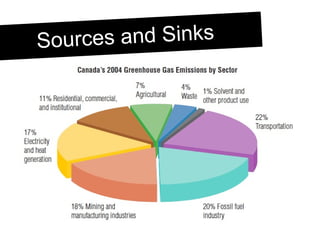
The document discusses sources and sinks of greenhouse gases and their contribution to climate change. It explains that the main natural greenhouse gas is water vapor, while the main human-caused one is carbon dioxide released from sources like burning fossil fuels. Forests normally act as carbon sinks by absorbing carbon dioxide through photosynthesis, but deforestation has reduced this, increasing atmospheric carbon levels. In addition to large industries, personal lifestyle choices and consumption patterns also generate significant greenhouse gas emissions through activities like waste disposal, manufacturing of disposable products, electricity use, transportation of goods, and more.