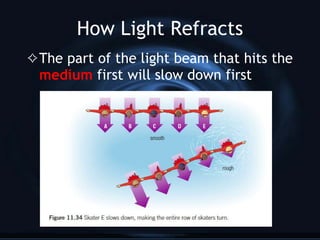
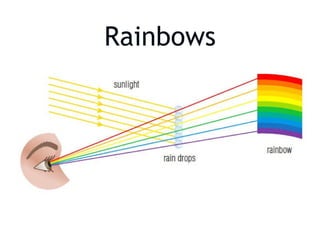
Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one medium to another. Light travels at different speeds in different media, causing it to change direction at the boundary between the two. The degree to which light is refracted depends on the index of refraction, which is a ratio comparing the speed of light in a medium to the speed of light in a vacuum. White light disperses into the colors of the visible spectrum when refracted due to different wavelengths bending by different amounts.