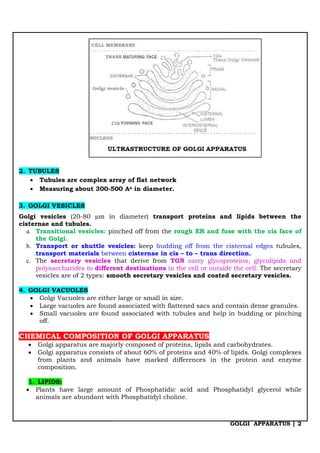
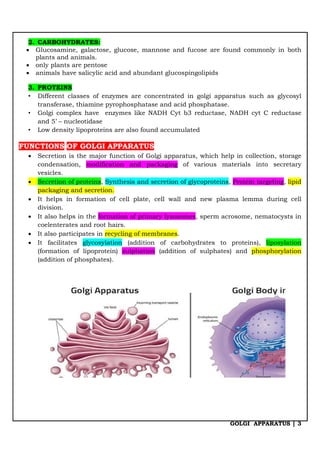
The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle involved in the collection, packaging, and secretion of biomolecules. Discovered by Camillo Golgi in 1898, it is present in all eukaryotic cells except for certain cell types, and comprises structures such as cisternae, vesicles, and tubules. Its main functions include secretion, modification of proteins, and lipid packaging, essential for various cellular processes.