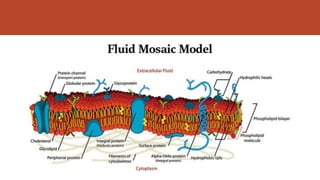
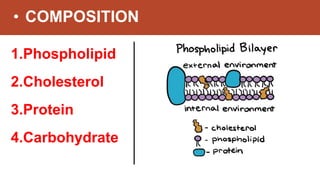
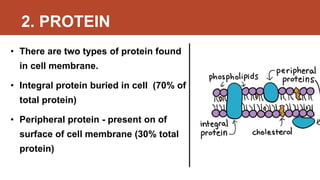
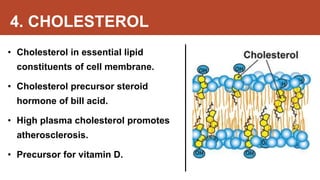
Habibullah Al Galib presents information on the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes. The fluid mosaic model proposes that cell membranes are composed of phospholipid molecules embedded with proteins that allow for fluidity and mosaic-like structure. Specifically, the model states that 40% of the membrane is lipid, 55% is protein, and 5% is carbohydrate. Lipid molecules are amphipathic with a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails. There are two types of membrane proteins - integral proteins embedded in the membrane and peripheral proteins on the surface. In addition, cholesterol is an essential lipid component that modulates membrane fluidity. The cell membrane functions to protect the cell, facilitate selective transport, and allow for cell adhesion through membrane