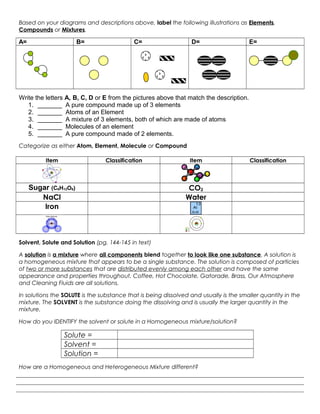
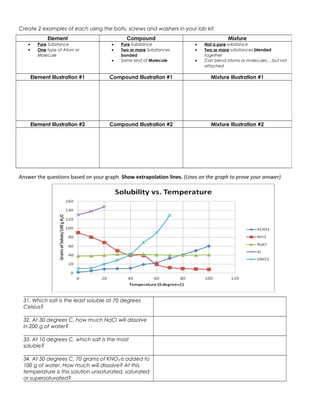
The document discusses the key differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures. Elements are pure substances made of only one type of atom, while compounds are pure substances made of two or more elements chemically bonded together. Mixtures are not pure substances and contain two or more substances blended together but not chemically bonded. Examples are provided of elements, compounds, and mixtures in various states. The document also discusses solvents, solutes, and solutions, defining a solution as a homogeneous mixture of a solute dissolved in a solvent. Readers are asked to identify examples as elements, compounds, mixtures, and to classify items as atoms, elements, molecules or compounds. Questions are provided to test understanding of these concepts.