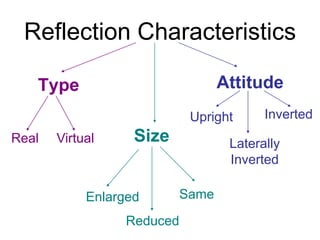
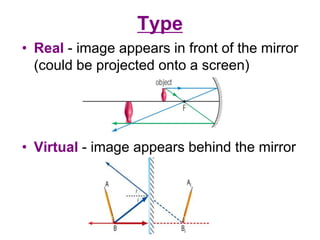
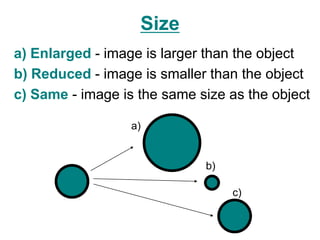
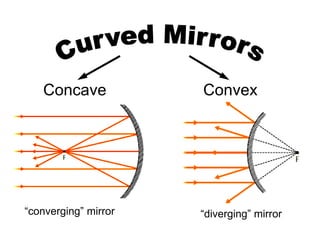
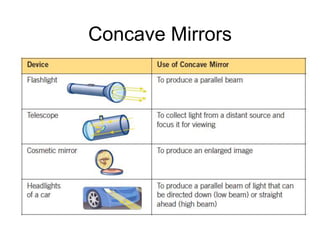
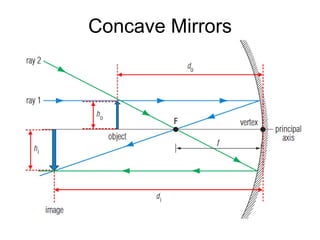
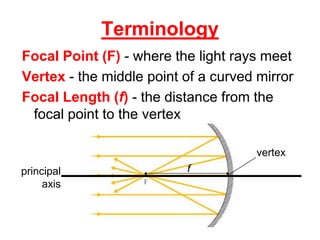
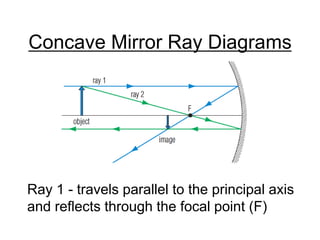
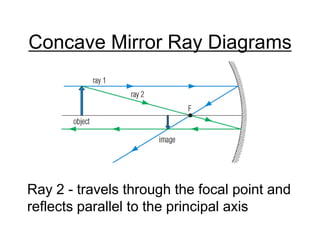
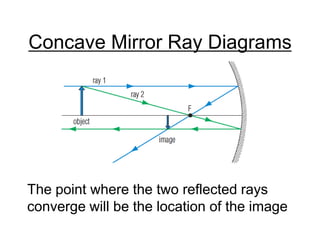
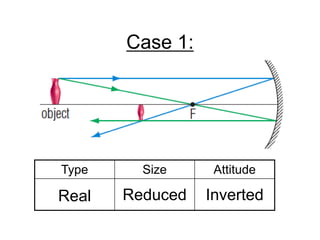
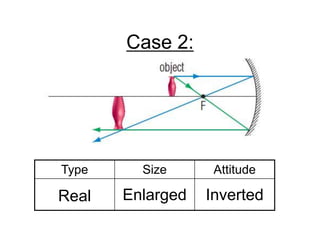
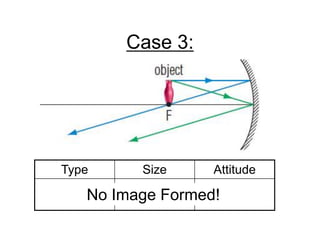
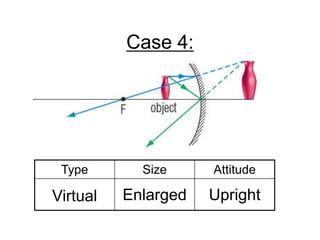
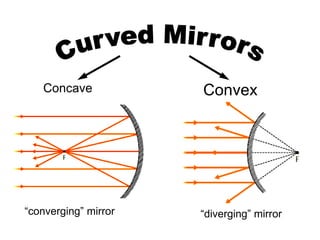
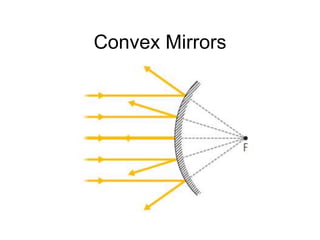
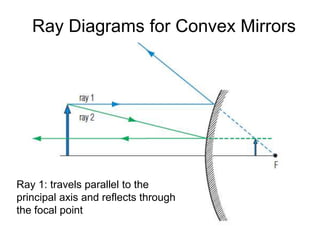
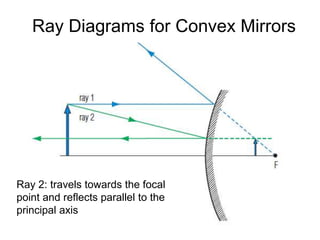
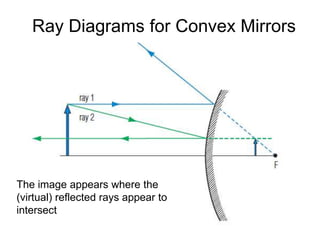
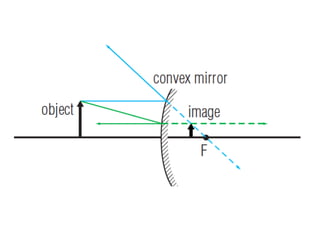
The document discusses the characteristics of curved mirrors, including concave and convex mirrors. It defines key terms like focal point, focal length, vertex, and describes the four cases of image formation for concave mirrors based on the object's distance from the mirror. Real images can be projected, virtual images appear behind the mirror. Concave mirrors form inverted and magnified or reduced real images. Convex mirrors always form upright, virtual and reduced images. Ray diagrams illustrate the reflection of light rays for both concave and convex mirrors.