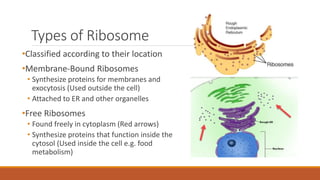
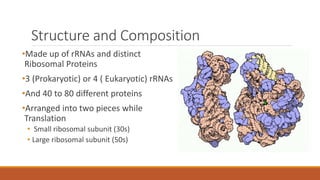
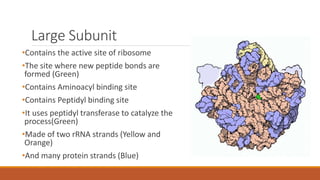
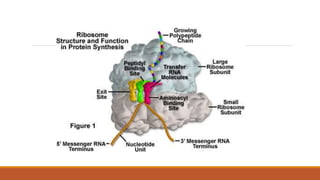
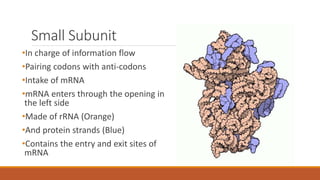
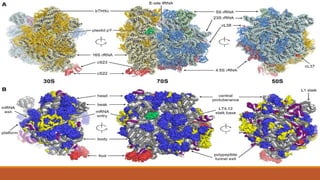
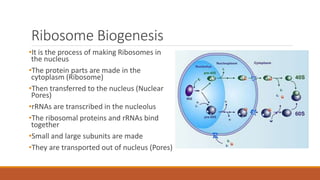
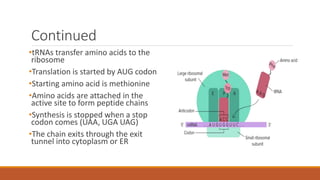
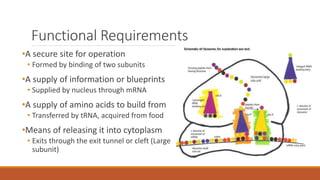
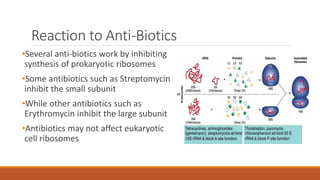
Ribosomes are the cell's sites of protein synthesis. They are composed of ribosomal RNA and proteins and exist as large and small subunits. Ribosomes were first observed in the 1950s and can be either membrane-bound or free in the cytoplasm. They translate mRNA into proteins through the attachment of amino acids. Ribosomes require mRNA, tRNAs carrying amino acids, and the proper subunits coming together to produce proteins, which are then released into the cell. Antibiotics can inhibit bacterial ribosomes and disrupt protein synthesis. Disorders of ribosome biogenesis can also cause diseases.