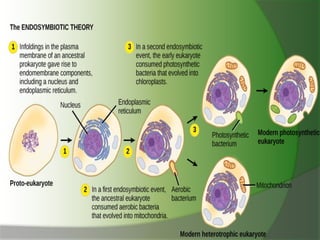
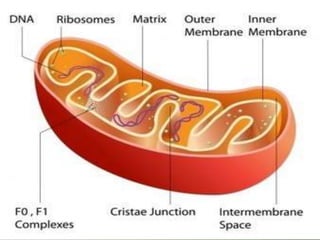
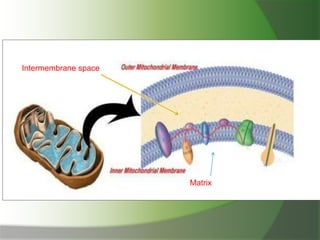
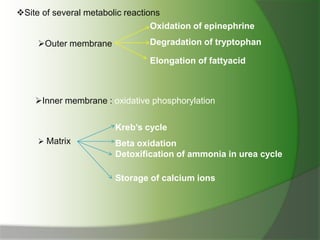
This document discusses mitochondria, double membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells that are often described as the "powerhouses" of cells. It provides details on the structure of mitochondria including their outer membrane, inner membrane, intermembrane space, cristae, and matrix. The key functions of mitochondria are also summarized as generating ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, containing their own DNA, and performing various metabolic reactions and other roles in processes like thermogenesis and apoptosis.

![INTRODUCTION
The mitochondrion (plural mitochond
ria) .[greek];
It is a double membrane-
bound organelle found eukaryotic
cells.
mito= thread
chondrion = granule like
Found in cytoplasm of the cell.
Power house of cell.
First observed by Richard Altman
(1894).
Term mitochondria was coined by
Carl Benda (1898).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellmitochondriappt-160424181440/85/Cell-mitochondria-ppt-2-320.jpg)

![In most animals ,
oozyte mitochondria [maternal] are the only
mitochondria that is inherited
.
Spermatazoa mitochondria [paternal] also
enters oocyte during fetilization,but destroyed
during early embryonic development.
Mechanism not yet ellucidated.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellmitochondriappt-160424181440/85/Cell-mitochondria-ppt-5-320.jpg)




![MITOCHONDRIAL DNA (mt DNA):
Double stranded, covalently closed,
circular molecule.
Occurs in multiple copies.
Most usually remains attached to inner
mitochondrial membrane.
Stores biological info required for growth
and multiplication of mitochondria.
Can undergo replication and duplication.
Human mt DNA 2 rRNA
22 tRNA
Not absolutely autonomous depends on
nuclear DNA.[partially autonomous]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellmitochondriappt-160424181440/85/Cell-mitochondria-ppt-12-320.jpg)
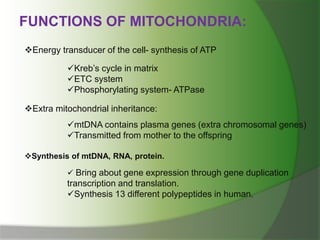
![OTHER FUNCTIONS:
production of heat ( non shivering thermogenesis).
[ The unharnessed potential energy of proton-electrochemical
gradient produced during ETC is released as heat.]
Role in apoptosis ( programmed cell death).
Synthesis of estrogen and testosterone.
Role in neurotransmitter metabolism.
Role on cholesterol metabolism.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellmitochondriappt-160424181440/85/Cell-mitochondria-ppt-15-320.jpg)
