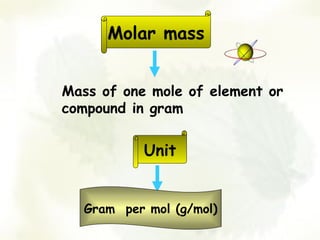
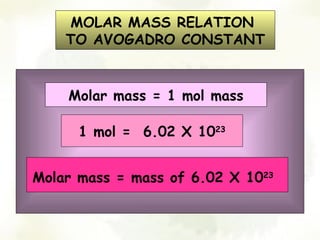
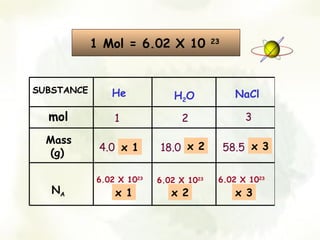
The document discusses the relationship between the number of moles, mass, and molar mass of substances. It defines molar mass as the mass of one mole of a substance in grams. Molar mass can be found on the periodic table for elements and is calculated by adding the molar masses of the constituent atoms for compounds. The document provides examples of calculating molar masses for common substances like water, sodium chloride, and aluminum and relates molar mass to Avogadro's constant of 6.022 x 10^23 particles per mole.