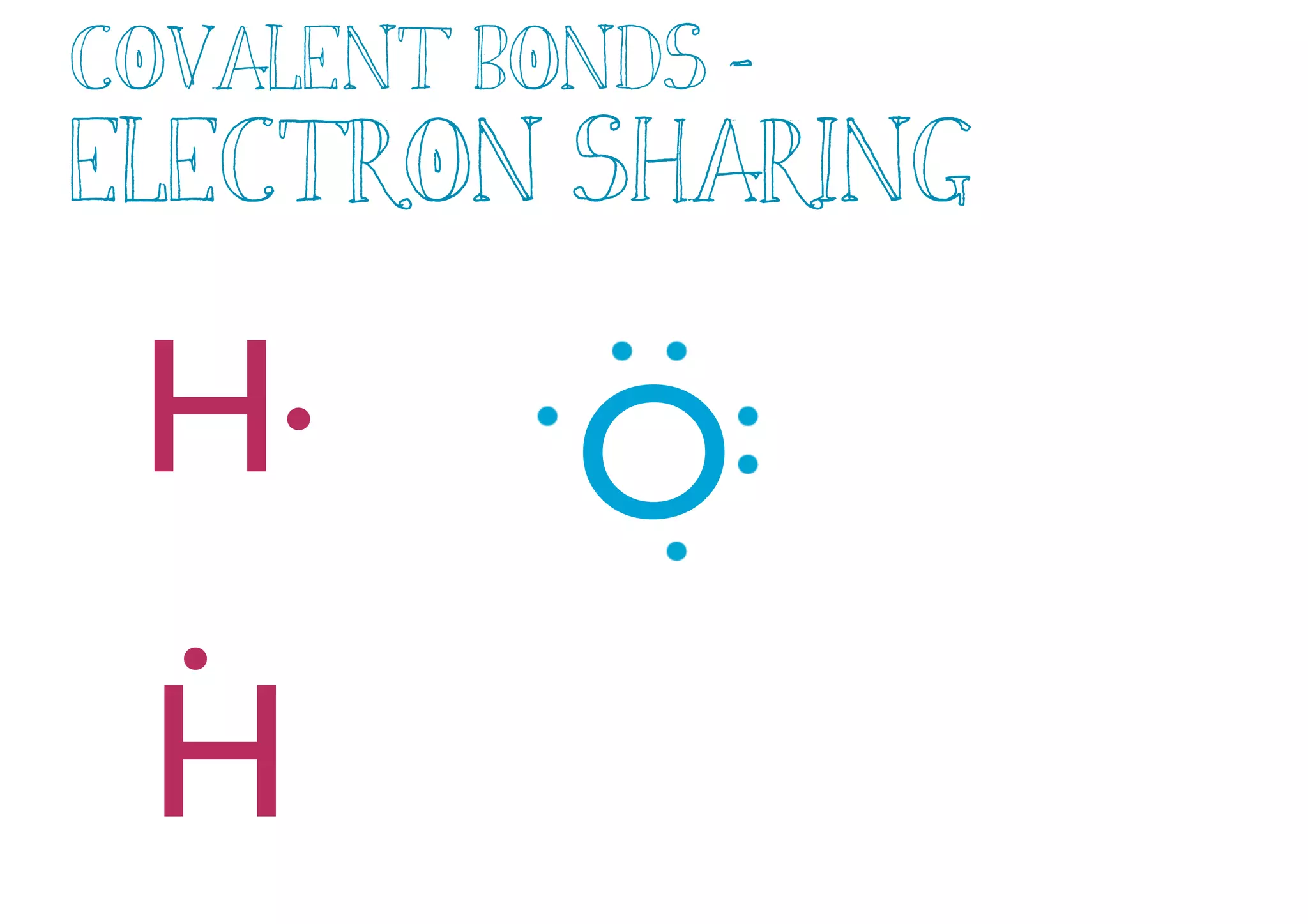
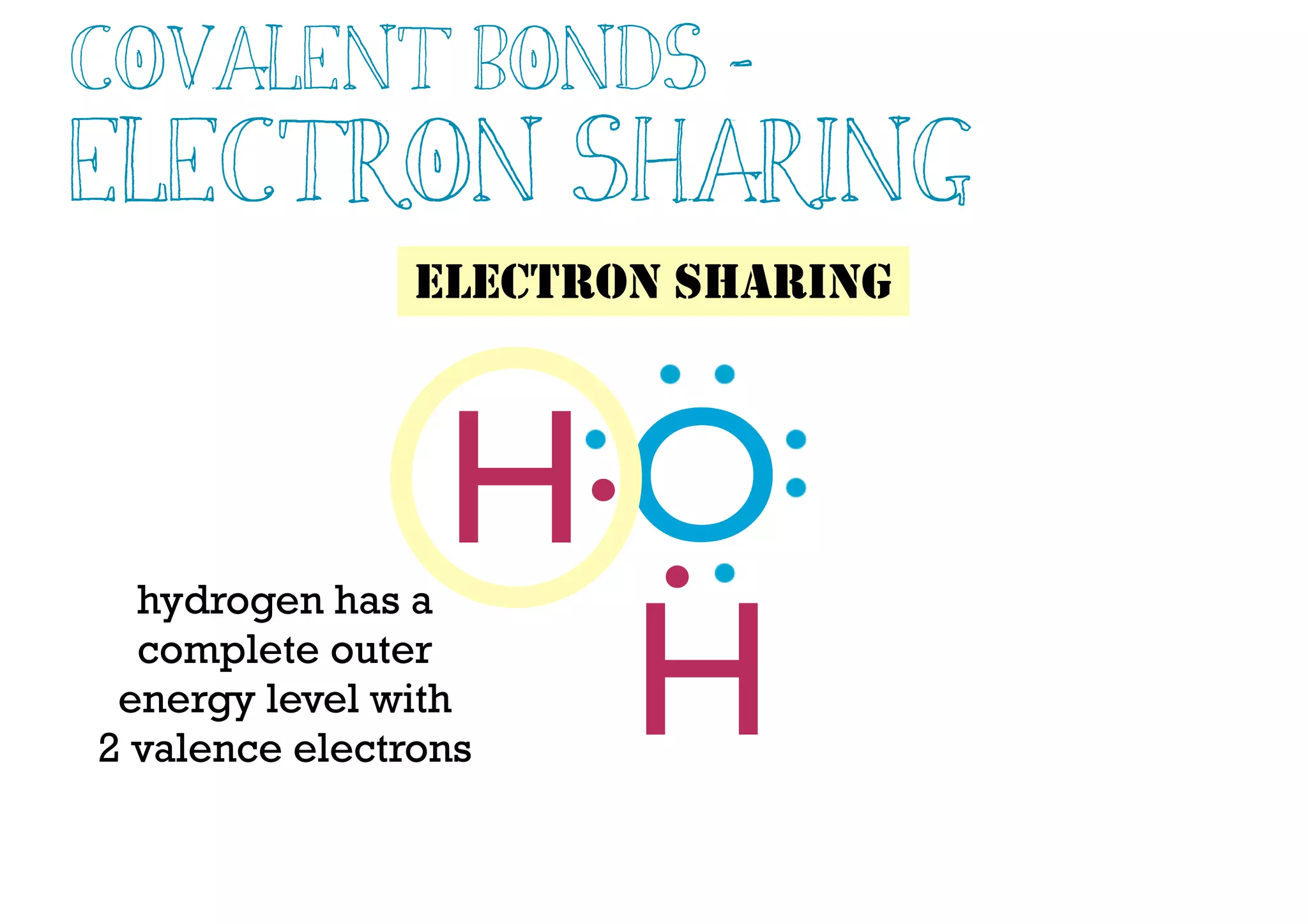
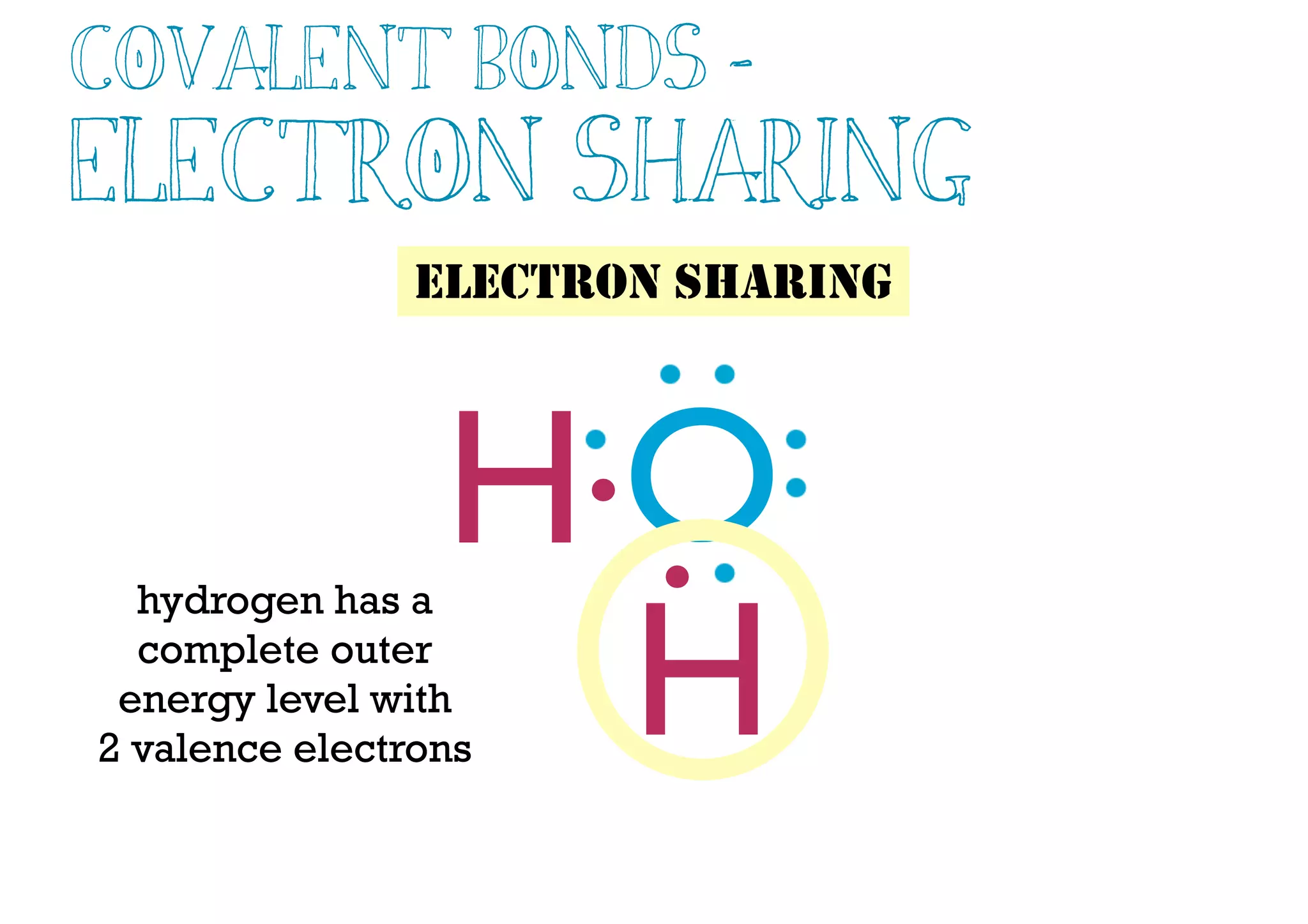
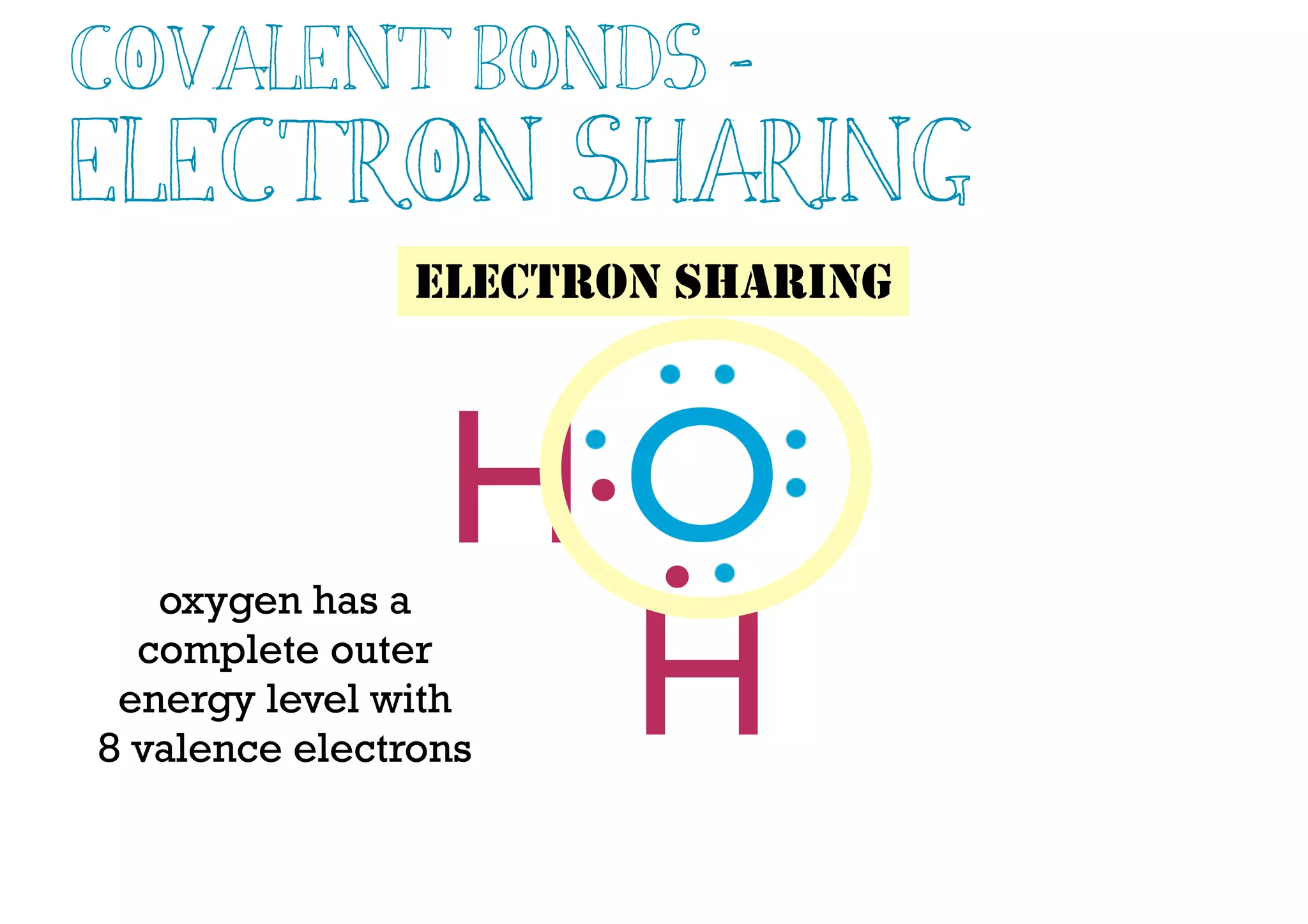
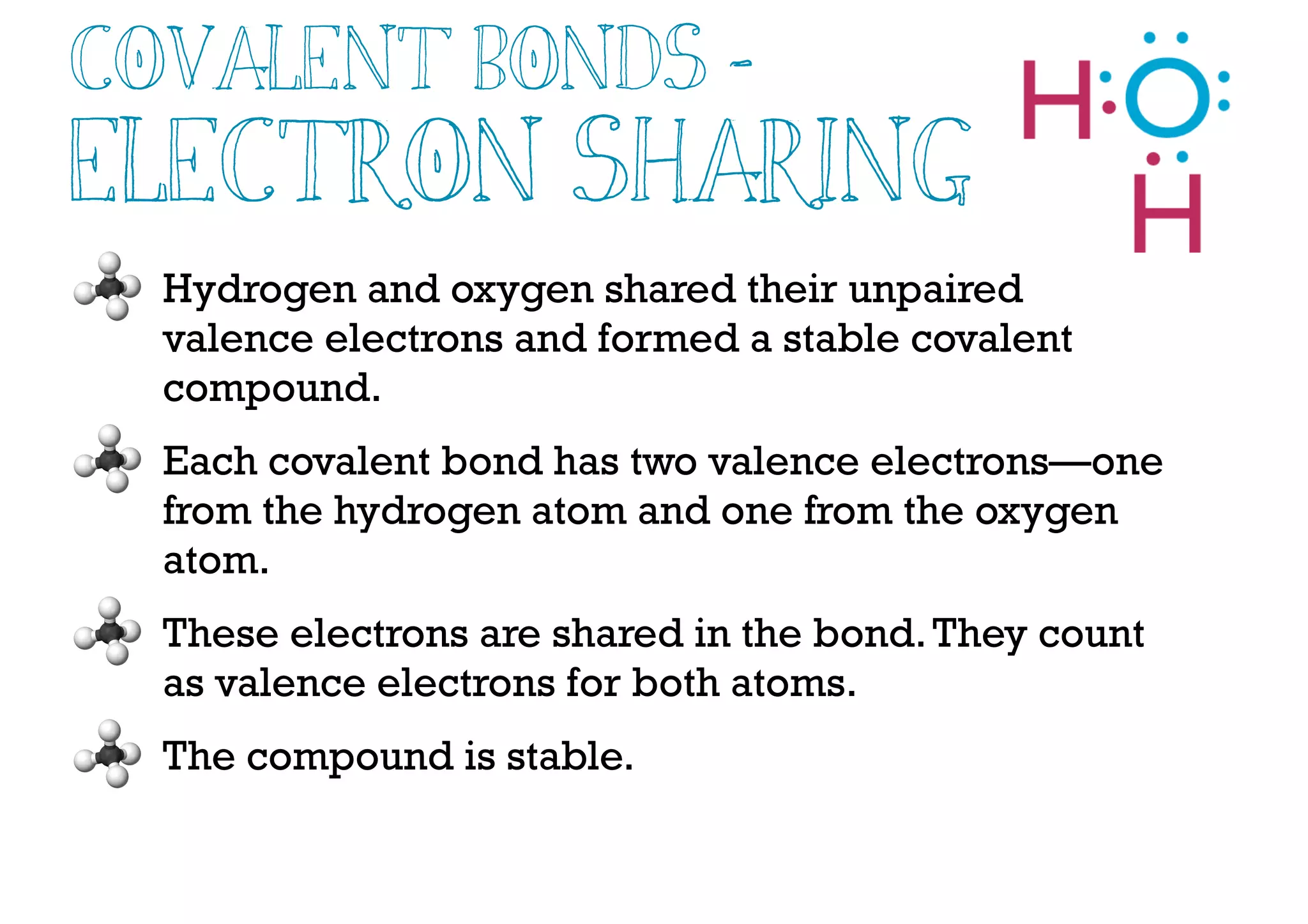
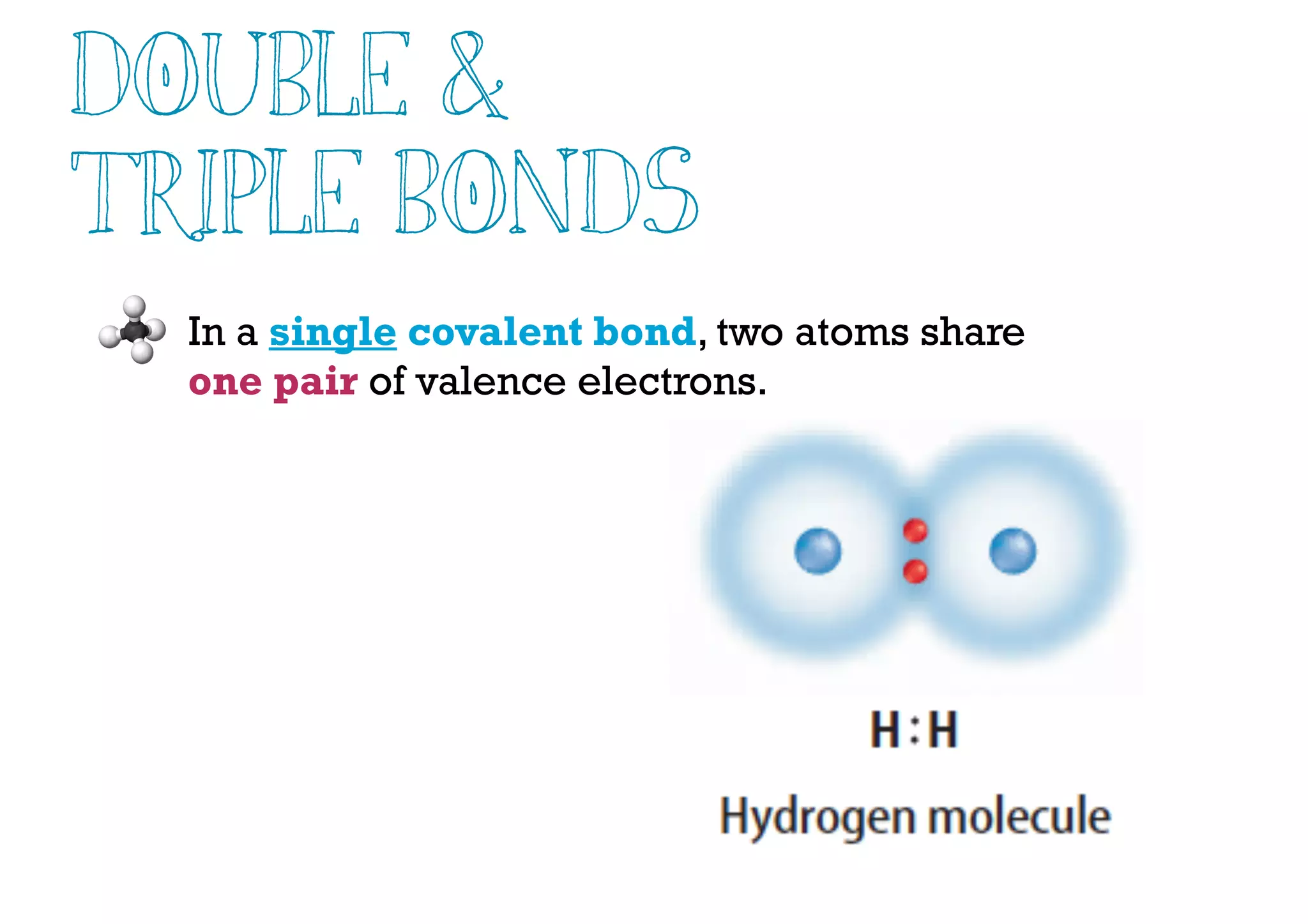
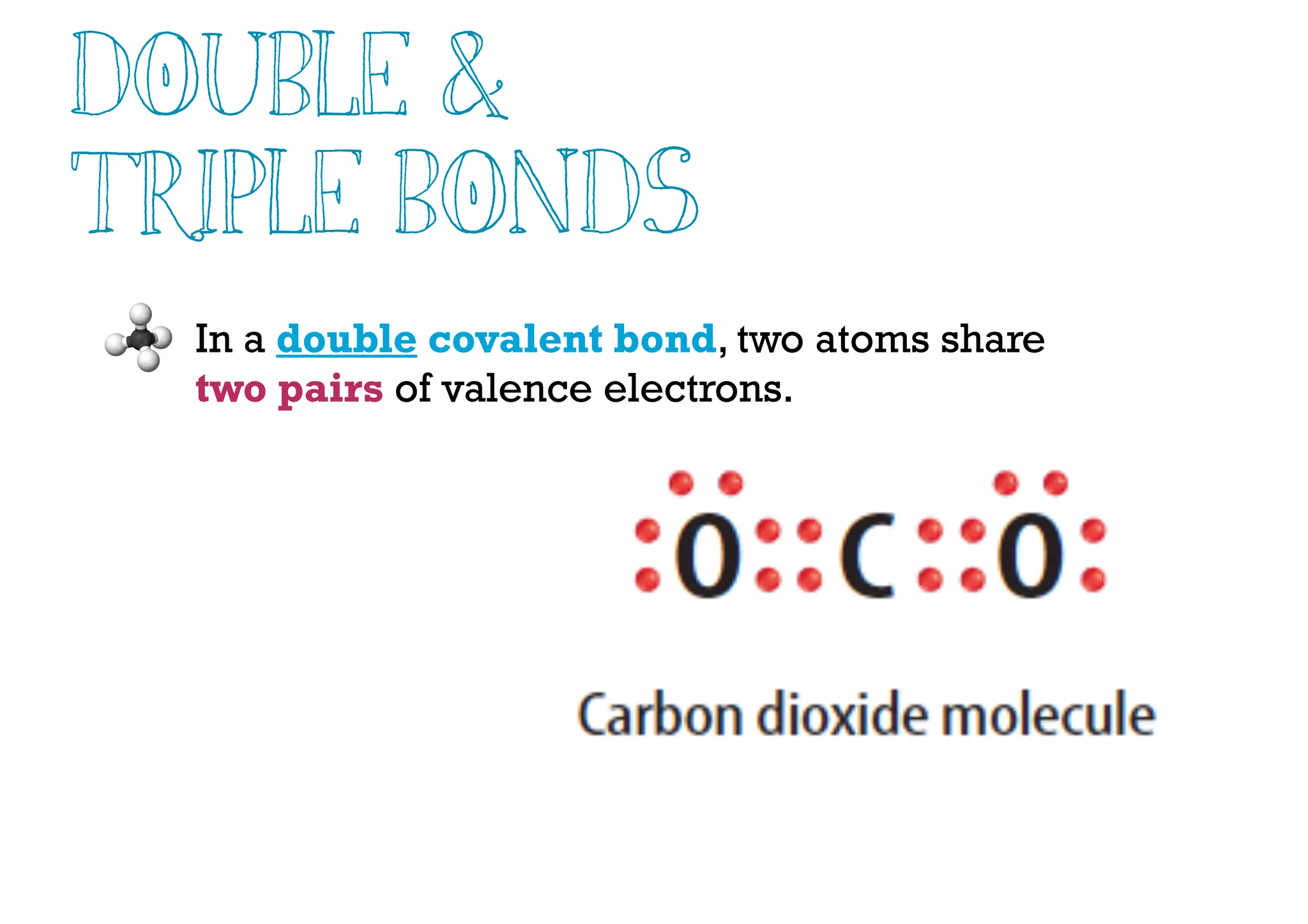
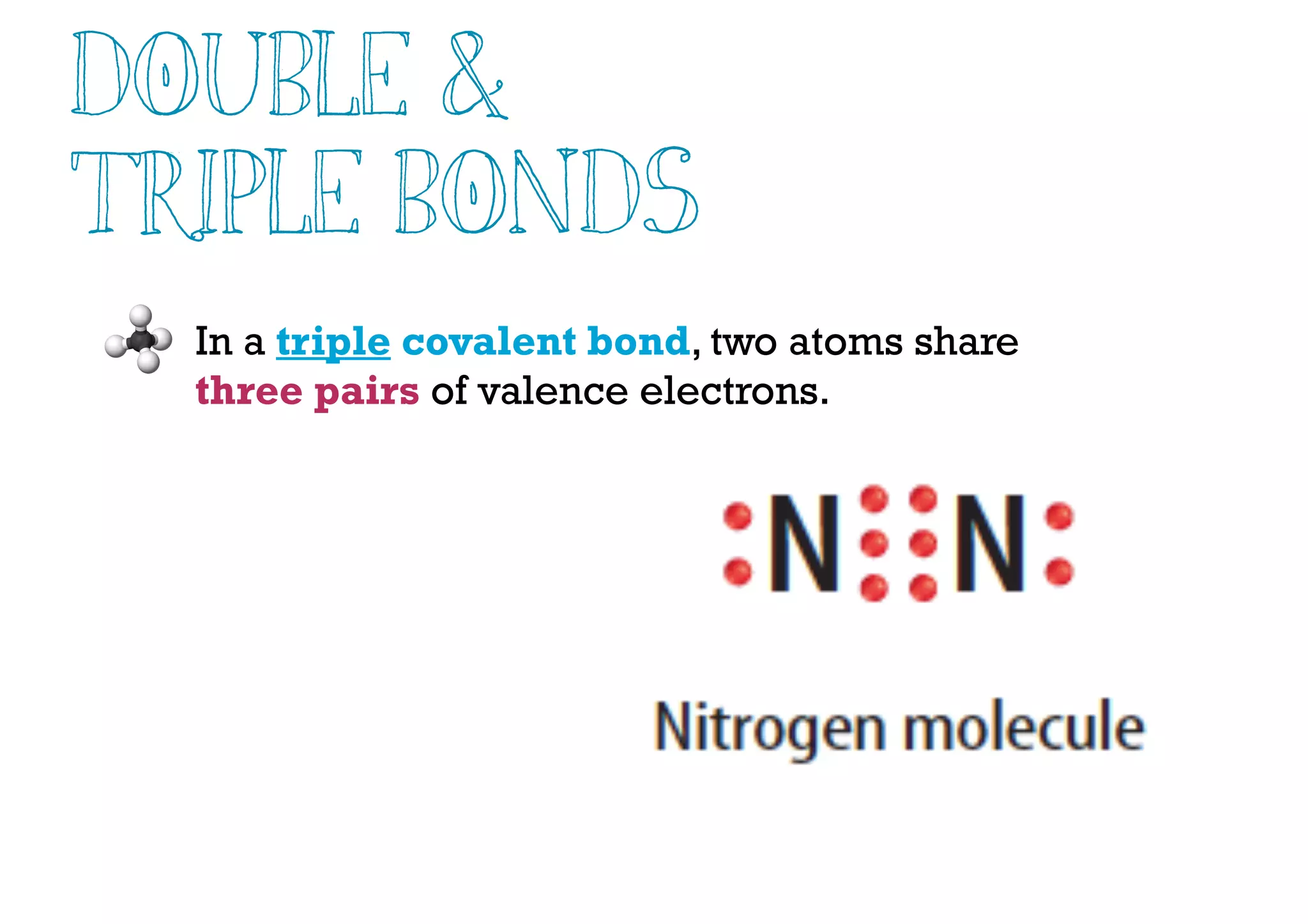
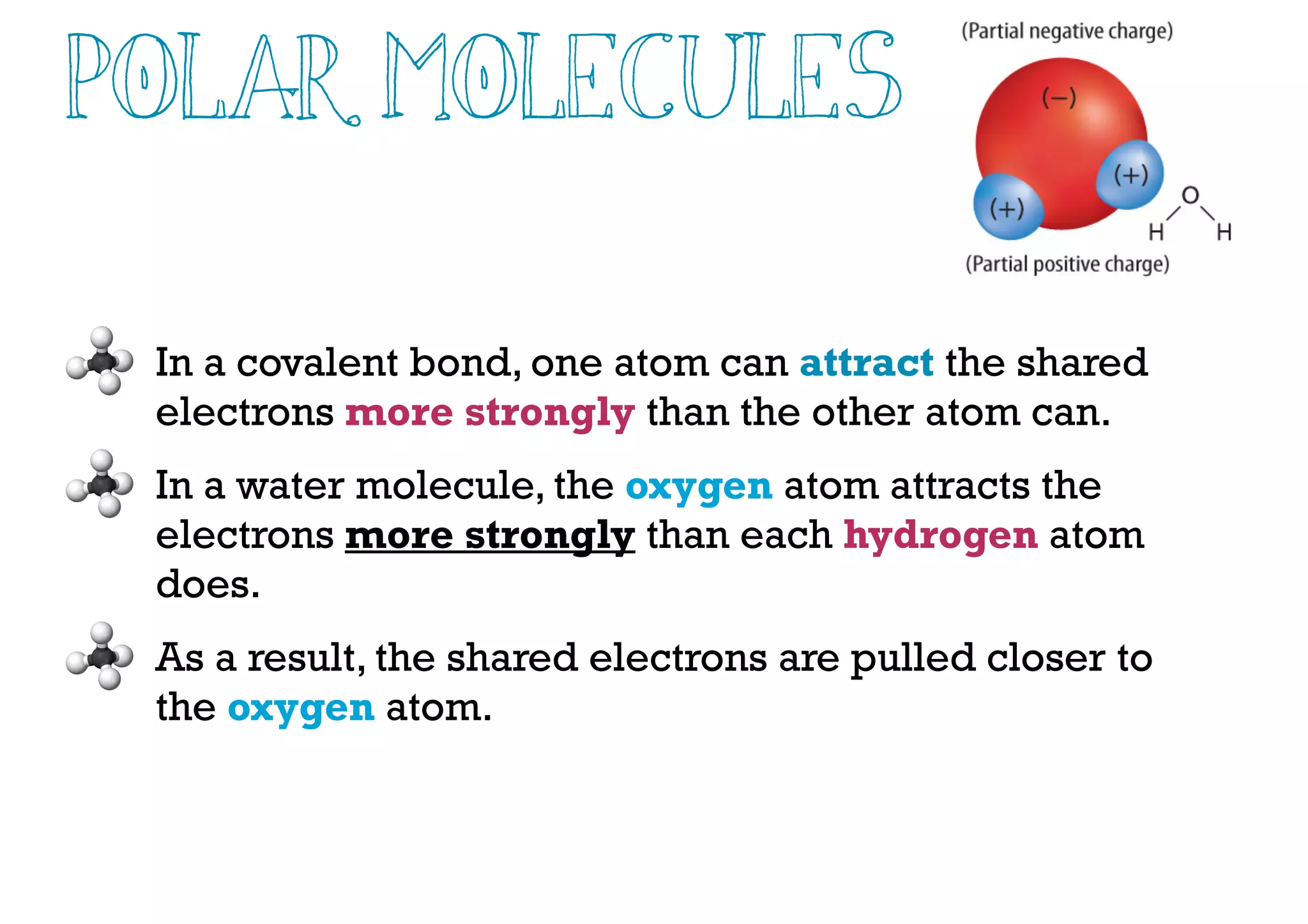
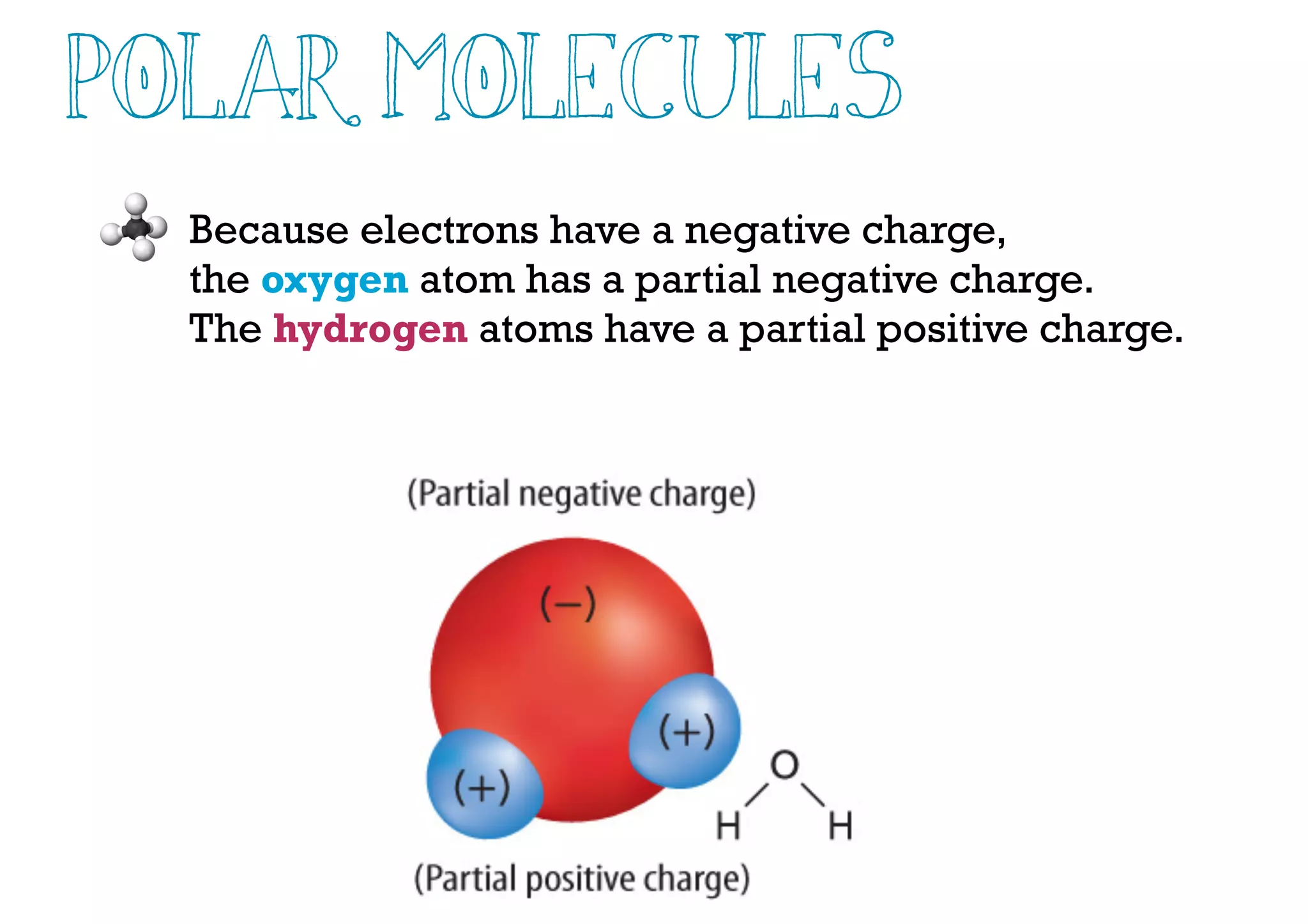
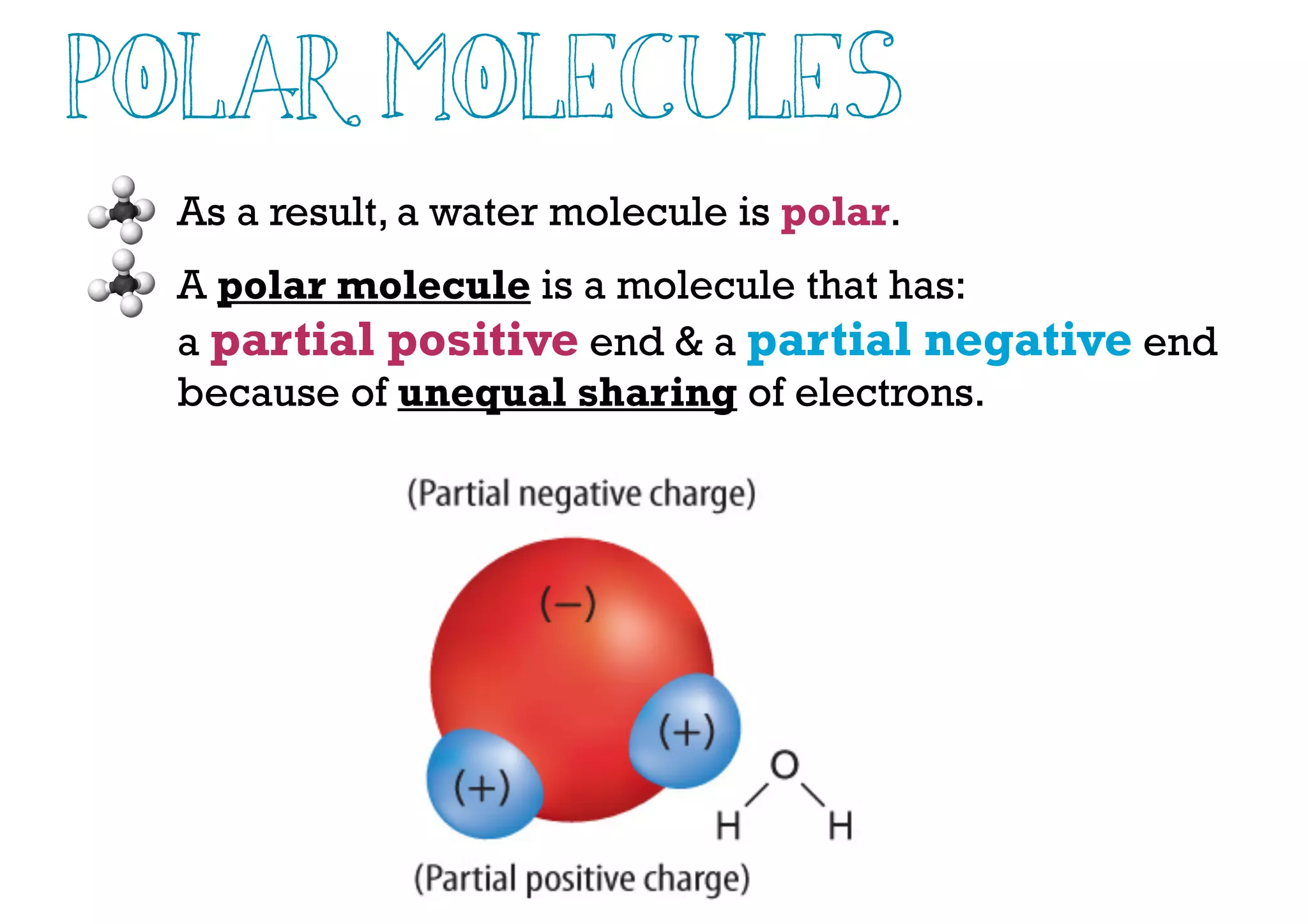
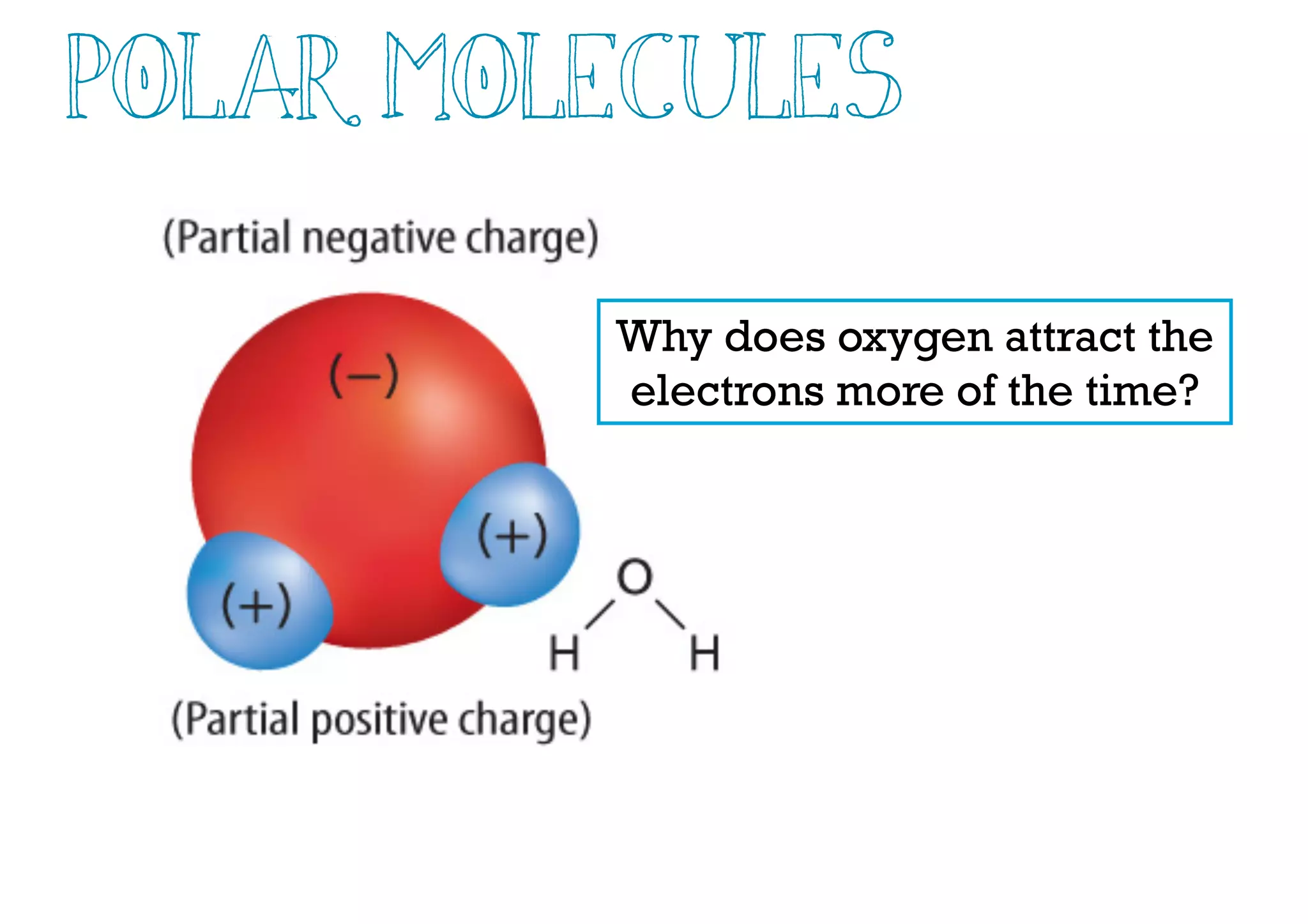
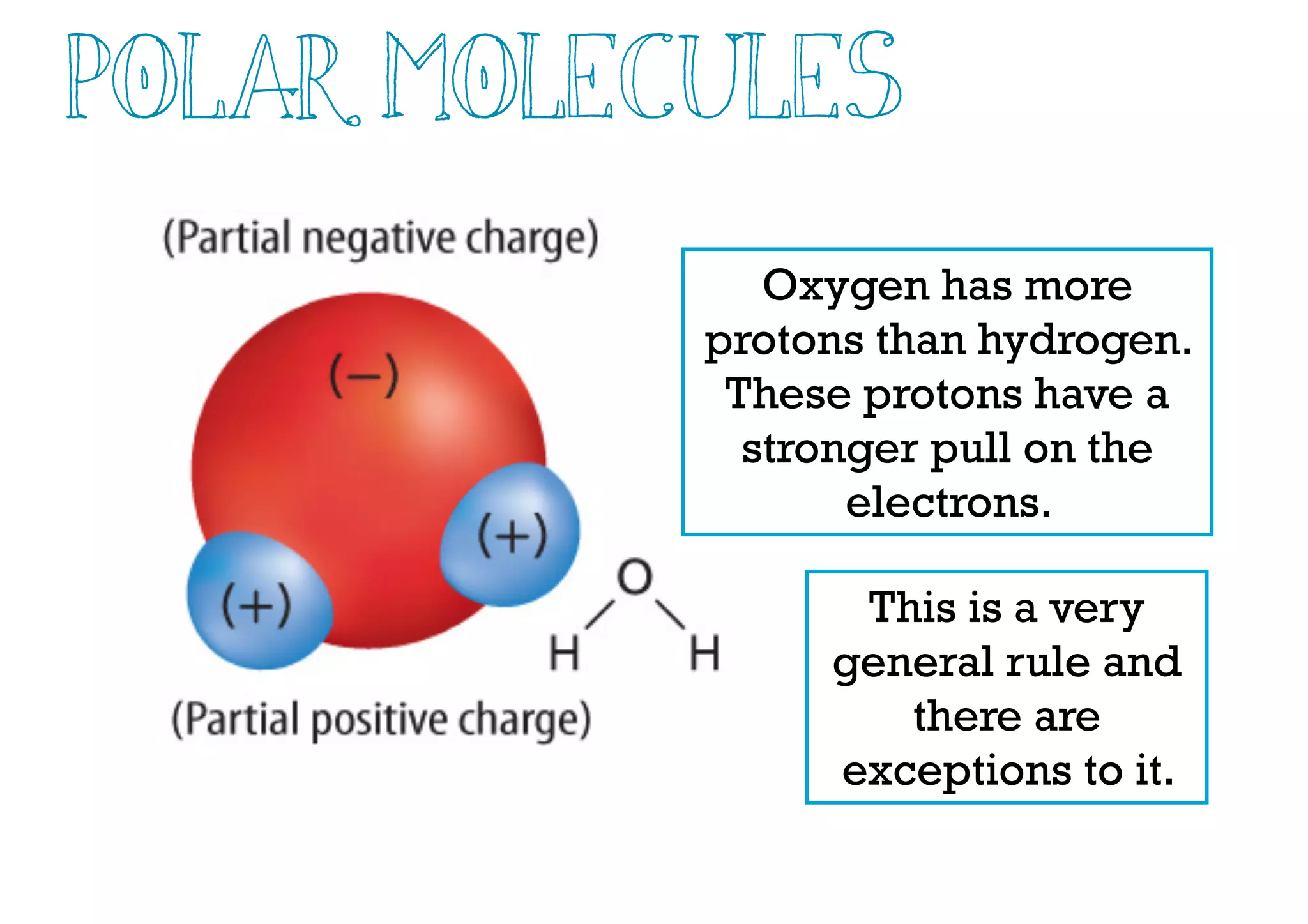
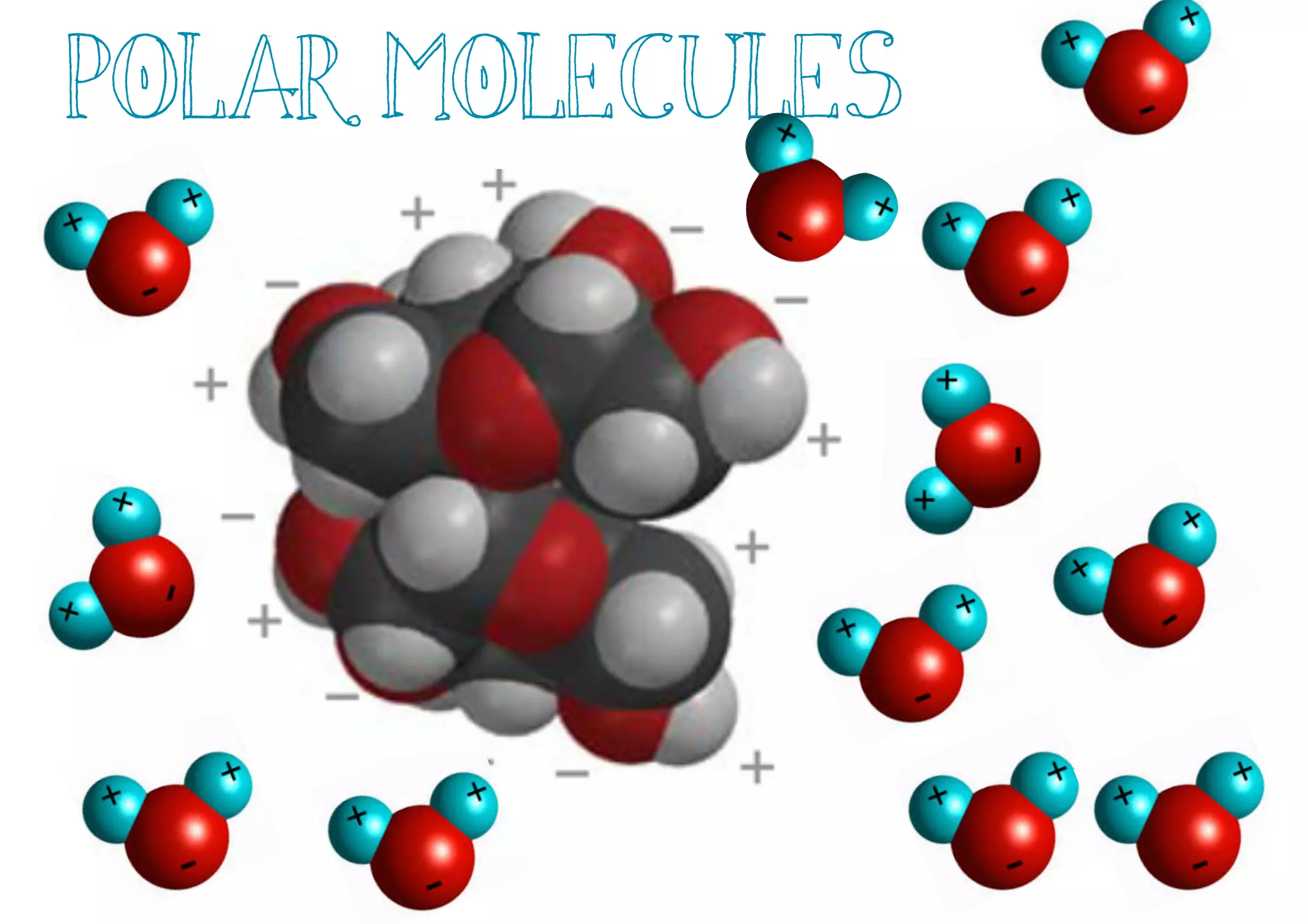
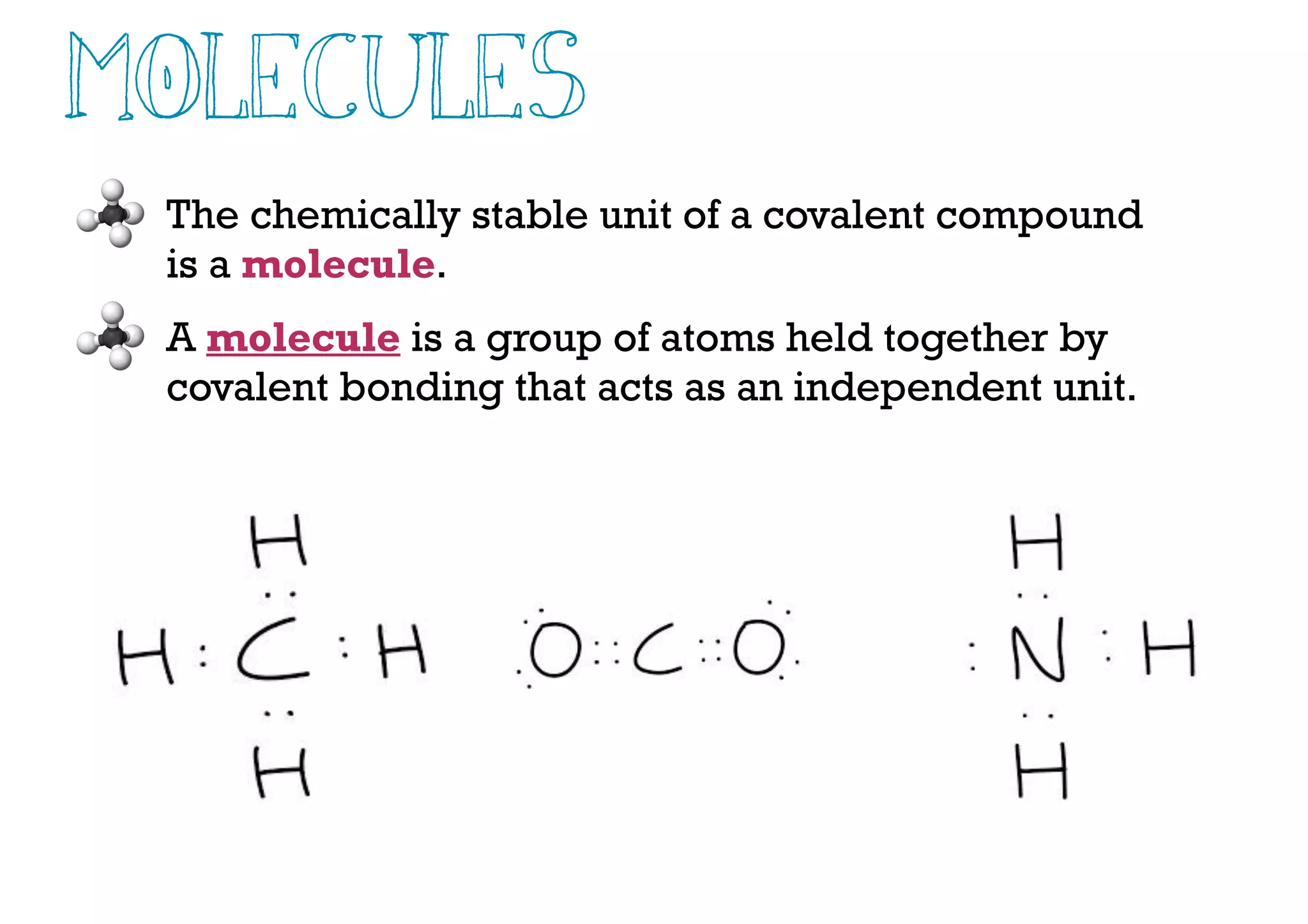Compounds are substances made of two or more elements that often have different properties than their constituent elements. Atoms bond together in compounds via chemical bonds formed by sharing valence electrons, called covalent bonds. A covalent bond forms when two atoms share one or more pairs of valence electrons, with single bonds sharing one pair and double or triple bonds sharing more pairs. The sharing of electrons leads to stable covalent compounds with properties like low melting and boiling points.