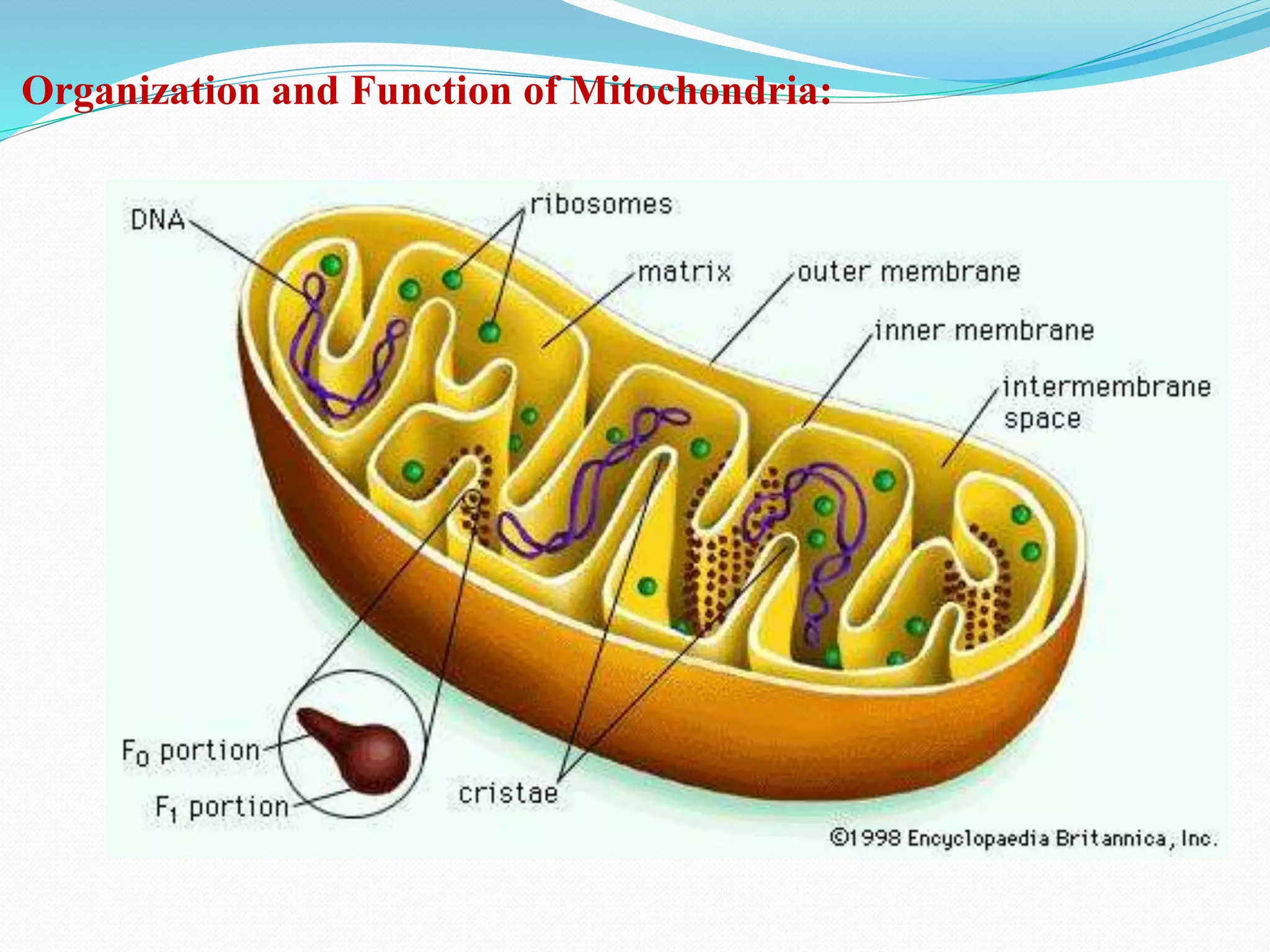
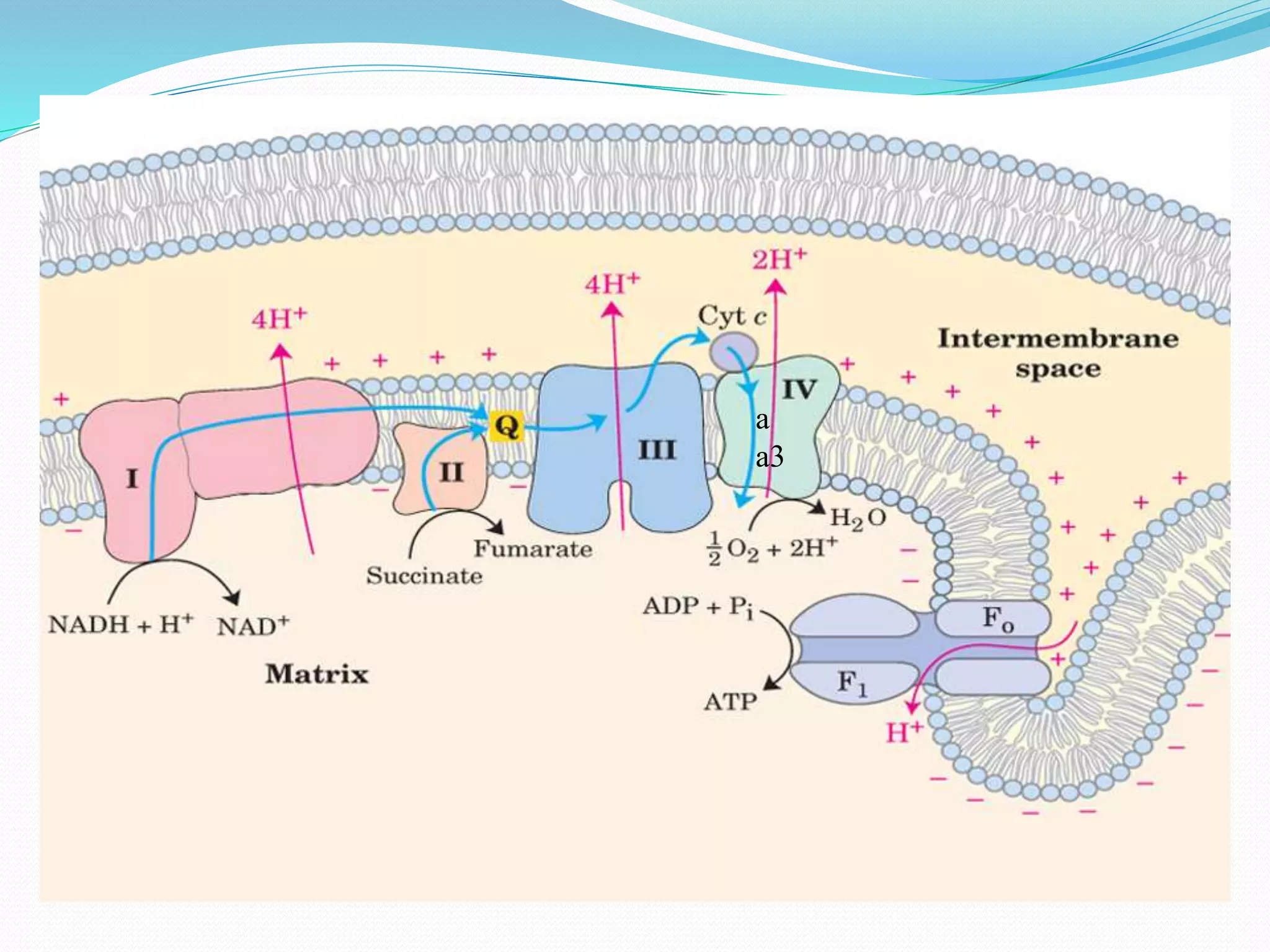
Mitochondria are semi-autonomous organelles found in eukaryotic cells referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell. They contain their own DNA separate from the cell's nucleus and likely evolved from bacteria in an endosymbiotic relationship. Mitochondria range from 0.5 to 1.0 micrometers in diameter and have an outer and inner membrane. Their primary function is producing energy through ATP synthesis in the inner membrane, but they are also involved in cellular signaling, differentiation, growth, and apoptosis.