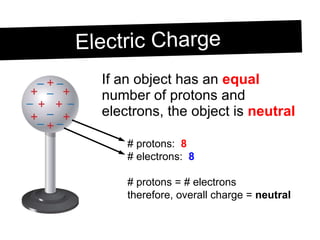
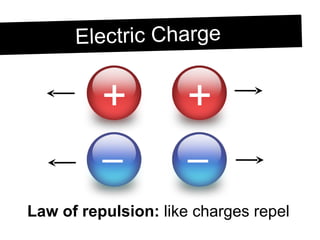
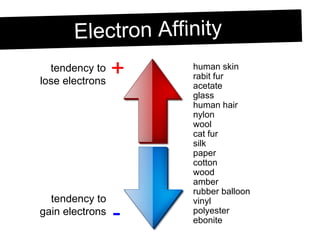
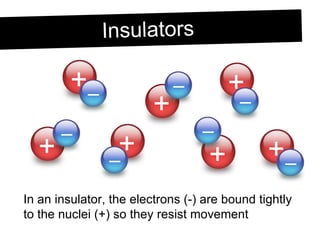
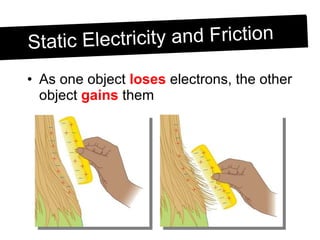
Static electricity occurs when objects become electrically charged through the transfer of electrons. Charging occurs when two materials are rubbed together, causing electrons to move from one material to the other. This leaves one material with an excess of electrons and a negative charge, and the other material with a deficit of electrons and a positive charge. The electric charges remain on the surface of the objects until they are given a path to ground or neutralize each other through contact or discharge.