Embed presentation
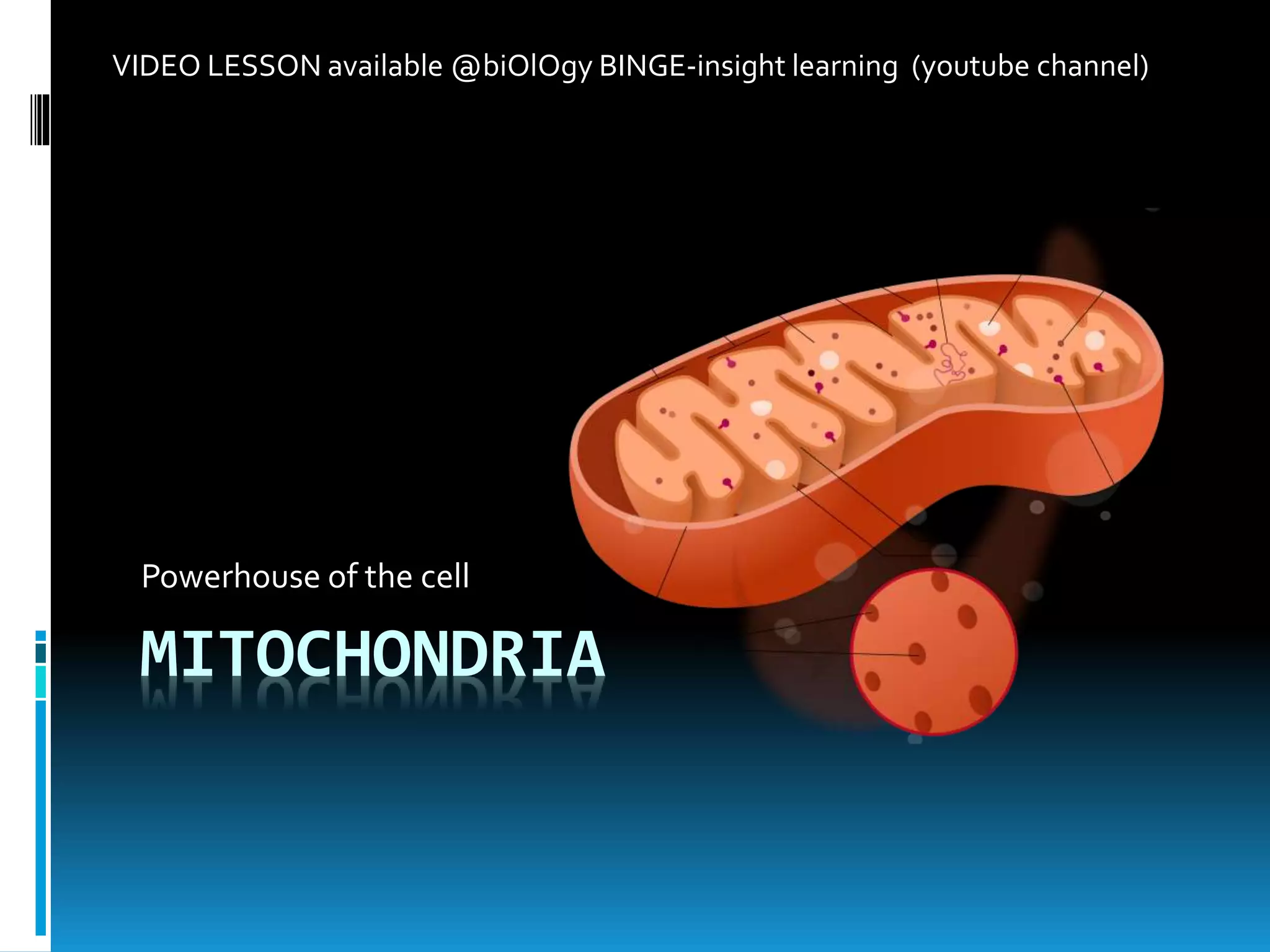


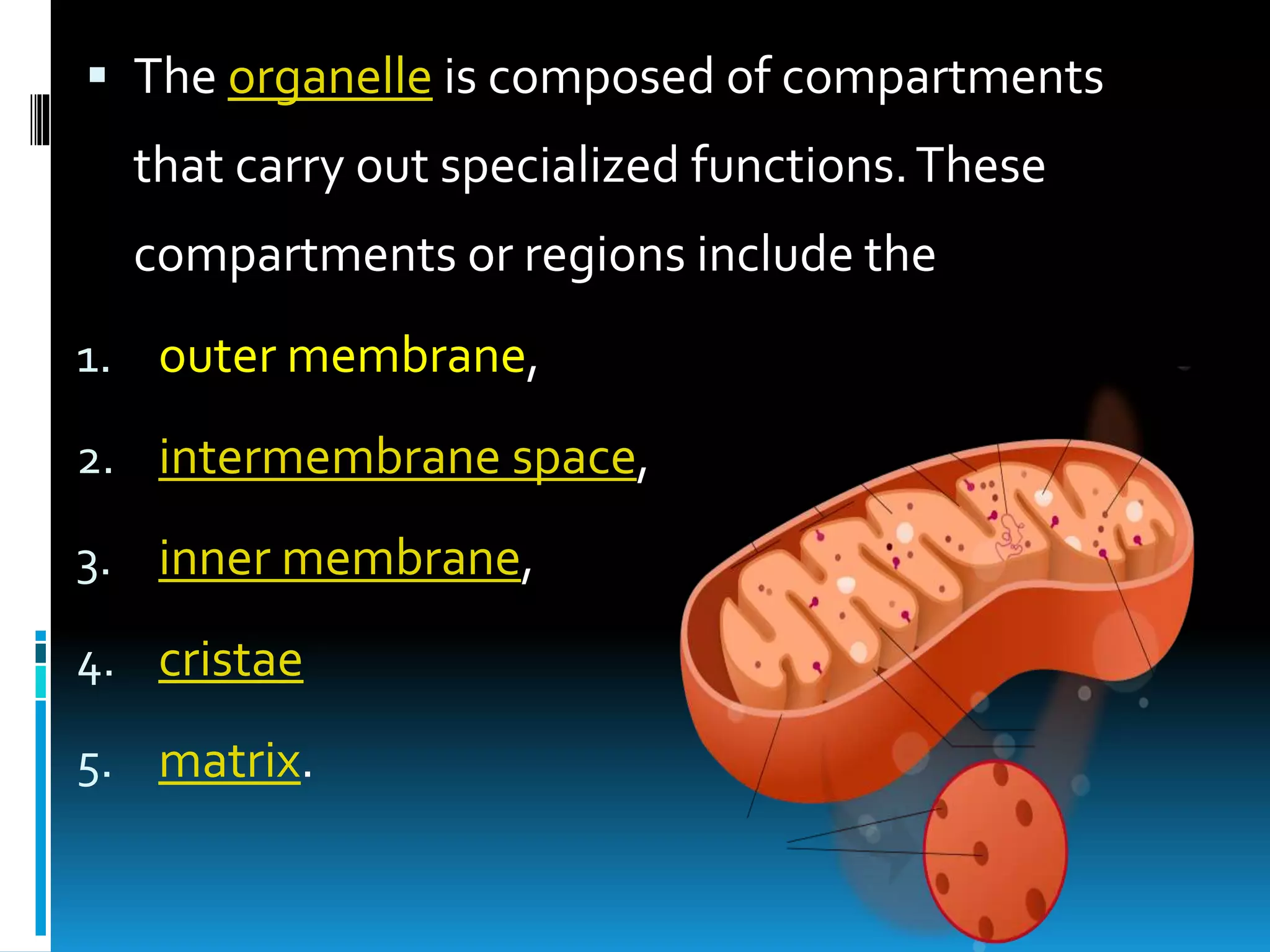

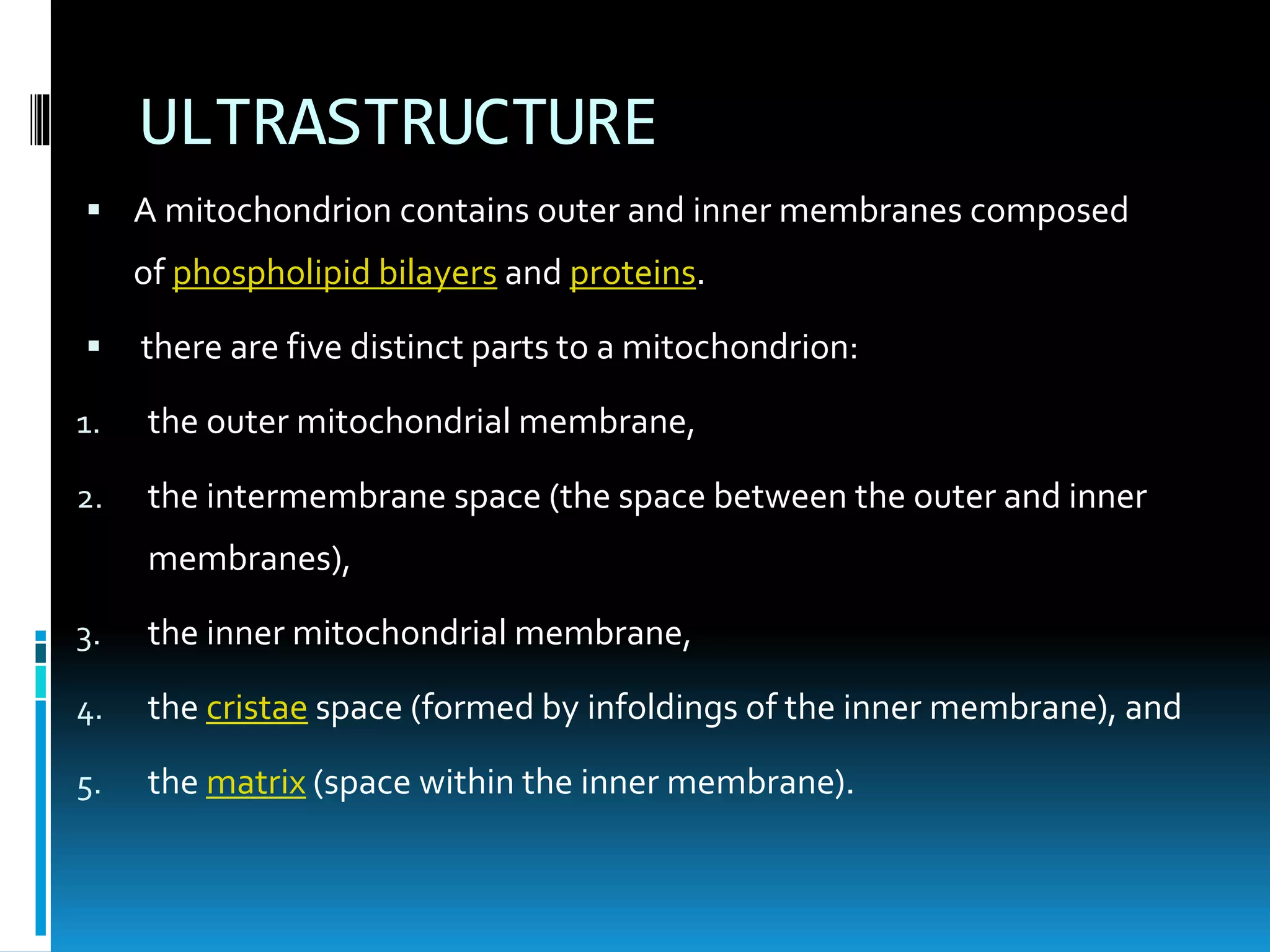




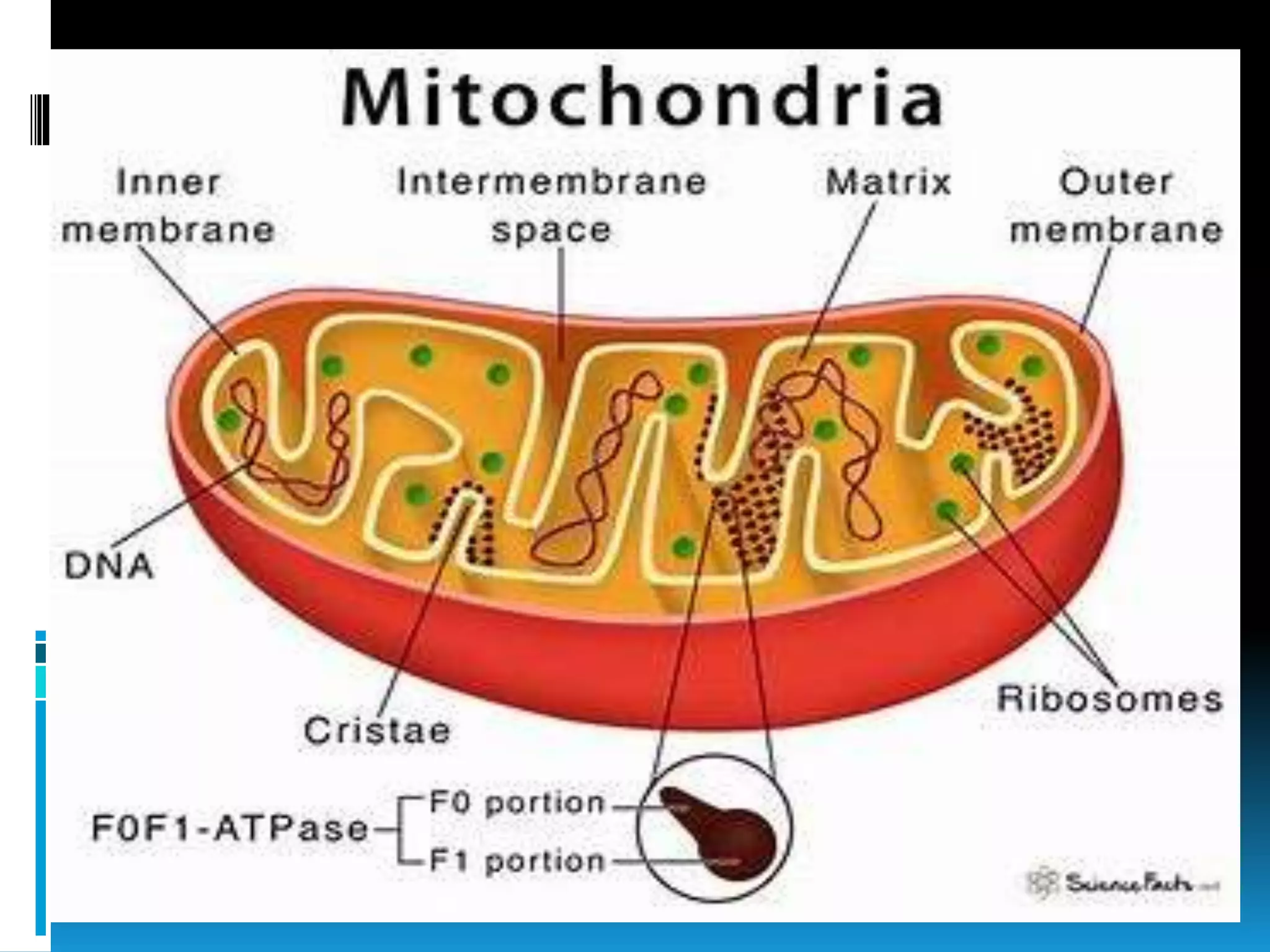

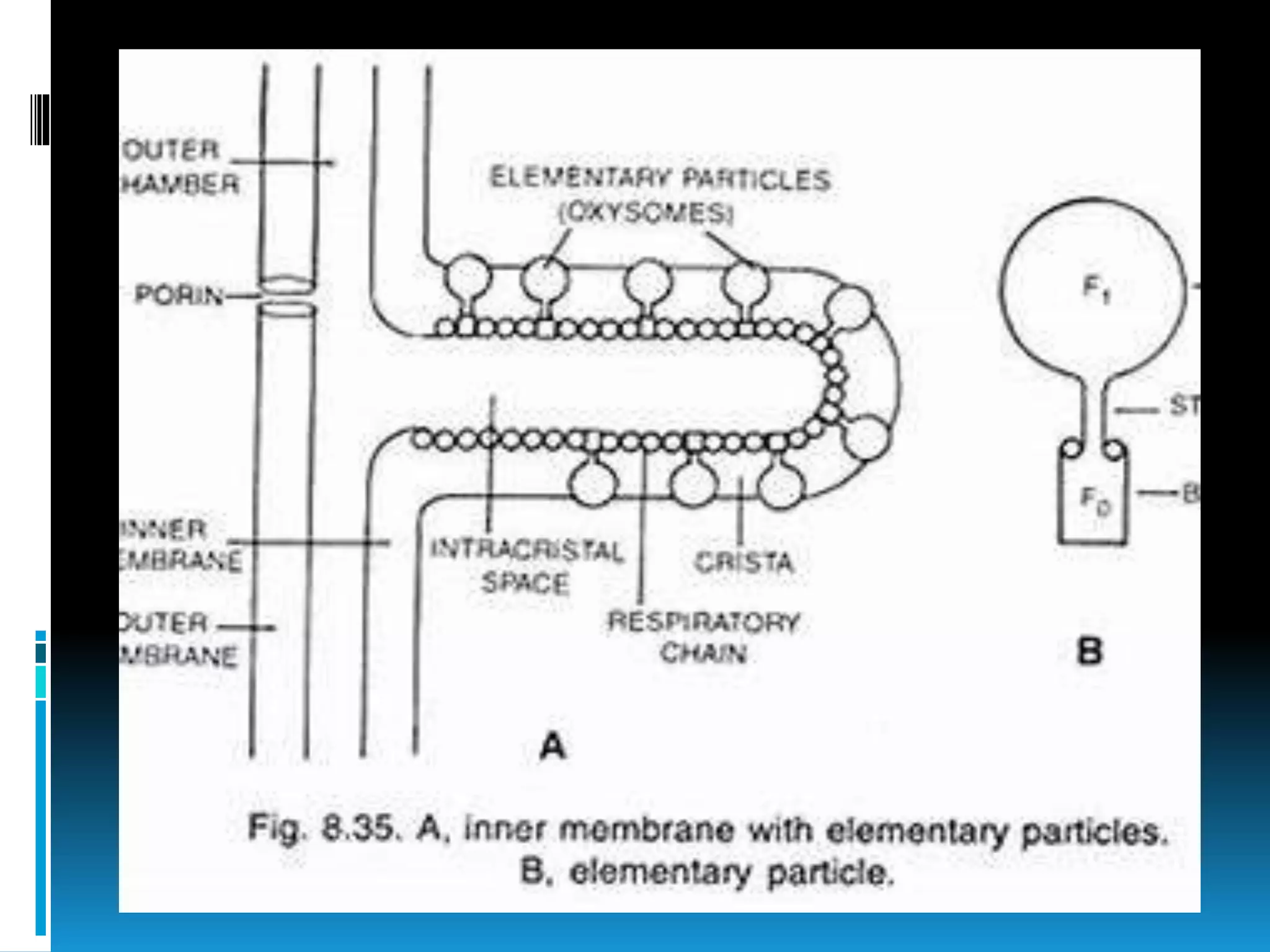


Mitochondria are double-membrane-bound organelles found in most eukaryotic cells, crucial for producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's energy currency. They perform various functions, including cell signaling, differentiation, and death, with their number varying significantly across different cell types. Mitochondria contain their own genome and complex structures, including the outer membrane, inner membrane, and matrix, enabling efficient energy conversion and metabolic processes.














