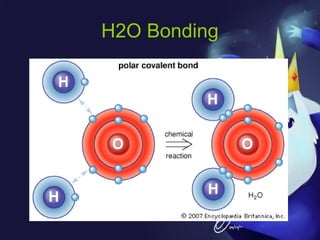
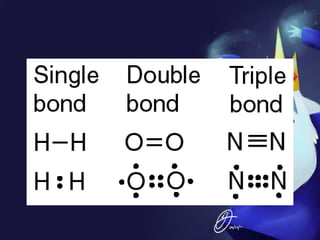
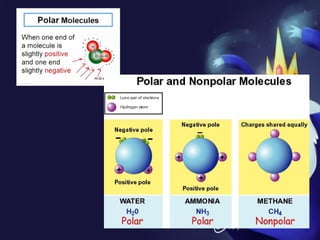
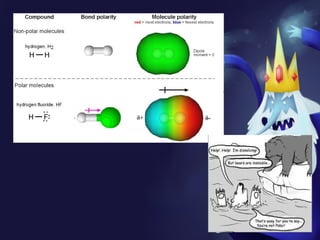
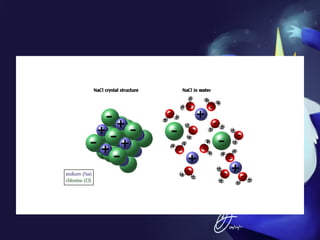
This document discusses covalent bonds and covalent compounds. It explains that covalent bonds form when two atoms share one or more pairs of valence electrons, becoming stable. Water (H2O) is used as an example where the oxygen atom shares electrons with the hydrogen atoms. Compounds can be polar or nonpolar depending on whether electron sharing is equal. Polar molecules like water can dissolve other polar substances like sugar due to electron attraction. Chemical formulas represent the elements and numbers of atoms in compounds.