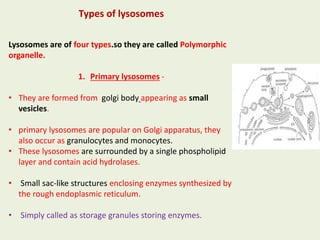
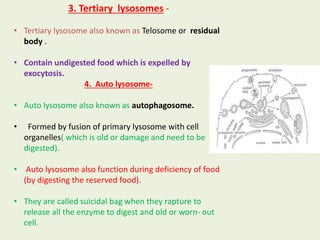
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain hydrolytic enzymes. They were discovered in 1955 and function to break down biomolecules through intracellular and extracellular digestion. Lysosomes occur in eukaryotic cells and vary in size, shape, and function. They are formed in the Golgi apparatus and contain around 50 enzymes including proteases, lipases, nucleases and more that function best in acidic environments. Lysosomes play several important roles including digesting cellular waste, breaking down pathogens during phagocytosis, and digesting old cell components through autophagy.