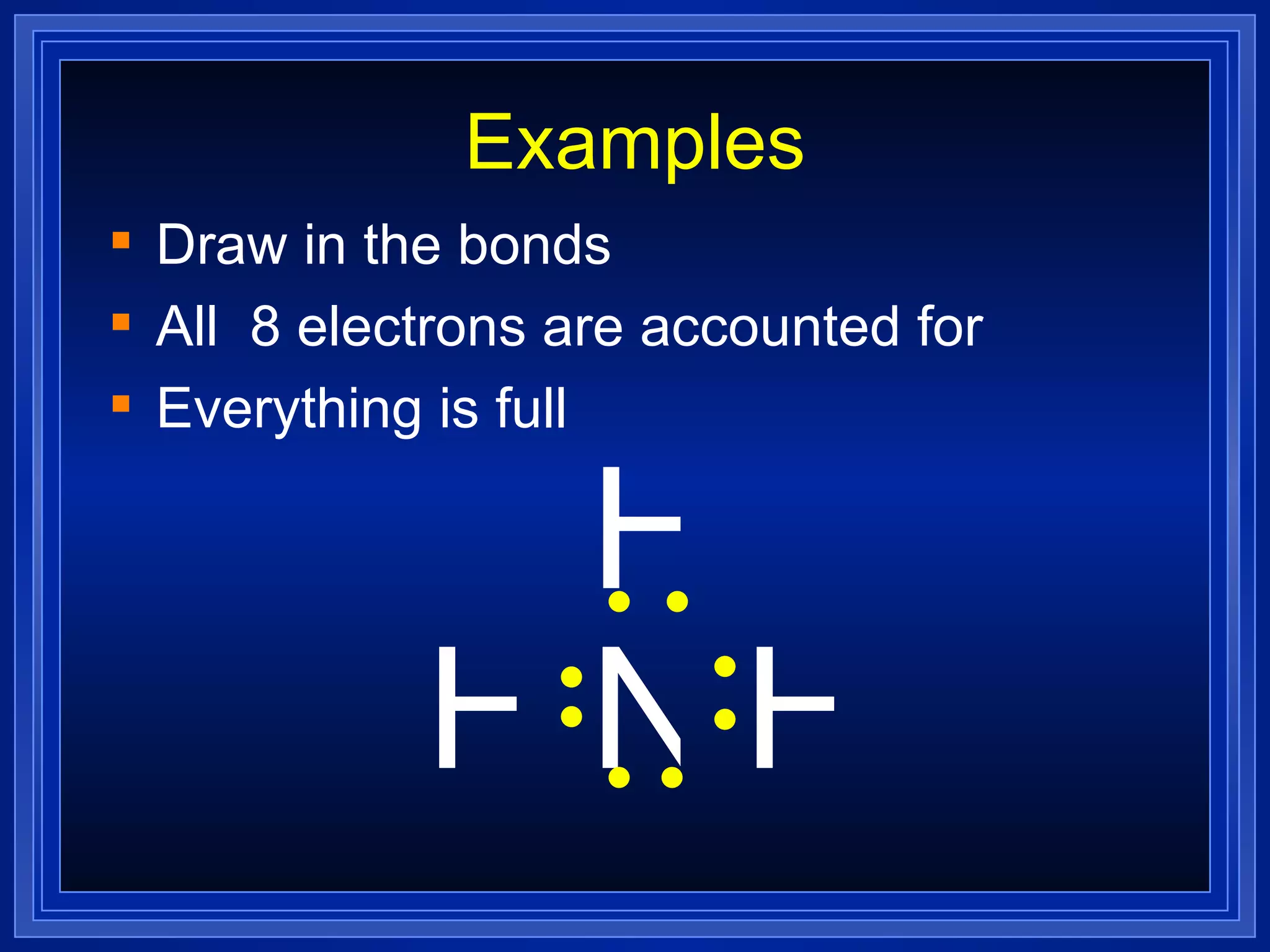
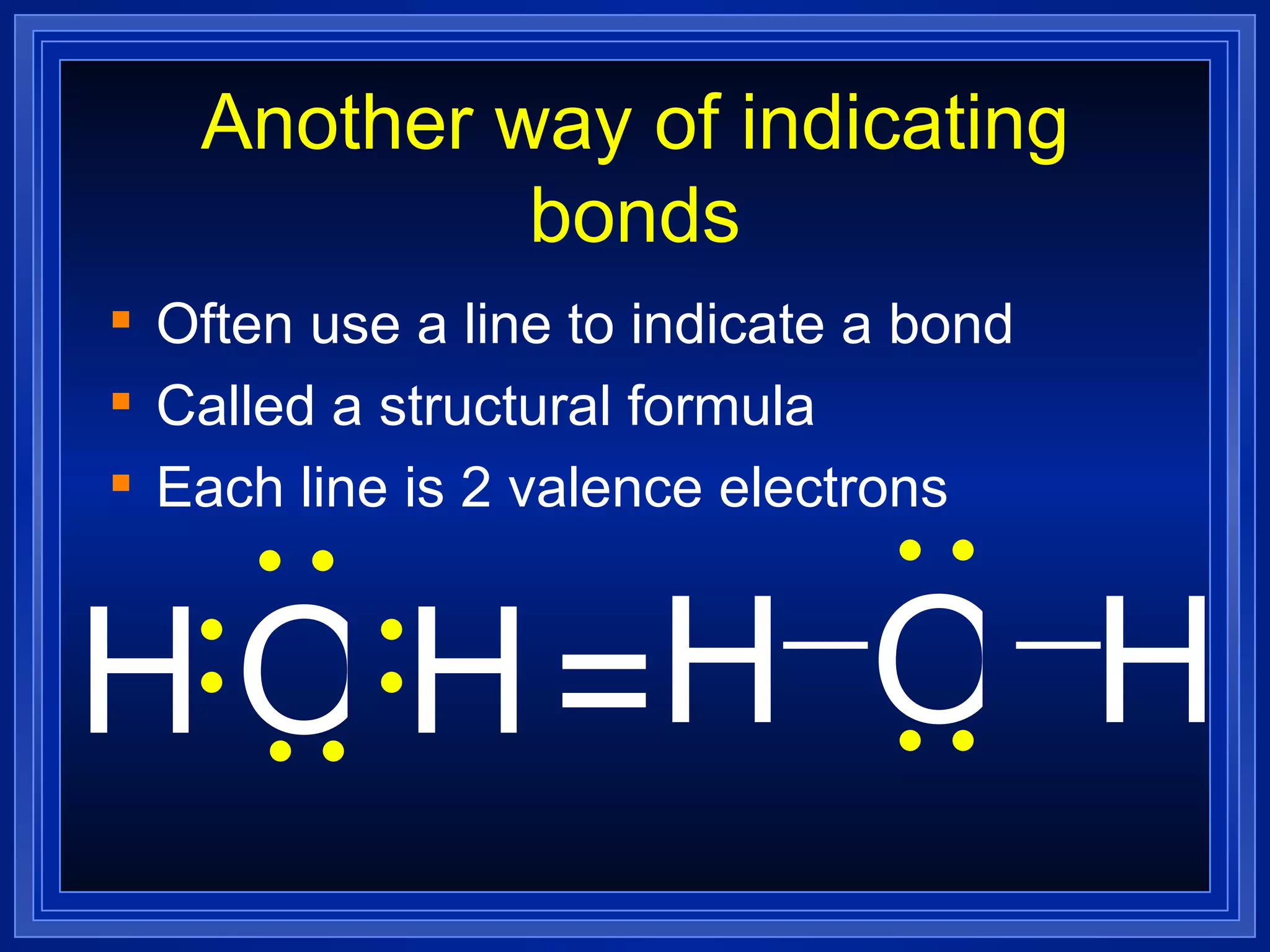
Covalent bonds result from the sharing of valence electrons between nonmetallic elements. Atoms joined by covalent bonds form molecules, the smallest units of a molecular substance. Molecules have a molecular formula showing the number and type of atoms, and may be represented by Lewis structures or structural formulas.
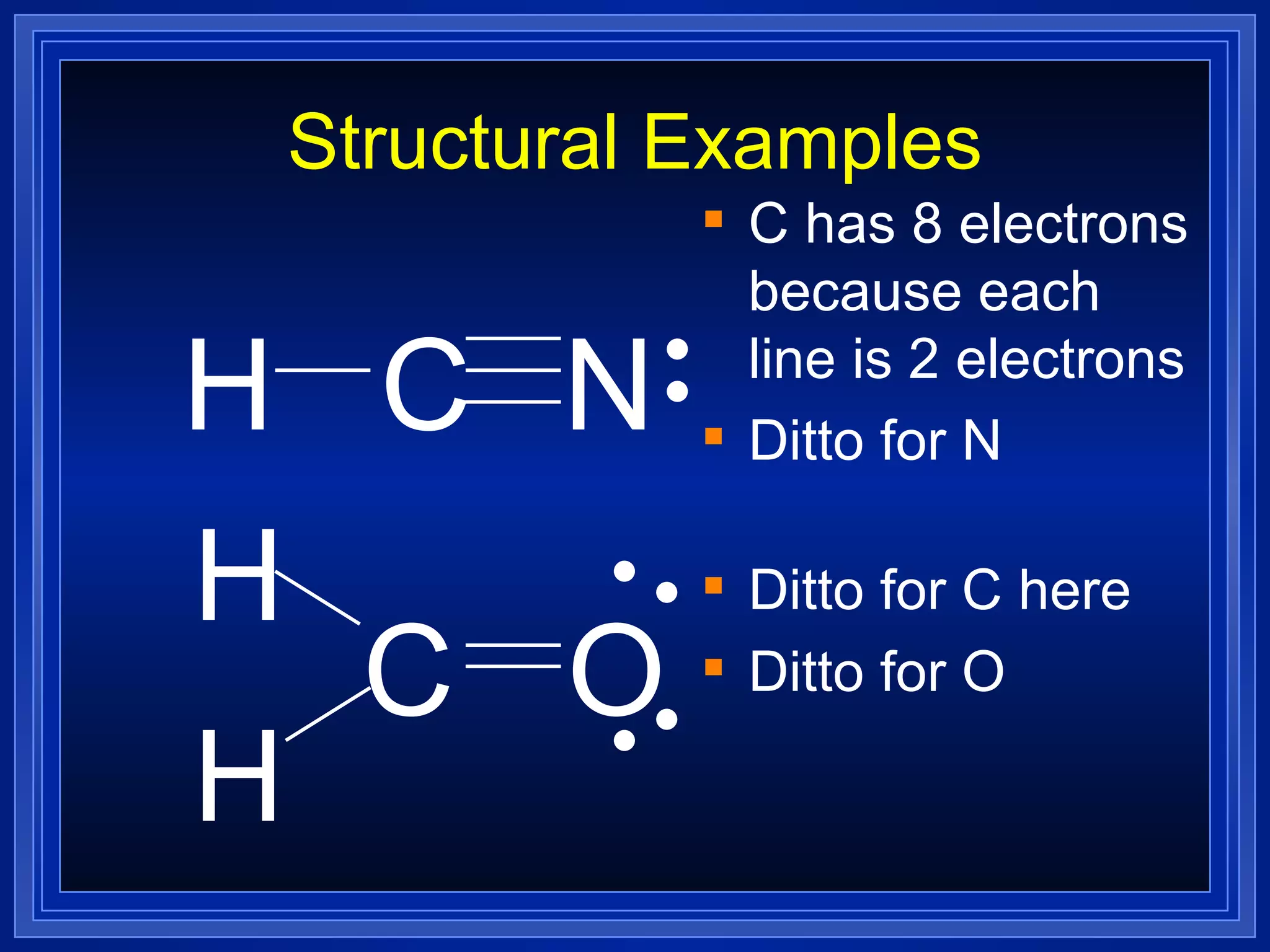
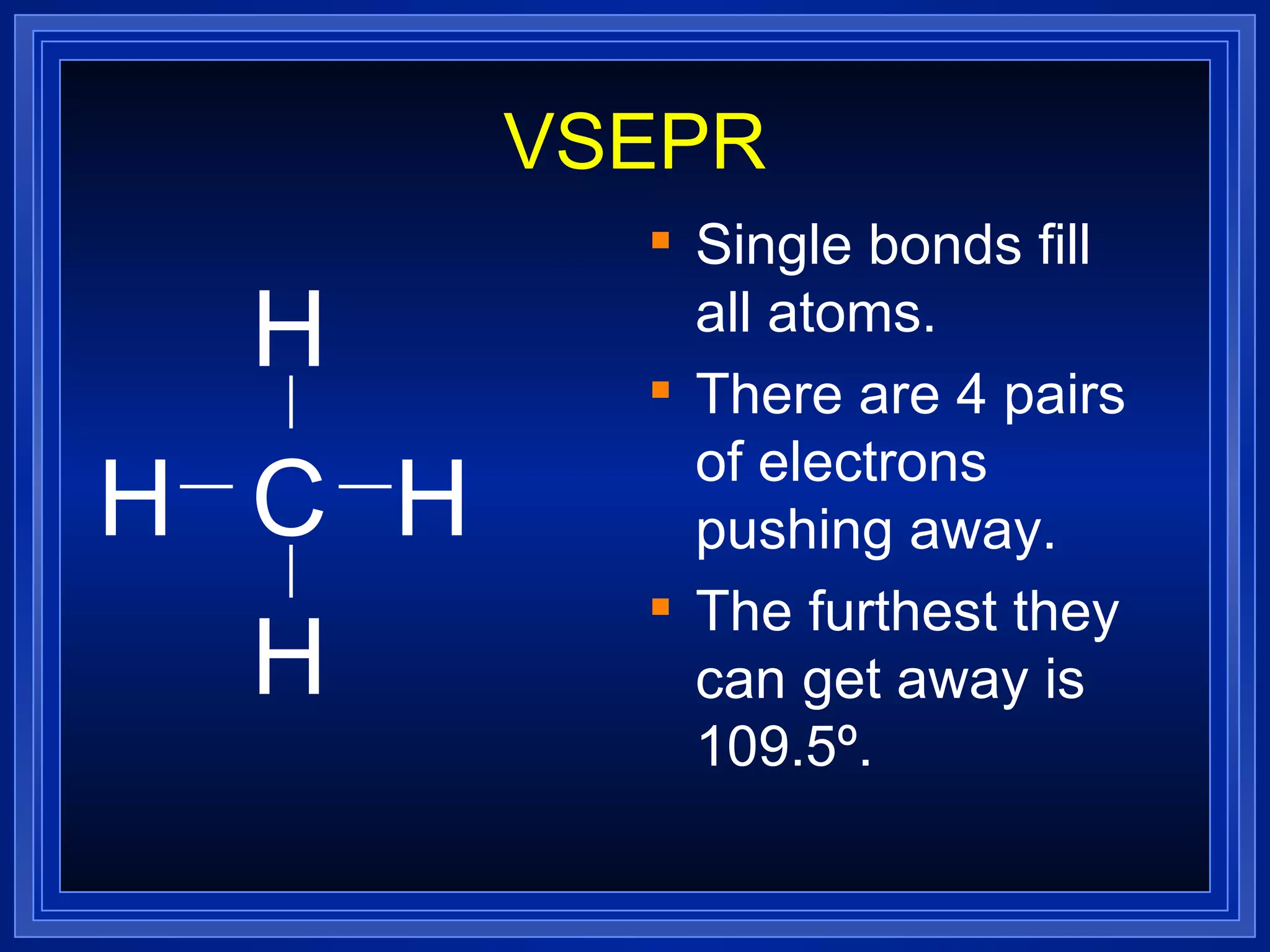
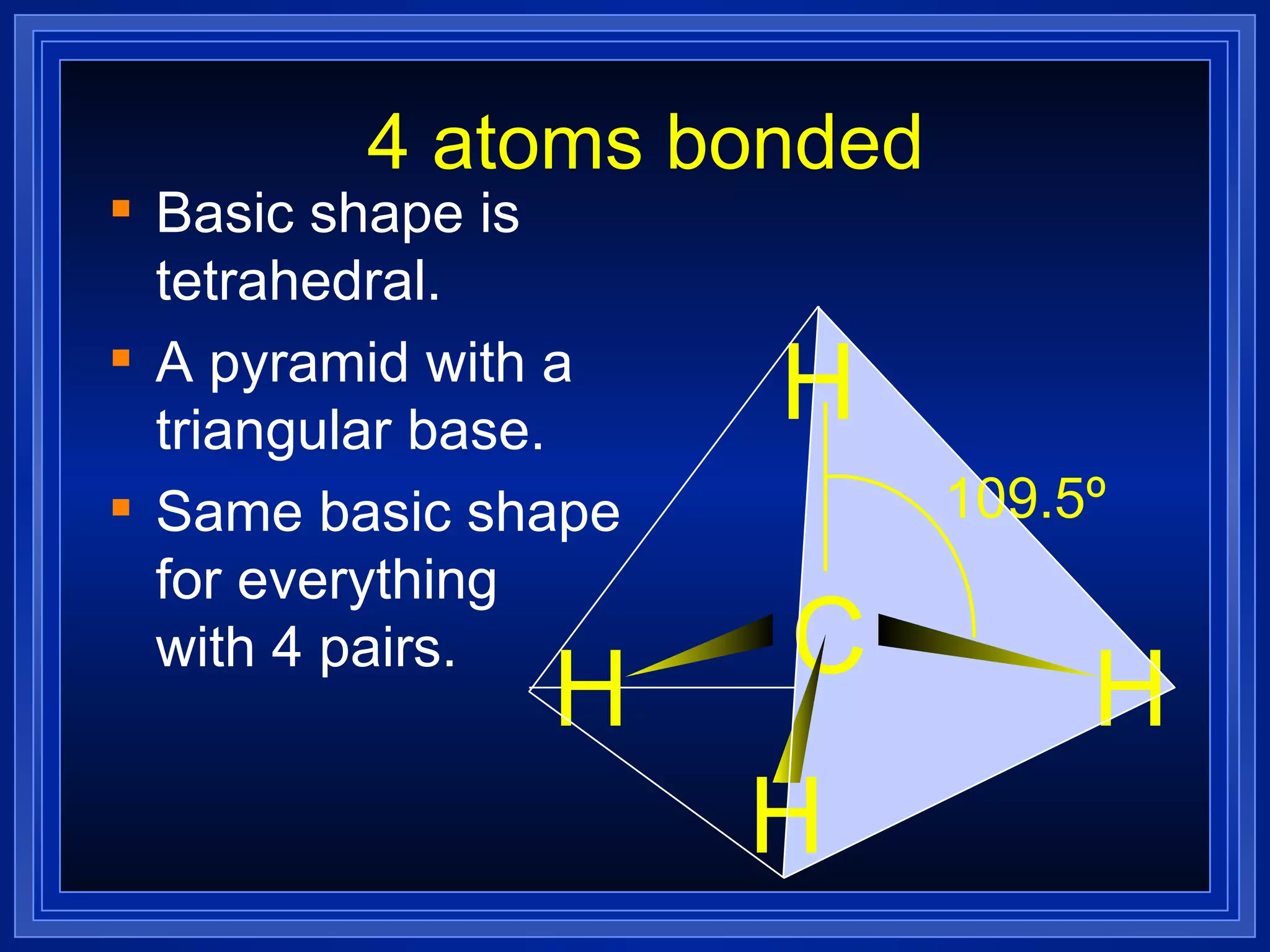
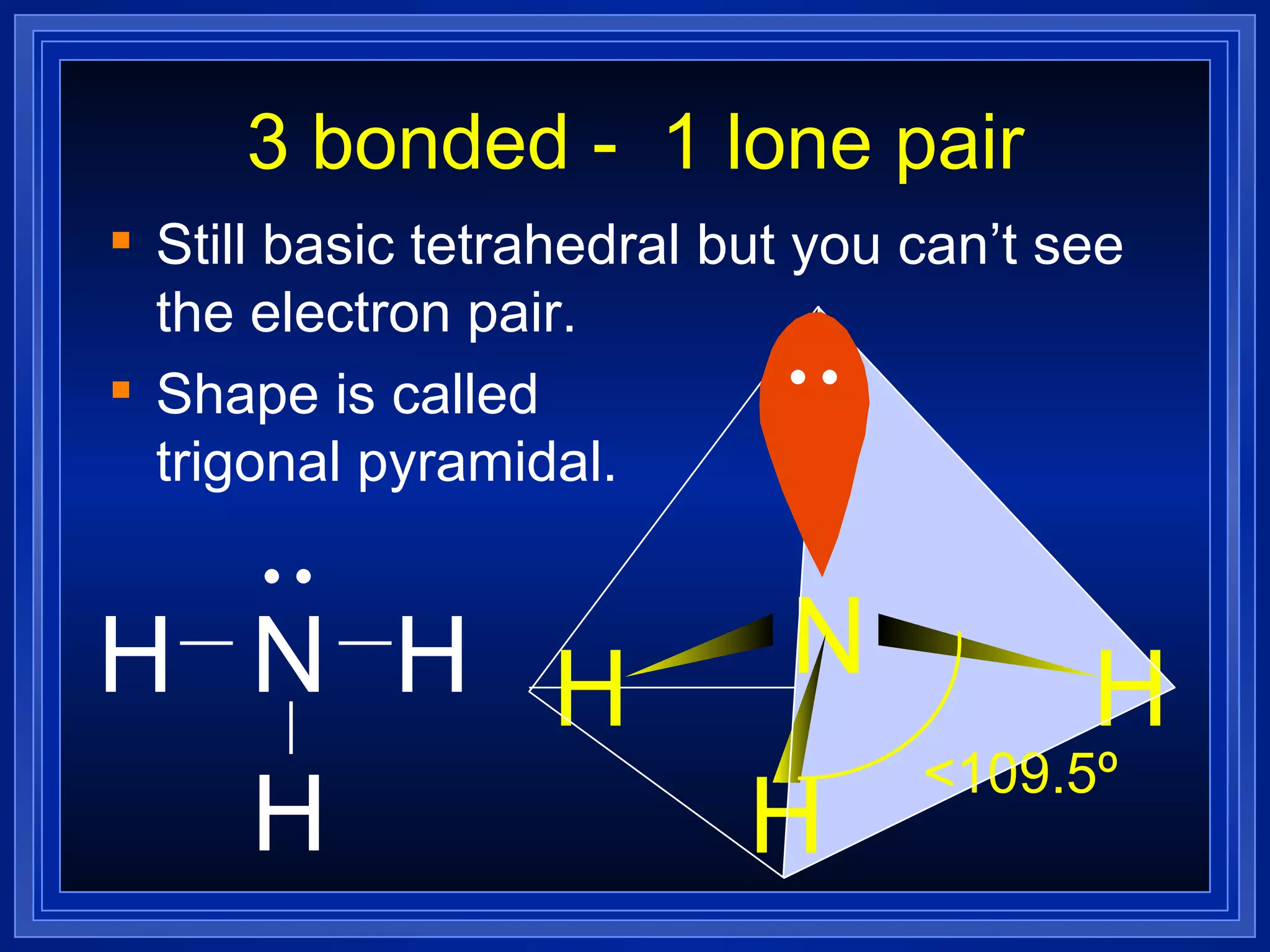
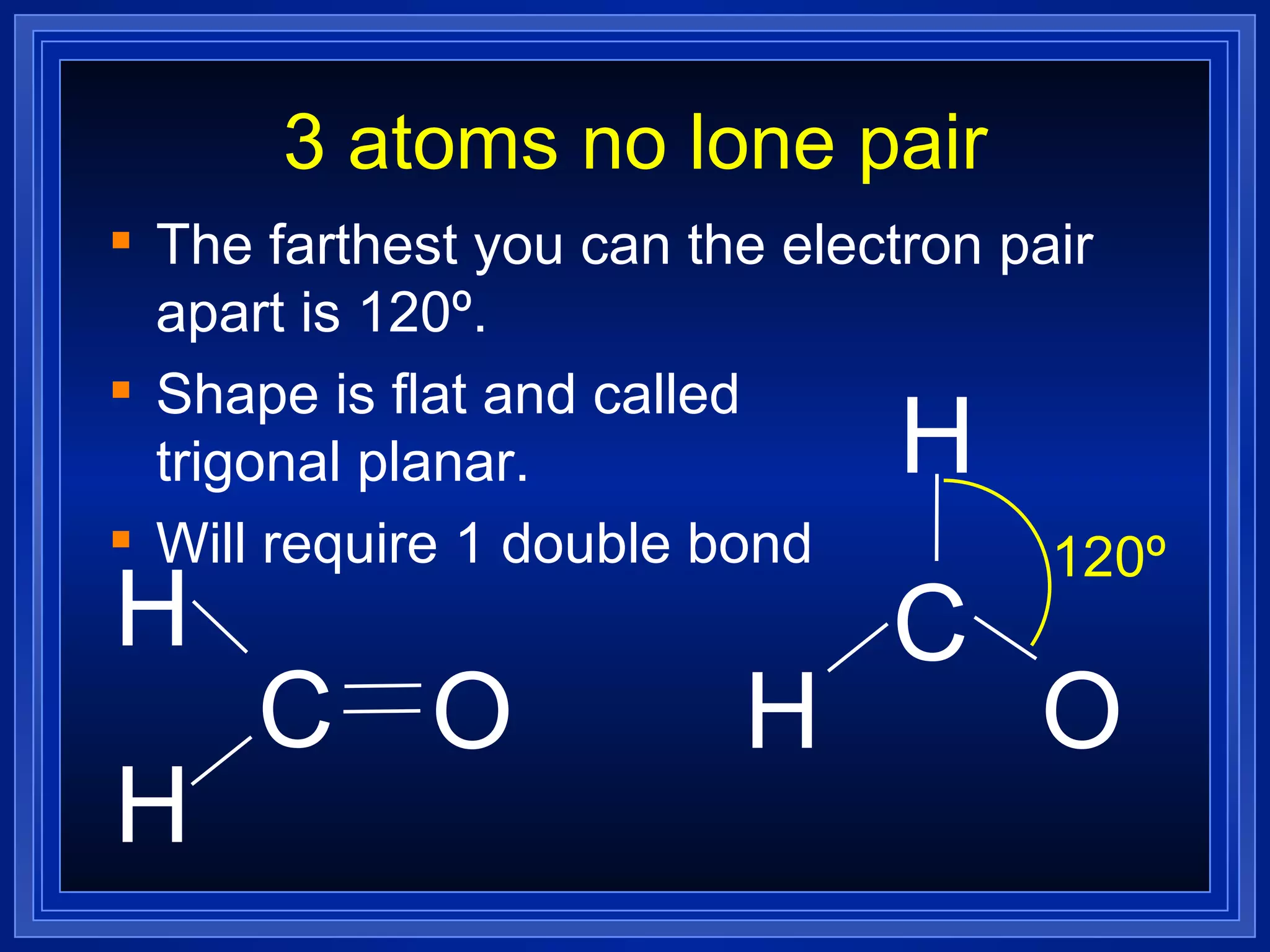
Multiple bonds can form when atoms share more than one pair of valence electrons. The octet rule describes how atoms bond to acquire a full outer shell of 8 electrons. Molecular shape is determined by VSEPR theory based on electron pair repulsion. Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals for bonding