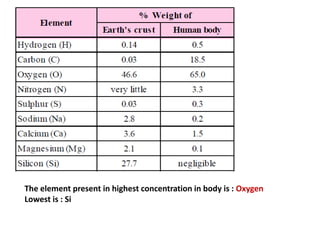
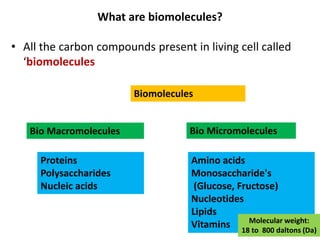
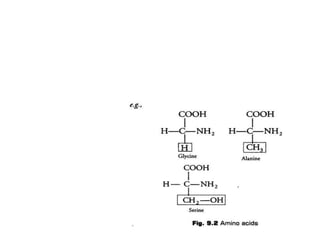
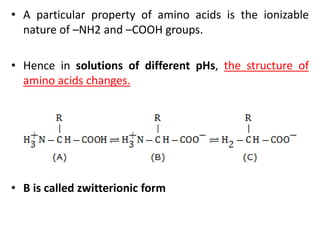
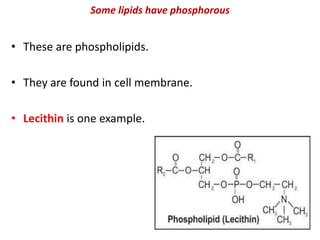
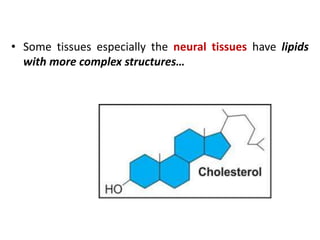
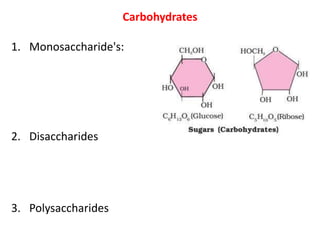
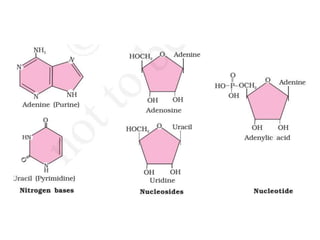
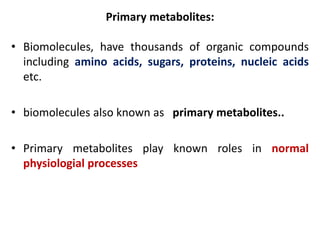
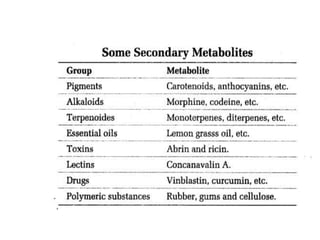
This document defines and describes the main types of biomolecules found in living organisms. It begins by explaining that chemical analysis of tissues reveals elements like carbon, hydrogen and oxygen that are present in higher concentrations than in non-living materials. The document then defines biomolecules as the carbon compounds present in living cells, dividing them into macromolecules and micromolecules. It provides examples of different classes of biomolecules including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and their monomers. The document explains how to analyze the chemical composition of tissues and describes some of the key properties and examples of amino acids, lipids, carbohydrates and nitrogen bases that make up nucleic acids. It concludes by distinguishing between primary metabolites