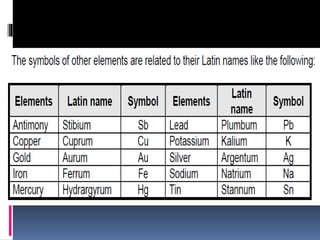
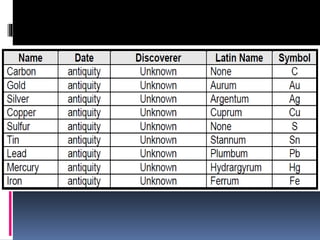
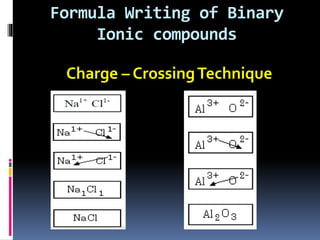
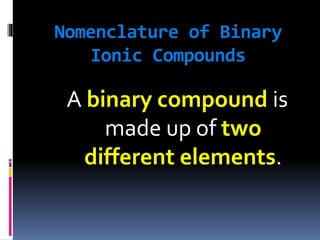
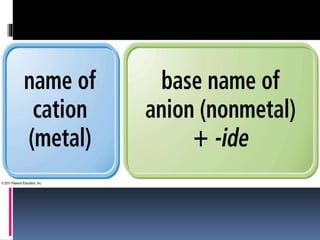
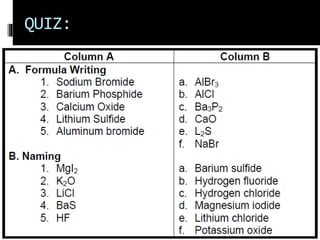
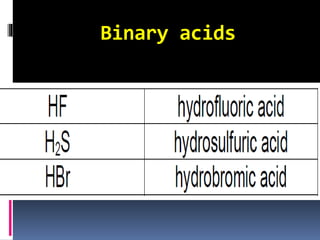
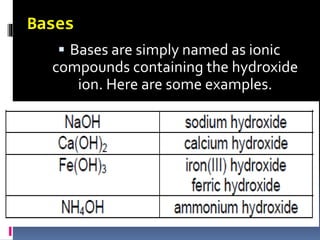
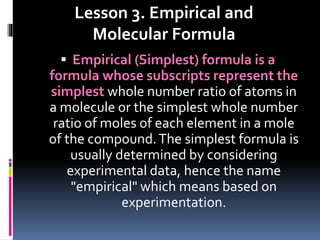
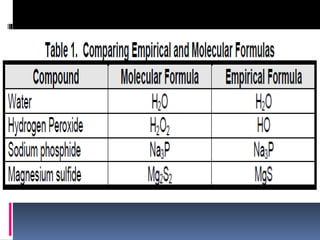
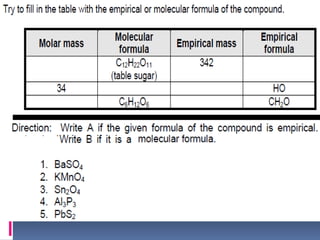
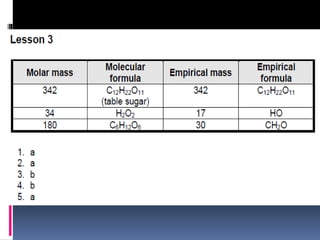
Chemical nomenclature is the system used to name chemical compounds. It allows chemists to communicate effectively. The name of a compound provides information about its structure. There are currently 114 known elements, some of which are gases while most are solids. In the early 1800s, Berzelius established the modern system of using the first letter of the element's name as its symbol. Chemical formulas represent the elements in a compound along with subscript numbers indicating mole ratios. Empirical formulas provide the simplest whole number ratio of atoms in a compound, while molecular formulas give the exact number of atoms in a molecule.