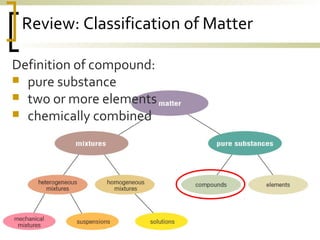
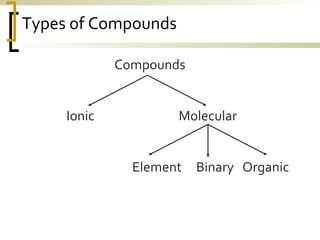
This document defines molecular compounds and provides examples. It discusses that molecular compounds are composed of non-metal elements that are chemically bonded through covalent bonds where atoms share electron pairs. Examples of common molecular compounds are given such as gases, hydrocarbons, alcohols, carbohydrates, and biological molecules. Methods for drawing and naming molecular compounds such as Lewis dot diagrams and structural formulas are also outlined.