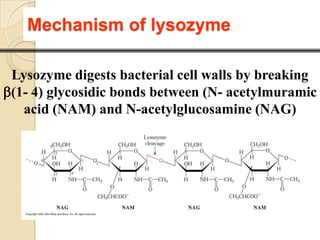
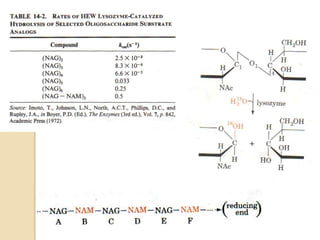
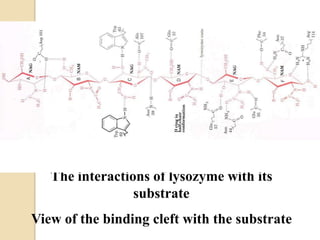
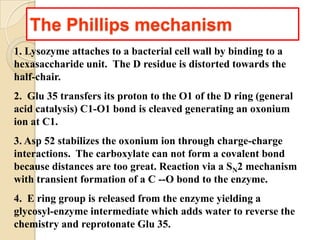
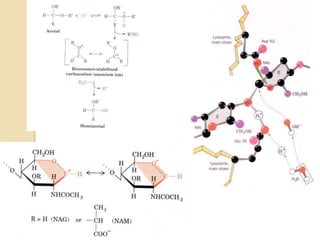
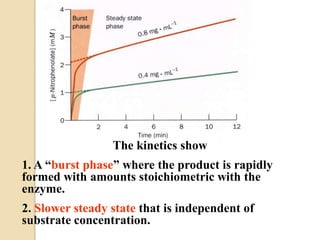
Lysozyme digests bacterial cell walls by breaking bonds between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetylglucosamine. It attaches to a hexasaccharide unit in the cell wall. Glucose 35 transfers a proton to cut the bond, generating an oxonium ion stabilized by Asp 52 via charge interactions. The product is released as the glycosyl-enzyme intermediate adds water.
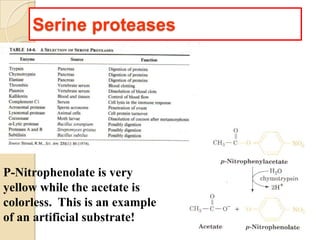
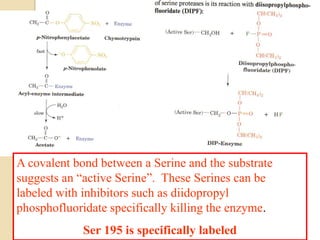
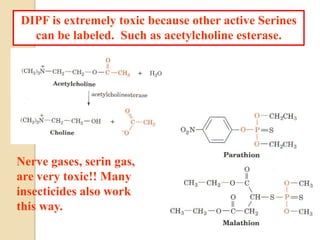
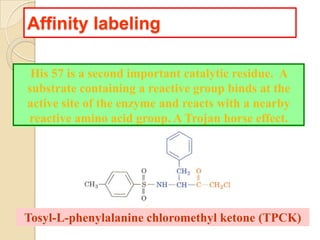
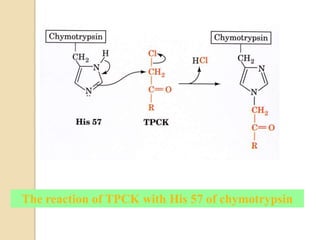
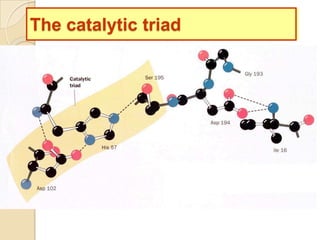
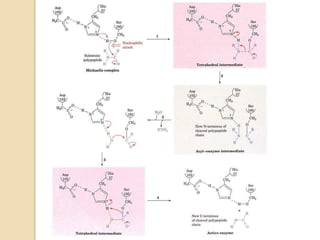
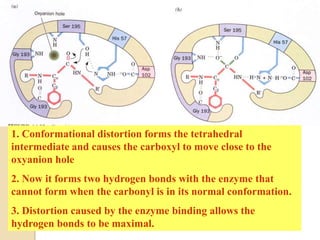
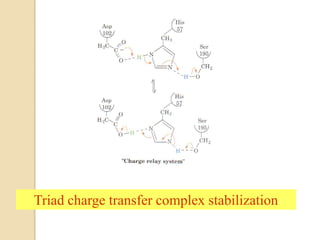
Serine proteases use a catalytic triad of Serine, Histidine, and Aspartic acid. Serine 195 performs a nucleophilic attack in a covalent catalysis step to form a tetrahedral intermediate. Histidine 52 donates a proton and Aspartic acid 102 is important for catalysis