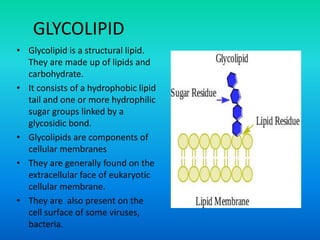
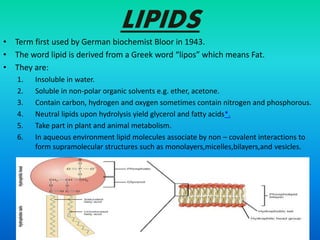
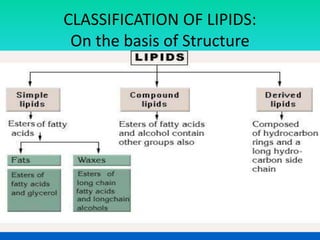
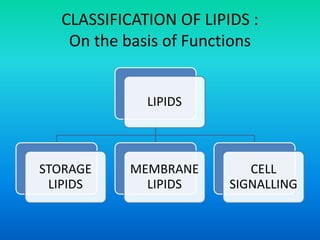
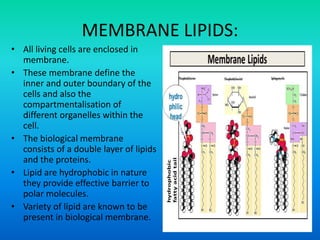
This document discusses the structure and classification of lipids. It begins by defining lipids as insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents, and containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Lipids are classified based on their structure and functions, which include storage, membrane, and cell signaling roles. Membrane lipids include phospholipids, glycolipids, and cholesterol. Phospholipids are the most abundant membrane lipid and include phosphoglycerides like lecithin, cephalins, and phosphoinositides. Glycolipids link a hydrophobic lipid tail to one or more hydrophilic sugar groups. Cholesterol contains four linked hydrocarbon rings and a hydrocarbon tail, and is present in almost all animal membranes.


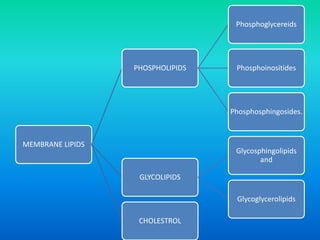


![PHOSPHOLIPID: Phosphoinositides
• Phosphatidylinositol is an acidic (anionic) phospholipid that basically,
consists of a phosphatidic acid backbone, linked via the phosphate
group to inositol (hexahydroxycyclohexane).
• Phosphoinositides are the phosphorylated derivatives of
phosphatidylinositol.
• They have three parts:
– a three-carbon backbone of glycerol,
– two long-chain fatty acids esterified to hydroxyl groups on carbons 1 and 2
(C1 and C2) of the glycerol and
– attached to a polar head group (the cyclic hexahydroxy alcohol called
inositol) that extends into the cytoplasm. [The inositol is present as the
stereoisomer, myo-inositol.]
• Examples: phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate, often called PIP3 ;
phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, often called PIP2
• *Phosphosphingosides: apparently lack in plants and the
microorganisms.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paperviii1i-200327041812/85/Lipids-Structure-and-Functions-11-320.jpg)