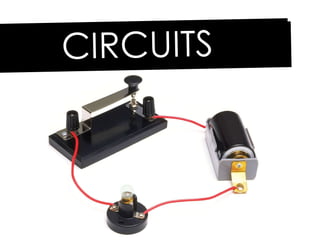
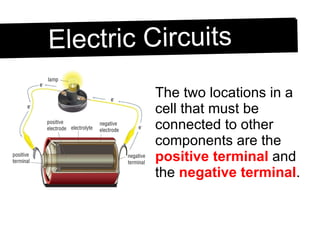
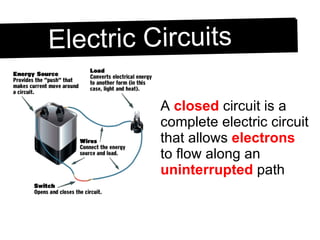
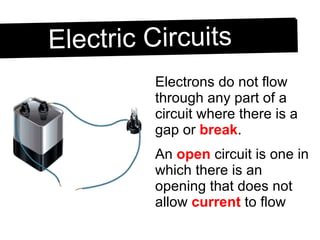
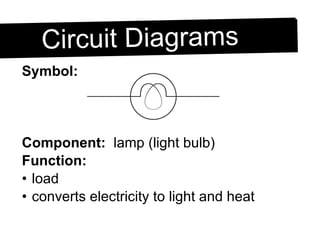
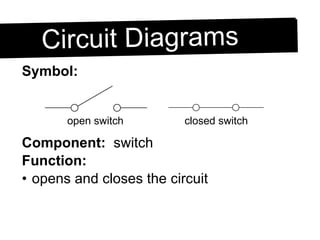
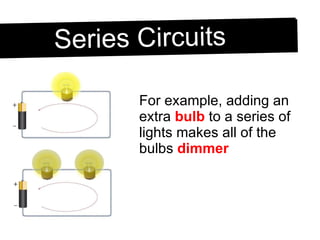
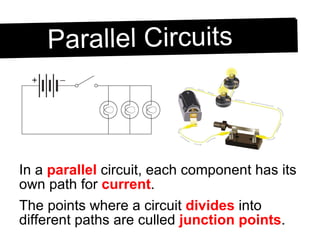
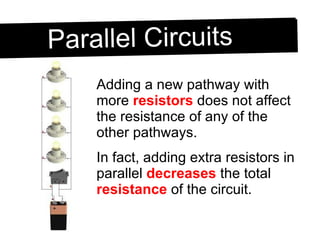
An electric circuit is a closed path that allows electrons to flow from an energy source and back. A closed circuit allows continuous electron flow, while an open circuit interrupts flow. Common circuit components include batteries, wires, switches, bulbs and resistors. Circuit diagrams use symbols to represent components and visualize connections before building real circuits. Series circuits have a single current path, so adding resistors increases total resistance and dims all bulbs. Parallel circuits provide multiple paths, so adding resistors decreases total resistance despite each path's resistance increasing.